Florian Kofler
for the ALFA study
fastWDM3D: Fast and Accurate 3D Healthy Tissue Inpainting
Jul 17, 2025


Abstract:Healthy tissue inpainting has significant applications, including the generation of pseudo-healthy baselines for tumor growth models and the facilitation of image registration. In previous editions of the BraTS Local Synthesis of Healthy Brain Tissue via Inpainting Challenge, denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) demonstrated qualitatively convincing results but suffered from low sampling speed. To mitigate this limitation, we adapted a 2D image generation approach, combining DDPMs with generative adversarial networks (GANs) and employing a variance-preserving noise schedule, for the task of 3D inpainting. Our experiments showed that the variance-preserving noise schedule and the selected reconstruction losses can be effectively utilized for high-quality 3D inpainting in a few time steps without requiring adversarial training. We applied our findings to a different architecture, a 3D wavelet diffusion model (WDM3D) that does not include a GAN component. The resulting model, denoted as fastWDM3D, obtained a SSIM of 0.8571, a MSE of 0.0079, and a PSNR of 22.26 on the BraTS inpainting test set. Remarkably, it achieved these scores using only two time steps, completing the 3D inpainting process in 1.81 s per image. When compared to other DDPMs used for healthy brain tissue inpainting, our model is up to 800 x faster while still achieving superior performance metrics. Our proposed method, fastWDM3D, represents a promising approach for fast and accurate healthy tissue inpainting. Our code is available at https://github.com/AliciaDurrer/fastWDM3D.
Automated Thoracolumbar Stump Rib Detection and Analysis in a Large CT Cohort
May 08, 2025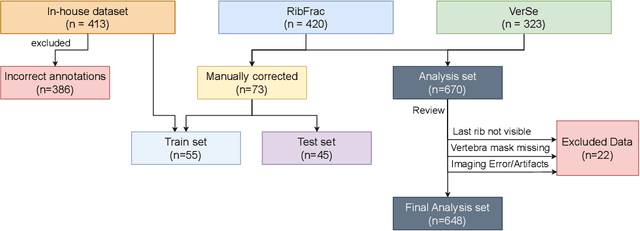
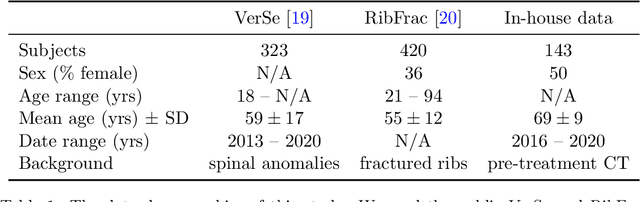
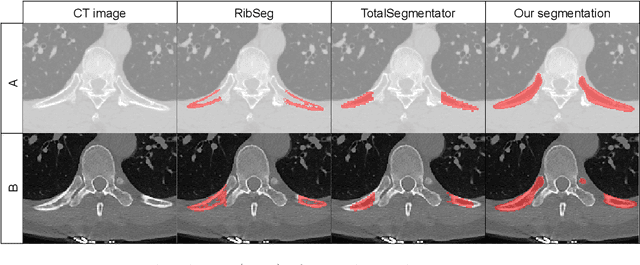
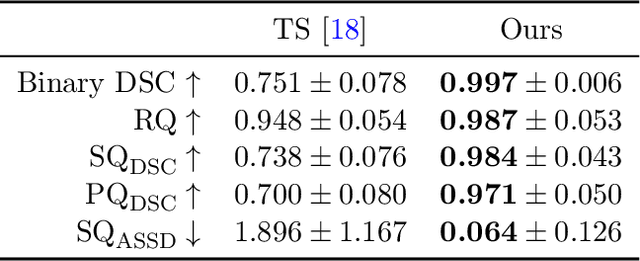
Abstract:Thoracolumbar stump ribs are one of the essential indicators of thoracolumbar transitional vertebrae or enumeration anomalies. While some studies manually assess these anomalies and describe the ribs qualitatively, this study aims to automate thoracolumbar stump rib detection and analyze their morphology quantitatively. To this end, we train a high-resolution deep-learning model for rib segmentation and show significant improvements compared to existing models (Dice score 0.997 vs. 0.779, p-value < 0.01). In addition, we use an iterative algorithm and piece-wise linear interpolation to assess the length of the ribs, showing a success rate of 98.2%. When analyzing morphological features, we show that stump ribs articulate more posteriorly at the vertebrae (-19.2 +- 3.8 vs -13.8 +- 2.5, p-value < 0.01), are thinner (260.6 +- 103.4 vs. 563.6 +- 127.1, p-value < 0.01), and are oriented more downwards and sideways within the first centimeters in contrast to full-length ribs. We show that with partially visible ribs, these features can achieve an F1-score of 0.84 in differentiating stump ribs from regular ones. We publish the model weights and masks for public use.
Analysis of the MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Metastases (BraTS-METS) 2025 Lighthouse Challenge: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre- and Post-treatment MRI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Despite continuous advancements in cancer treatment, brain metastatic disease remains a significant complication of primary cancer and is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. One approach for improving diagnosis, management, and outcomes is to implement algorithms based on artificial intelligence for the automated segmentation of both pre- and post-treatment MRI brain images. Such algorithms rely on volumetric criteria for lesion identification and treatment response assessment, which are still not available in clinical practice. Therefore, it is critical to establish tools for rapid volumetric segmentations methods that can be translated to clinical practice and that are trained on high quality annotated data. The BraTS-METS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge aims to address this critical need by establishing inter-rater and intra-rater variability in dataset annotation by generating high quality annotated datasets from four individual instances of segmentation by neuroradiologists while being recorded on video (two instances doing "from scratch" and two instances after AI pre-segmentation). This high-quality annotated dataset will be used for testing phase in 2025 Lighthouse challenge and will be publicly released at the completion of the challenge. The 2025 Lighthouse challenge will also release the 2023 and 2024 segmented datasets that were annotated using an established pipeline of pre-segmentation, student annotation, two neuroradiologists checking, and one neuroradiologist finalizing the process. It builds upon its previous edition by including post-treatment cases in the dataset. Using these high-quality annotated datasets, the 2025 Lighthouse challenge plans to test benchmark algorithms for automated segmentation of pre-and post-treatment brain metastases (BM), trained on diverse and multi-institutional datasets of MRI images obtained from patients with brain metastases.
MultiOrg: A Multi-rater Organoid-detection Dataset
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:High-throughput image analysis in the biomedical domain has gained significant attention in recent years, driving advancements in drug discovery, disease prediction, and personalized medicine. Organoids, specifically, are an active area of research, providing excellent models for human organs and their functions. Automating the quantification of organoids in microscopy images would provide an effective solution to overcome substantial manual quantification bottlenecks, particularly in high-throughput image analysis. However, there is a notable lack of open biomedical datasets, in contrast to other domains, such as autonomous driving, and, notably, only few of them have attempted to quantify annotation uncertainty. In this work, we present MultiOrg a comprehensive organoid dataset tailored for object detection tasks with uncertainty quantification. This dataset comprises over 400 high-resolution 2d microscopy images and curated annotations of more than 60,000 organoids. Most importantly, it includes three label sets for the test data, independently annotated by two experts at distinct time points. We additionally provide a benchmark for organoid detection, and make the best model available through an easily installable, interactive plugin for the popular image visualization tool Napari, to perform organoid quantification.
Improving the Precision of CNNs for Magnetic Resonance Spectral Modeling
Sep 10, 2024


Abstract:Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging is a widely available imaging modality that can non-invasively provide a metabolic profile of the tissue of interest, yet is challenging to integrate clinically. One major reason is the expensive, expert data processing and analysis that is required. Using machine learning to predict MRS-related quantities offers avenues around this problem, but deep learning models bring their own challenges, especially model trust. Current research trends focus primarily on mean error metrics, but comprehensive precision metrics are also needed, e.g. standard deviations, confidence intervals, etc.. This work highlights why more comprehensive error characterization is important and how to improve the precision of CNNs for spectral modeling, a quantitative task. The results highlight advantages and trade-offs of these techniques that should be considered when addressing such regression tasks with CNNs. Detailed insights into the underlying mechanisms of each technique, and how they interact with other techniques, are discussed in depth.
ISLES'24: Improving final infarct prediction in ischemic stroke using multimodal imaging and clinical data
Aug 20, 2024
Abstract:Accurate estimation of core (irreversibly damaged tissue) and penumbra (salvageable tissue) volumes is essential for ischemic stroke treatment decisions. Perfusion CT, the clinical standard, estimates these volumes but is affected by variations in deconvolution algorithms, implementations, and thresholds. Core tissue expands over time, with growth rates influenced by thrombus location, collateral circulation, and inherent patient-specific factors. Understanding this tissue growth is crucial for determining the need to transfer patients to comprehensive stroke centers, predicting the benefits of additional reperfusion attempts during mechanical thrombectomy, and forecasting final clinical outcomes. This work presents the ISLES'24 challenge, which addresses final post-treatment stroke infarct prediction from pre-interventional acute stroke imaging and clinical data. ISLES'24 establishes a unique 360-degree setting where all feasibly accessible clinical data are available for participants, including full CT acute stroke imaging, sub-acute follow-up MRI, and clinical tabular data. The contributions of this work are two-fold: first, we introduce a standardized benchmarking of final stroke infarct segmentation algorithms through the ISLES'24 challenge; second, we provide insights into infarct segmentation using multimodal imaging and clinical data strategies by identifying outperforming methods on a finely curated dataset. The outputs of this challenge are anticipated to enhance clinical decision-making and improve patient outcome predictions. All ISLES'24 materials, including data, performance evaluation scripts, and leading algorithmic strategies, are available to the research community following \url{https://isles-24.grand-challenge.org/}.
BraTS-PEDs: Results of the Multi-Consortium International Pediatric Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge 2023
Jul 11, 2024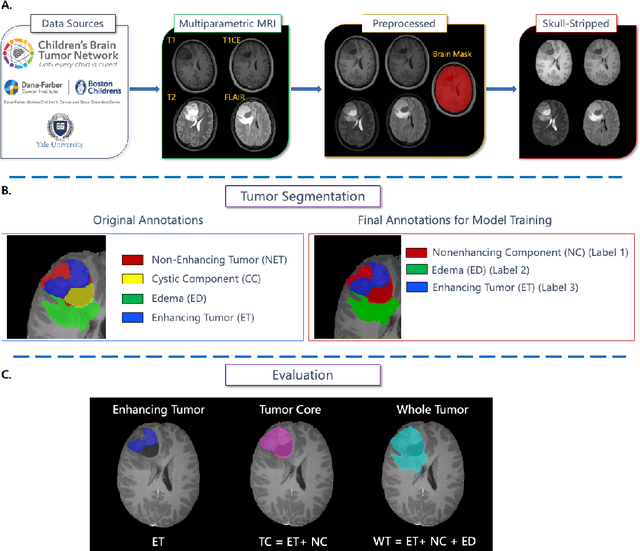

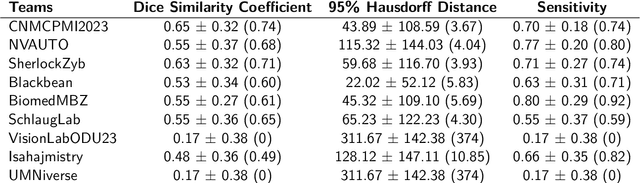
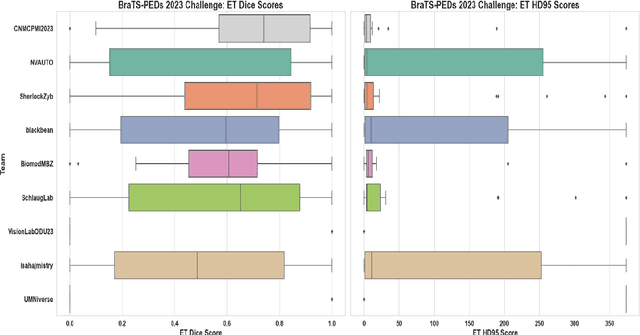
Abstract:Pediatric central nervous system tumors are the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in children. The five-year survival rate for high-grade glioma in children is less than 20%. The development of new treatments is dependent upon multi-institutional collaborative clinical trials requiring reproducible and accurate centralized response assessment. We present the results of the BraTS-PEDs 2023 challenge, the first Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge focused on pediatric brain tumors. This challenge utilized data acquired from multiple international consortia dedicated to pediatric neuro-oncology and clinical trials. BraTS-PEDs 2023 aimed to evaluate volumetric segmentation algorithms for pediatric brain gliomas from magnetic resonance imaging using standardized quantitative performance evaluation metrics employed across the BraTS 2023 challenges. The top-performing AI approaches for pediatric tumor analysis included ensembles of nnU-Net and Swin UNETR, Auto3DSeg, or nnU-Net with a self-supervised framework. The BraTSPEDs 2023 challenge fostered collaboration between clinicians (neuro-oncologists, neuroradiologists) and AI/imaging scientists, promoting faster data sharing and the development of automated volumetric analysis techniques. These advancements could significantly benefit clinical trials and improve the care of children with brain tumors.
Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge 2024: Meningioma Radiotherapy Planning Automated Segmentation
May 28, 2024Abstract:The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation Meningioma Radiotherapy (BraTS-MEN-RT) challenge aims to advance automated segmentation algorithms using the largest known multi-institutional dataset of radiotherapy planning brain MRIs with expert-annotated target labels for patients with intact or post-operative meningioma that underwent either conventional external beam radiotherapy or stereotactic radiosurgery. Each case includes a defaced 3D post-contrast T1-weighted radiotherapy planning MRI in its native acquisition space, accompanied by a single-label "target volume" representing the gross tumor volume (GTV) and any at-risk post-operative site. Target volume annotations adhere to established radiotherapy planning protocols, ensuring consistency across cases and institutions. For pre-operative meningiomas, the target volume encompasses the entire GTV and associated nodular dural tail, while for post-operative cases, it includes at-risk resection cavity margins as determined by the treating institution. Case annotations were reviewed and approved by expert neuroradiologists and radiation oncologists. Participating teams will develop, containerize, and evaluate automated segmentation models using this comprehensive dataset. Model performance will be assessed using the lesion-wise Dice Similarity Coefficient and the 95% Hausdorff distance. The top-performing teams will be recognized at the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention Conference in October 2024. BraTS-MEN-RT is expected to significantly advance automated radiotherapy planning by enabling precise tumor segmentation and facilitating tailored treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge: Glioma Segmentation on Post-treatment MRI
May 28, 2024
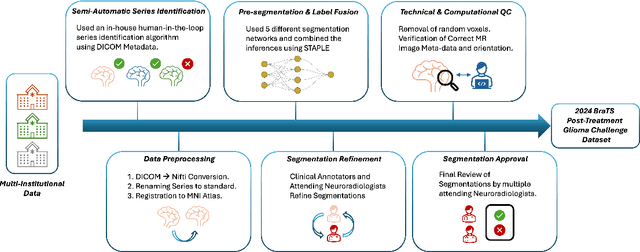
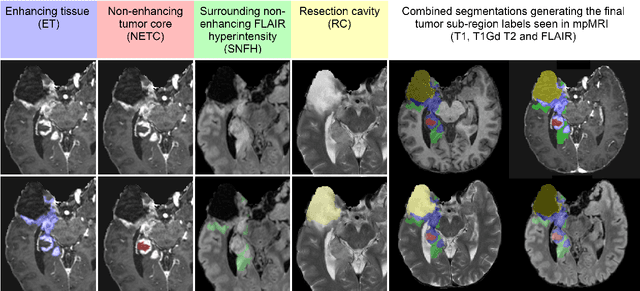
Abstract:Gliomas are the most common malignant primary brain tumors in adults and one of the deadliest types of cancer. There are many challenges in treatment and monitoring due to the genetic diversity and high intrinsic heterogeneity in appearance, shape, histology, and treatment response. Treatments include surgery, radiation, and systemic therapies, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) playing a key role in treatment planning and post-treatment longitudinal assessment. The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge on post-treatment glioma MRI will provide a community standard and benchmark for state-of-the-art automated segmentation models based on the largest expert-annotated post-treatment glioma MRI dataset. Challenge competitors will develop automated segmentation models to predict four distinct tumor sub-regions consisting of enhancing tissue (ET), surrounding non-enhancing T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) hyperintensity (SNFH), non-enhancing tumor core (NETC), and resection cavity (RC). Models will be evaluated on separate validation and test datasets using standardized performance metrics utilized across the BraTS 2024 cluster of challenges, including lesion-wise Dice Similarity Coefficient and Hausdorff Distance. Models developed during this challenge will advance the field of automated MRI segmentation and contribute to their integration into clinical practice, ultimately enhancing patient care.
Analysis of the BraTS 2023 Intracranial Meningioma Segmentation Challenge
May 16, 2024



Abstract:We describe the design and results from the BraTS 2023 Intracranial Meningioma Segmentation Challenge. The BraTS Meningioma Challenge differed from prior BraTS Glioma challenges in that it focused on meningiomas, which are typically benign extra-axial tumors with diverse radiologic and anatomical presentation and a propensity for multiplicity. Nine participating teams each developed deep-learning automated segmentation models using image data from the largest multi-institutional systematically expert annotated multilabel multi-sequence meningioma MRI dataset to date, which included 1000 training set cases, 141 validation set cases, and 283 hidden test set cases. Each case included T2, T2/FLAIR, T1, and T1Gd brain MRI sequences with associated tumor compartment labels delineating enhancing tumor, non-enhancing tumor, and surrounding non-enhancing T2/FLAIR hyperintensity. Participant automated segmentation models were evaluated and ranked based on a scoring system evaluating lesion-wise metrics including dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and 95% Hausdorff Distance. The top ranked team had a lesion-wise median dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.976, 0.976, and 0.964 for enhancing tumor, tumor core, and whole tumor, respectively and a corresponding average DSC of 0.899, 0.904, and 0.871, respectively. These results serve as state-of-the-art benchmarks for future pre-operative meningioma automated segmentation algorithms. Additionally, we found that 1286 of 1424 cases (90.3%) had at least 1 compartment voxel abutting the edge of the skull-stripped image edge, which requires further investigation into optimal pre-processing face anonymization steps.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge