Rami Al-Maskari
SELMA3D challenge: Self-supervised learning for 3D light-sheet microscopy image segmentation
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Recent innovations in light sheet microscopy, paired with developments in tissue clearing techniques, enable the 3D imaging of large mammalian tissues with cellular resolution. Combined with the progress in large-scale data analysis, driven by deep learning, these innovations empower researchers to rapidly investigate the morphological and functional properties of diverse biological samples. Segmentation, a crucial preliminary step in the analysis process, can be automated using domain-specific deep learning models with expert-level performance. However, these models exhibit high sensitivity to domain shifts, leading to a significant drop in accuracy when applied to data outside their training distribution. To address this limitation, and inspired by the recent success of self-supervised learning in training generalizable models, we organized the SELMA3D Challenge during the MICCAI 2024 conference. SELMA3D provides a vast collection of light-sheet images from cleared mice and human brains, comprising 35 large 3D images-each with over 1000^3 voxels-and 315 annotated small patches for finetuning, preliminary testing and final testing. The dataset encompasses diverse biological structures, including vessel-like and spot-like structures. Five teams participated in all phases of the challenge, and their proposed methods are reviewed in this paper. Quantitative and qualitative results from most participating teams demonstrate that self-supervised learning on large datasets improves segmentation model performance and generalization. We will continue to support and extend SELMA3D as an inaugural MICCAI challenge focused on self-supervised learning for 3D microscopy image segmentation.
Benchmarking the CoW with the TopCoW Challenge: Topology-Aware Anatomical Segmentation of the Circle of Willis for CTA and MRA
Dec 29, 2023



Abstract:The Circle of Willis (CoW) is an important network of arteries connecting major circulations of the brain. Its vascular architecture is believed to affect the risk, severity, and clinical outcome of serious neuro-vascular diseases. However, characterizing the highly variable CoW anatomy is still a manual and time-consuming expert task. The CoW is usually imaged by two angiographic imaging modalities, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA), but there exist limited public datasets with annotations on CoW anatomy, especially for CTA. Therefore we organized the TopCoW Challenge in 2023 with the release of an annotated CoW dataset and invited submissions worldwide for the CoW segmentation task, which attracted over 140 registered participants from four continents. TopCoW dataset was the first public dataset with voxel-level annotations for CoW's 13 vessel components, made possible by virtual-reality (VR) technology. It was also the first dataset with paired MRA and CTA from the same patients. TopCoW challenge aimed to tackle the CoW characterization problem as a multiclass anatomical segmentation task with an emphasis on topological metrics. The top performing teams managed to segment many CoW components to Dice scores around 90%, but with lower scores for communicating arteries and rare variants. There were also topological mistakes for predictions with high Dice scores. Additional topological analysis revealed further areas for improvement in detecting certain CoW components and matching CoW variant's topology accurately. TopCoW represented a first attempt at benchmarking the CoW anatomical segmentation task for MRA and CTA, both morphologically and topologically.
Panoptica -- instance-wise evaluation of 3D semantic and instance segmentation maps
Dec 05, 2023



Abstract:This paper introduces panoptica, a versatile and performance-optimized package designed for computing instance-wise segmentation quality metrics from 2D and 3D segmentation maps. panoptica addresses the limitations of existing metrics and provides a modular framework that complements the original intersection over union-based panoptic quality with other metrics, such as the distance metric Average Symmetric Surface Distance. The package is open-source, implemented in Python, and accompanied by comprehensive documentation and tutorials. panoptica employs a three-step metrics computation process to cover diverse use cases. The efficacy of panoptica is demonstrated on various real-world biomedical datasets, where an instance-wise evaluation is instrumental for an accurate representation of the underlying clinical task. Overall, we envision panoptica as a valuable tool facilitating in-depth evaluation of segmentation methods.
Approaching Peak Ground Truth
Dec 31, 2022

Abstract:Machine learning models are typically evaluated by computing similarity with reference annotations and trained by maximizing similarity with such. Especially in the bio-medical domain, annotations are subjective and suffer from low inter- and intra-rater reliability. Since annotations only reflect the annotation entity's interpretation of the real world, this can lead to sub-optimal predictions even though the model achieves high similarity scores. Here, the theoretical concept of Peak Ground Truth (PGT) is introduced. PGT marks the point beyond which an increase in similarity with the reference annotation stops translating to better Real World Model Performance (RWMP). Additionally, a quantitative technique to approximate PGT by computing inter- and intra-rater reliability is proposed. Finally, three categories of PGT-aware strategies to evaluate and improve model performance are reviewed.
blob loss: instance imbalance aware loss functions for semantic segmentation
May 17, 2022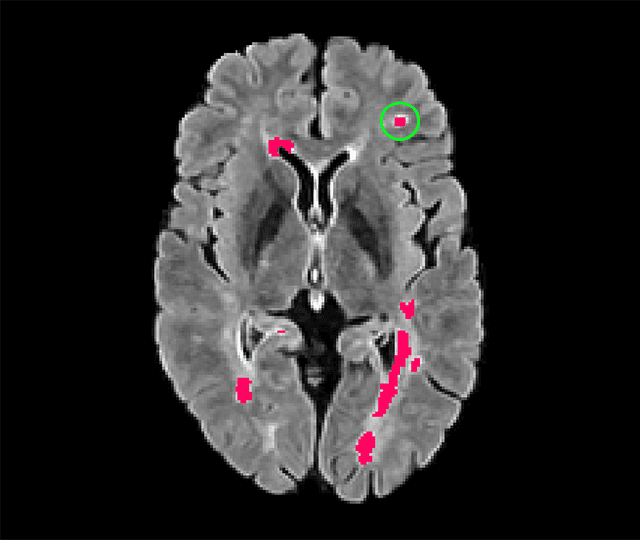
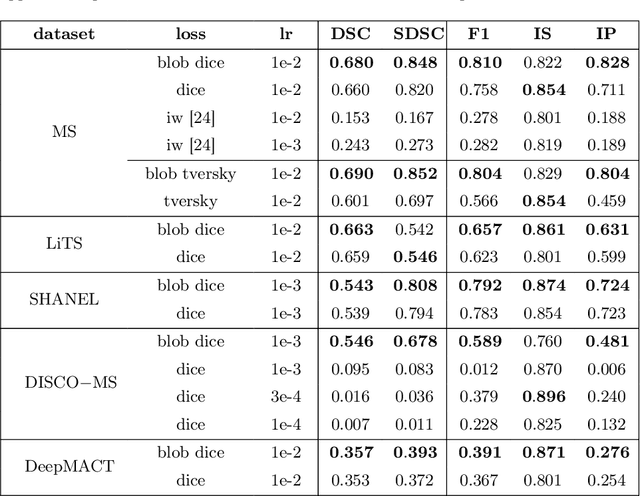

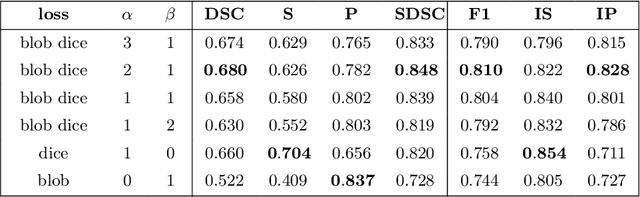
Abstract:Deep convolutional neural networks have proven to be remarkably effective in semantic segmentation tasks. Most popular loss functions were introduced targeting improved volumetric scores, such as the Sorensen Dice coefficient. By design, DSC can tackle class imbalance; however, it does not recognize instance imbalance within a class. As a result, a large foreground instance can dominate minor instances and still produce a satisfactory Sorensen Dice coefficient. Nevertheless, missing out on instances will lead to poor detection performance. This represents a critical issue in applications such as disease progression monitoring. For example, it is imperative to locate and surveil small-scale lesions in the follow-up of multiple sclerosis patients. We propose a novel family of loss functions, nicknamed blob loss, primarily aimed at maximizing instance-level detection metrics, such as F1 score and sensitivity. Blob loss is designed for semantic segmentation problems in which the instances are the connected components within a class. We extensively evaluate a DSC-based blob loss in five complex 3D semantic segmentation tasks featuring pronounced instance heterogeneity in terms of texture and morphology. Compared to soft Dice loss, we achieve 5 percent improvement for MS lesions, 3 percent improvement for liver tumor, and an average 2 percent improvement for Microscopy segmentation tasks considering F1 score.
METGAN: Generative Tumour Inpainting and Modality Synthesis in Light Sheet Microscopy
Apr 23, 2021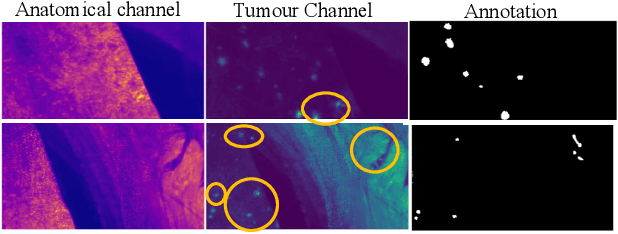
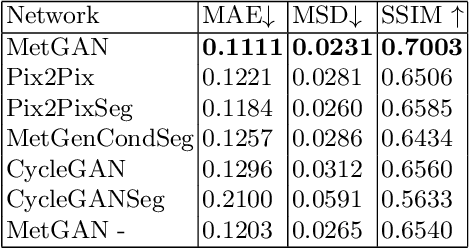
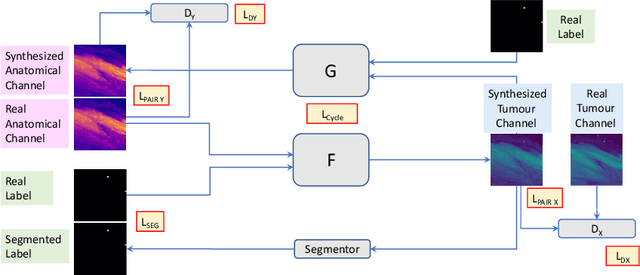
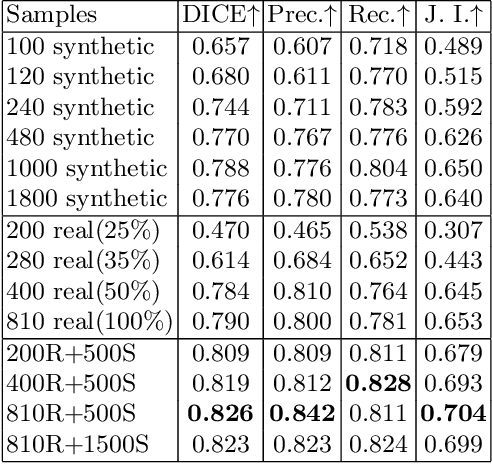
Abstract:Novel multimodal imaging methods are capable of generating extensive, super high resolution datasets for preclinical research. Yet, a massive lack of annotations prevents the broad use of deep learning to analyze such data. So far, existing generative models fail to mitigate this problem because of frequent labeling errors. In this paper, we introduce a novel generative method which leverages real anatomical information to generate realistic image-label pairs of tumours. We construct a dual-pathway generator, for the anatomical image and label, trained in a cycle-consistent setup, constrained by an independent, pretrained segmentor. The generated images yield significant quantitative improvement compared to existing methods. To validate the quality of synthesis, we train segmentation networks on a dataset augmented with the synthetic data, substantially improving the segmentation over baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge