Stefan Kesselheim
Lossy Neural Compression for Geospatial Analytics: A Review
Mar 03, 2025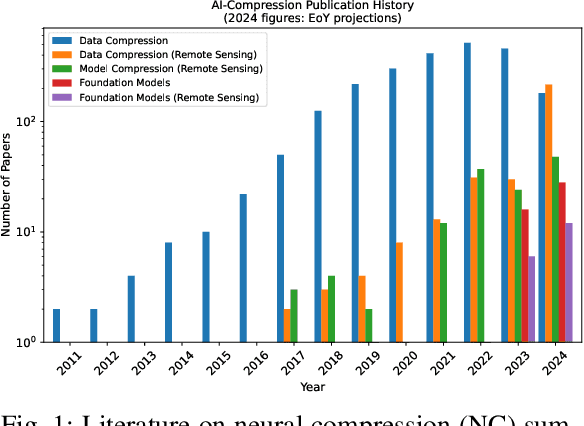
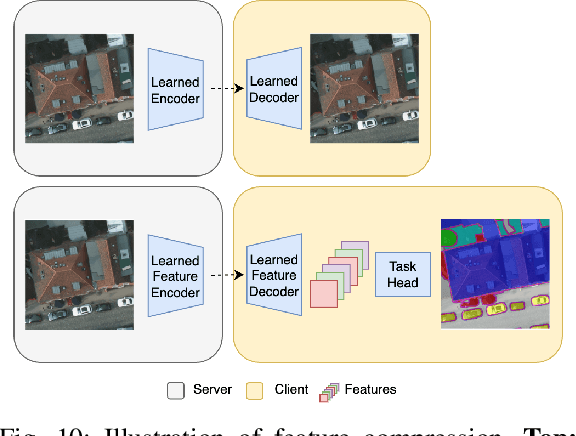
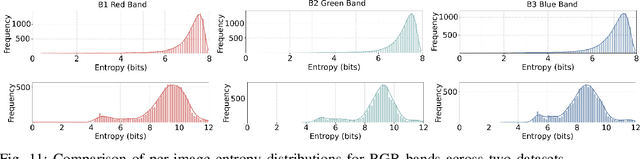
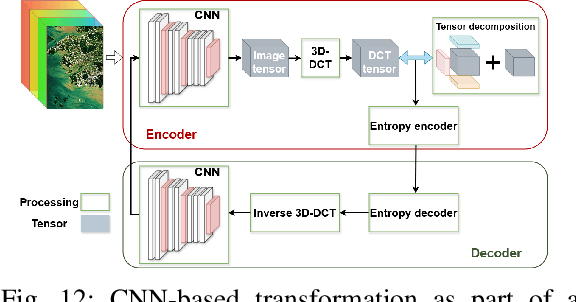
Abstract:Over the past decades, there has been an explosion in the amount of available Earth Observation (EO) data. The unprecedented coverage of the Earth's surface and atmosphere by satellite imagery has resulted in large volumes of data that must be transmitted to ground stations, stored in data centers, and distributed to end users. Modern Earth System Models (ESMs) face similar challenges, operating at high spatial and temporal resolutions, producing petabytes of data per simulated day. Data compression has gained relevance over the past decade, with neural compression (NC) emerging from deep learning and information theory, making EO data and ESM outputs ideal candidates due to their abundance of unlabeled data. In this review, we outline recent developments in NC applied to geospatial data. We introduce the fundamental concepts of NC including seminal works in its traditional applications to image and video compression domains with focus on lossy compression. We discuss the unique characteristics of EO and ESM data, contrasting them with "natural images", and explain the additional challenges and opportunities they present. Moreover, we review current applications of NC across various EO modalities and explore the limited efforts in ESM compression to date. The advent of self-supervised learning (SSL) and foundation models (FM) has advanced methods to efficiently distill representations from vast unlabeled data. We connect these developments to NC for EO, highlighting the similarities between the two fields and elaborate on the potential of transferring compressed feature representations for machine--to--machine communication. Based on insights drawn from this review, we devise future directions relevant to applications in EO and ESM.
Learnable polynomial, trigonometric, and tropical activations
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates scalable neural networks with learnable activation functions based on orthogonal function bases and tropical polynomials, targeting ImageNet-1K classification and next token prediction on OpenWebText. Traditional activations, such as ReLU, are static. In contrast, learnable activations enable the network to adapt dynamically during training. However, stability issues, such as vanishing or exploding gradients, arise with improper variance management in deeper networks. To remedy this, we propose an initialization scheme that single-handedly preserves unitary variance in transformers and convolutional networks, ensuring stable gradient flow even in deep architectures. Extensive experiments demonstrate that networks with Hermite, Fourier, and Tropical-based learnable activations significantly improve over GPT-2 and ConvNeXt networks in terms of accuracy and perplexity in train and test, highlighting the viability of learnable activations in large-scale tasks. The activation functions developed here are the subject of a library coded entirely in pure PyTorch: torchortho, available at https://github.com/K-H-Ismail/torchortho.
The Artificial Scientist -- in-transit Machine Learning of Plasma Simulations
Jan 06, 2025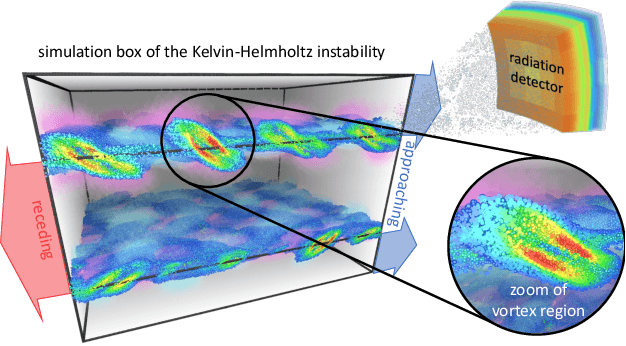
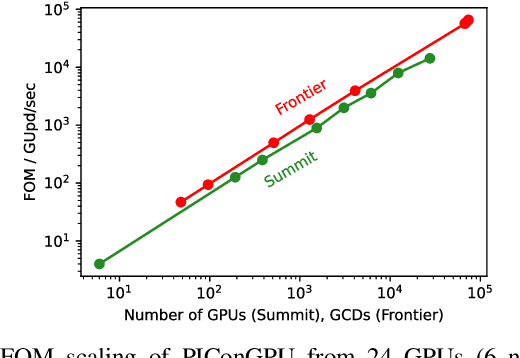
Abstract:Increasing HPC cluster sizes and large-scale simulations that produce petabytes of data per run, create massive IO and storage challenges for analysis. Deep learning-based techniques, in particular, make use of these amounts of domain data to extract patterns that help build scientific understanding. Here, we demonstrate a streaming workflow in which simulation data is streamed directly to a machine-learning (ML) framework, circumventing the file system bottleneck. Data is transformed in transit, asynchronously to the simulation and the training of the model. With the presented workflow, data operations can be performed in common and easy-to-use programming languages, freeing the application user from adapting the application output routines. As a proof-of-concept we consider a GPU accelerated particle-in-cell (PIConGPU) simulation of the Kelvin- Helmholtz instability (KHI). We employ experience replay to avoid catastrophic forgetting in learning from this non-steady process in a continual manner. We detail challenges addressed while porting and scaling to Frontier exascale system.
Scaling Image Tokenizers with Grouped Spherical Quantization
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Vision tokenizers have gained a lot of attraction due to their scalability and compactness; previous works depend on old-school GAN-based hyperparameters, biased comparisons, and a lack of comprehensive analysis of the scaling behaviours. To tackle those issues, we introduce Grouped Spherical Quantization (GSQ), featuring spherical codebook initialization and lookup regularization to constrain codebook latent to a spherical surface. Our empirical analysis of image tokenizer training strategies demonstrates that GSQ-GAN achieves superior reconstruction quality over state-of-the-art methods with fewer training iterations, providing a solid foundation for scaling studies. Building on this, we systematically examine the scaling behaviours of GSQ, specifically in latent dimensionality, codebook size, and compression ratios, and their impact on model performance. Our findings reveal distinct behaviours at high and low spatial compression levels, underscoring challenges in representing high-dimensional latent spaces. We show that GSQ can restructure high-dimensional latent into compact, low-dimensional spaces, thus enabling efficient scaling with improved quality. As a result, GSQ-GAN achieves a 16x down-sampling with a reconstruction FID (rFID) of 0.50.
OneProt: Towards Multi-Modal Protein Foundation Models
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent AI advances have enabled multi-modal systems to model and translate diverse information spaces. Extending beyond text and vision, we introduce OneProt, a multi-modal AI for proteins that integrates structural, sequence, alignment, and binding site data. Using the ImageBind framework, OneProt aligns the latent spaces of modality encoders along protein sequences. It demonstrates strong performance in retrieval tasks and surpasses state-of-the-art methods in various downstream tasks, including metal ion binding classification, gene-ontology annotation, and enzyme function prediction. This work expands multi-modal capabilities in protein models, paving the way for applications in drug discovery, biocatalytic reaction planning, and protein engineering.
Time Transfer: On Optimal Learning Rate and Batch Size In The Infinite Data Limit
Oct 08, 2024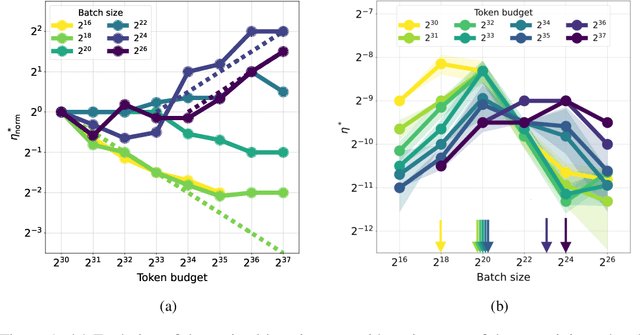
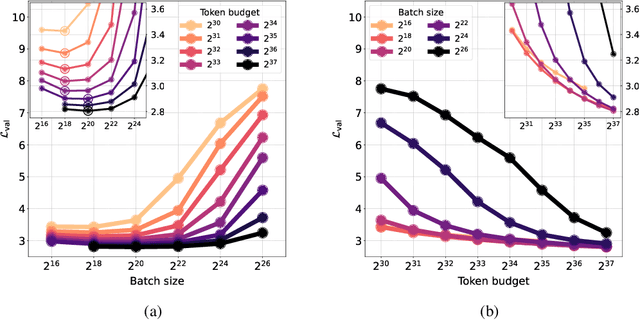
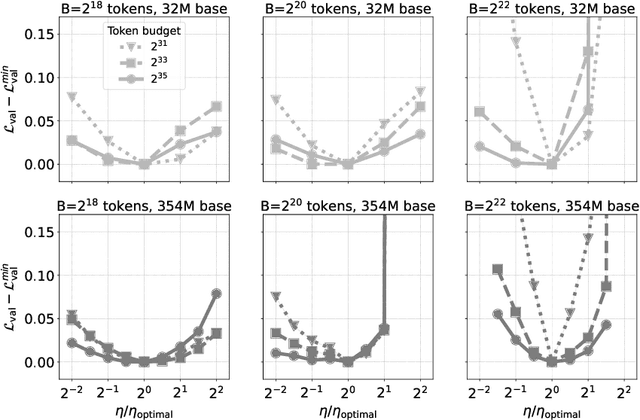
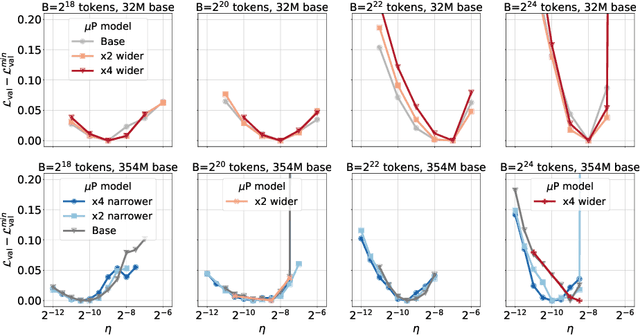
Abstract:One of the main challenges in optimal scaling of large language models (LLMs) is the prohibitive cost of hyperparameter tuning, particularly learning rate $\eta$ and batch size $B$. While techniques like $\mu$P (Yang et al., 2022) provide scaling rules for optimal $\eta$ transfer in the infinite model size limit, the optimal scaling behavior in the infinite data size limit ($T \to \infty$) remains unknown. We fill in this gap by observing for the first time an interplay of three optimal $\eta$ scaling regimes: $\eta \propto \sqrt{T}$, $\eta \propto 1$, and $\eta \propto 1/\sqrt{T}$ with transitions controlled by $B$ and its relation to the time-evolving critical batch size $B_\mathrm{crit} \propto T$. Furthermore, we show that the optimal batch size is positively correlated with $B_\mathrm{crit}$: keeping it fixed becomes suboptimal over time even if learning rate is scaled optimally. Surprisingly, our results demonstrate that the observed optimal $\eta$ and $B$ dynamics are preserved with $\mu$P model scaling, challenging the conventional view of $B_\mathrm{crit}$ dependence solely on loss value. Complementing optimality, we examine the sensitivity of loss to changes in learning rate, where we find the sensitivity to decrease with $T \to \infty$ and to remain constant with $\mu$P model scaling. We hope our results make the first step towards a unified picture of the joint optimal data and model scaling.
Tokenizer Choice For LLM Training: Negligible or Crucial?
Oct 18, 2023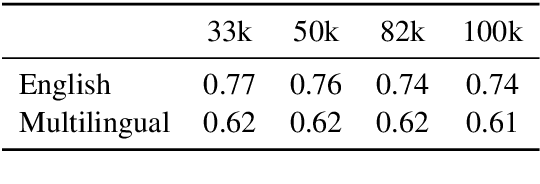
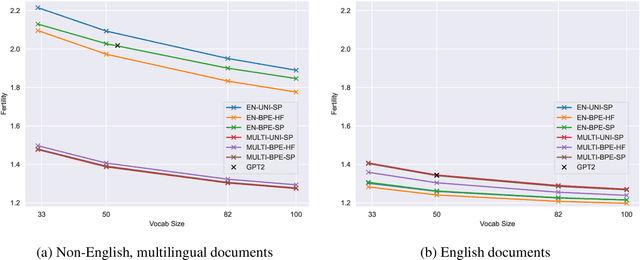
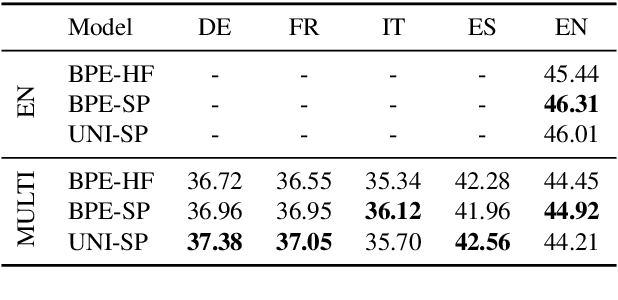
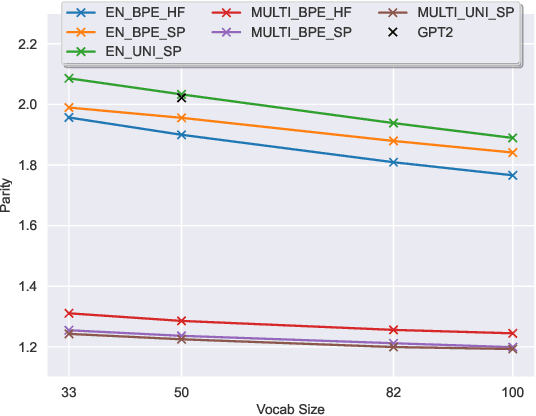
Abstract:The recent success of LLMs has been predominantly driven by curating the training dataset composition, scaling of model architectures and dataset sizes and advancements in pretraining objectives, leaving tokenizer influence as a blind spot. Shedding light on this underexplored area, we conduct a comprehensive study on the influence of tokenizer choice on LLM downstream performance by training 24 mono- and multilingual LLMs at a 2.6B parameter scale, ablating different tokenizer algorithms and parameterizations. Our studies highlight that the tokenizer choice can significantly impact the model's downstream performance, training and inference costs. In particular, we find that the common tokenizer evaluation metrics fertility and parity are not always predictive of model downstream performance, rendering these metrics a questionable proxy for the model's downstream performance. Furthermore, we show that multilingual tokenizers trained on the five most frequent European languages require vocabulary size increases of factor three in comparison to English. While English-only tokenizers have been applied to the training of multi-lingual LLMs, we find that this approach results in a severe downstream performance degradation and additional training costs of up to 68%, due to an inefficient tokenization vocabulary.
Physics informed Neural Networks applied to the description of wave-particle resonance in kinetic simulations of fusion plasmas
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:The Vlasov-Poisson system is employed in its reduced form version (1D1V) as a test bed for the applicability of Physics Informed Neural Network (PINN) to the wave-particle resonance. Two examples are explored: the Landau damping and the bump-on-tail instability. PINN is first tested as a compression method for the solution of the Vlasov-Poisson system and compared to the standard neural networks. Second, the application of PINN to solving the Vlasov-Poisson system is also presented with the special emphasis on the integral part, which motivates the implementation of a PINN variant, called Integrable PINN (I-PINN), based on the automatic-differentiation to solve the partial differential equation and on the automatic-integration to solve the integral equation.
A Comparative Study on Generative Models for High Resolution Solar Observation Imaging
Apr 14, 2023Abstract:Solar activity is one of the main drivers of variability in our solar system and the key source of space weather phenomena that affect Earth and near Earth space. The extensive record of high resolution extreme ultraviolet (EUV) observations from the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) offers an unprecedented, very large dataset of solar images. In this work, we make use of this comprehensive dataset to investigate capabilities of current state-of-the-art generative models to accurately capture the data distribution behind the observed solar activity states. Starting from StyleGAN-based methods, we uncover severe deficits of this model family in handling fine-scale details of solar images when training on high resolution samples, contrary to training on natural face images. When switching to the diffusion based generative model family, we observe strong improvements of fine-scale detail generation. For the GAN family, we are able to achieve similar improvements in fine-scale generation when turning to ProjectedGANs, which uses multi-scale discriminators with a pre-trained frozen feature extractor. We conduct ablation studies to clarify mechanisms responsible for proper fine-scale handling. Using distributed training on supercomputers, we are able to train generative models for up to 1024x1024 resolution that produce high quality samples indistinguishable to human experts, as suggested by the evaluation we conduct. We make all code, models and workflows used in this study publicly available at \url{https://github.com/SLAMPAI/generative-models-for-highres-solar-images}.
Hearts Gym: Learning Reinforcement Learning as a Team Event
Sep 07, 2022Abstract:Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors of this paper organized a Reinforcement Learning (RL) course for a graduate school in the field of data science. We describe the strategy and materials for creating an exciting learning experience despite the ubiquitous Zoom fatigue and evaluate the course qualitatively. The key organizational features are a focus on a competitive hands-on setting in teams, supported by a minimum of lectures providing the essential background on RL. The practical part of the course revolved around Hearts Gym, an RL environment for the card game Hearts that we developed as an entry-level tutorial to RL. Participants were tasked with training agents to explore reward shaping and other RL hyperparameters. For a final evaluation, the agents of the participants competed against each other.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge