Li-Rong Dai
Trusted Mamba Contrastive Network for Multi-View Clustering
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:Multi-view clustering can partition data samples into their categories by learning a consensus representation in an unsupervised way and has received more and more attention in recent years. However, there is an untrusted fusion problem. The reasons for this problem are as follows: 1) The current methods ignore the presence of noise or redundant information in the view; 2) The similarity of contrastive learning comes from the same sample rather than the same cluster in deep multi-view clustering. It causes multi-view fusion in the wrong direction. This paper proposes a novel multi-view clustering network to address this problem, termed as Trusted Mamba Contrastive Network (TMCN). Specifically, we present a new Trusted Mamba Fusion Network (TMFN), which achieves a trusted fusion of multi-view data through a selective mechanism. Moreover, we align the fused representation and the view-specific representation using the Average-similarity Contrastive Learning (AsCL) module. AsCL increases the similarity of view presentation from the same cluster, not merely from the same sample. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results in deep multi-view clustering tasks.
Adaptive Confidence Multi-View Hashing for Multimedia Retrieval
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:The multi-view hash method converts heterogeneous data from multiple views into binary hash codes, which is one of the critical technologies in multimedia retrieval. However, the current methods mainly explore the complementarity among multiple views while lacking confidence learning and fusion. Moreover, in practical application scenarios, the single-view data contain redundant noise. To conduct the confidence learning and eliminate unnecessary noise, we propose a novel Adaptive Confidence Multi-View Hashing (ACMVH) method. First, a confidence network is developed to extract useful information from various single-view features and remove noise information. Furthermore, an adaptive confidence multi-view network is employed to measure the confidence of each view and then fuse multi-view features through a weighted summation. Lastly, a dilation network is designed to further enhance the feature representation of the fused features. To the best of our knowledge, we pioneer the application of confidence learning into the field of multimedia retrieval. Extensive experiments on two public datasets show that the proposed ACMVH performs better than state-of-the-art methods (maximum increase of 3.24%). The source code is available at https://github.com/HackerHyper/ACMVH.
Semantic VAD: Low-Latency Voice Activity Detection for Speech Interaction
May 21, 2023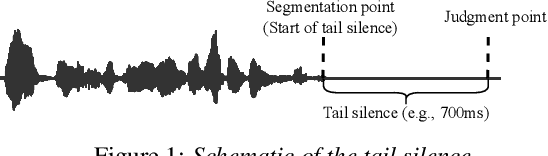
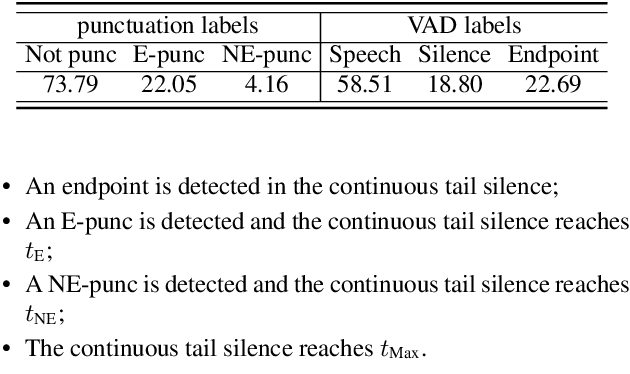
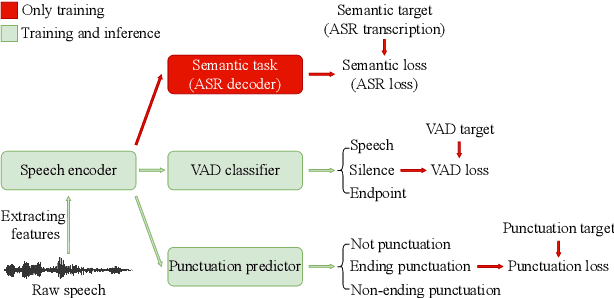
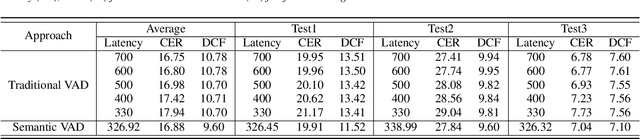
Abstract:For speech interaction, voice activity detection (VAD) is often used as a front-end. However, traditional VAD algorithms usually need to wait for a continuous tail silence to reach a preset maximum duration before segmentation, resulting in a large latency that affects user experience. In this paper, we propose a novel semantic VAD for low-latency segmentation. Different from existing methods, a frame-level punctuation prediction task is added to the semantic VAD, and the artificial endpoint is included in the classification category in addition to the often-used speech presence and absence. To enhance the semantic information of the model, we also incorporate an automatic speech recognition (ASR) related semantic loss. Evaluations on an internal dataset show that the proposed method can reduce the average latency by 53.3% without significant deterioration of character error rate in the back-end ASR compared to the traditional VAD approach.
CASA-ASR: Context-Aware Speaker-Attributed ASR
May 21, 2023



Abstract:Recently, speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (SA-ASR) has attracted a wide attention, which aims at answering the question ``who spoke what''. Different from modular systems, end-to-end (E2E) SA-ASR minimizes the speaker-dependent recognition errors directly and shows a promising applicability. In this paper, we propose a context-aware SA-ASR (CASA-ASR) model by enhancing the contextual modeling ability of E2E SA-ASR. Specifically, in CASA-ASR, a contextual text encoder is involved to aggregate the semantic information of the whole utterance, and a context-dependent scorer is employed to model the speaker discriminability by contrasting with speakers in the context. In addition, a two-pass decoding strategy is further proposed to fully leverage the contextual modeling ability resulting in a better recognition performance. Experimental results on AliMeeting corpus show that the proposed CASA-ASR model outperforms the original E2E SA-ASR system with a relative improvement of 11.76% in terms of speaker-dependent character error rate.
Joint Generative-Contrastive Representation Learning for Anomalous Sound Detection
May 20, 2023


Abstract:In this paper, we propose a joint generative and contrastive representation learning method (GeCo) for anomalous sound detection (ASD). GeCo exploits a Predictive AutoEncoder (PAE) equipped with self-attention as a generative model to perform frame-level prediction. The output of the PAE together with original normal samples, are used for supervised contrastive representative learning in a multi-task framework. Besides cross-entropy loss between classes, contrastive loss is used to separate PAE output and original samples within each class. GeCo aims to better capture context information among frames, thanks to the self-attention mechanism for PAE model. Furthermore, GeCo combines generative and contrastive learning from which we aim to yield more effective and informative representations, compared to existing methods. Extensive experiments have been conducted on the DCASE2020 Task2 development dataset, showing that GeCo outperforms state-of-the-art generative and discriminative methods.
AST-SED: An Effective Sound Event Detection Method Based on Audio Spectrogram Transformer
Mar 07, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an effective sound event detection (SED) method based on the audio spectrogram transformer (AST) model, pretrained on the large-scale AudioSet for audio tagging (AT) task, termed AST-SED. Pretrained AST models have recently shown promise on DCASE2022 challenge task4 where they help mitigate a lack of sufficient real annotated data. However, mainly due to differences between the AT and SED tasks, it is suboptimal to directly utilize outputs from a pretrained AST model. Hence the proposed AST-SED adopts an encoder-decoder architecture to enable effective and efficient fine-tuning without needing to redesign or retrain the AST model. Specifically, the Frequency-wise Transformer Encoder (FTE) consists of transformers with self attention along the frequency axis to address multiple overlapped audio events issue in a single clip. The Local Gated Recurrent Units Decoder (LGD) consists of nearest-neighbor interpolation (NNI) and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Units (Bi-GRU) to compensate for temporal resolution loss in the pretrained AST model output. Experimental results on DCASE2022 task4 development set have demonstrated the superiority of the proposed AST-SED with FTE-LGD architecture. Specifically, the Event-Based F1-score (EB-F1) of 59.60% and Polyphonic Sound detection Score scenario1 (PSDS1) score of 0.5140 significantly outperform CRNN and other pretrained AST-based systems.
A Comparative Study on multichannel Speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition in Multi-party Meetings
Nov 01, 2022Abstract:Speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (SA-ASR) in multiparty meeting scenarios is one of the most valuable and challenging ASR task. It was shown that single-channel frame-level diarization with serialized output training (SC-FD-SOT), single-channel word-level diarization with SOT (SC-WD-SOT) and joint training of single-channel target-speaker separation and ASR (SC-TS-ASR) can be exploited to partially solve this problem. SC-FD-SOT obtains the speaker-attributed transcriptions by aligning the speaker diarization results with the ASR hypotheses, SC-WD-SOT uses word-level diarization to get rid of the alignment dependence on timestamps, and SC-TS-ASR jointly trains target-speaker separation and ASR modules, which achieves the best performance. In this paper, we propose three corresponding multichannel (MC) SA-ASR approaches, namely MC-FD-SOT, MC-WD-SOT and MC-TS-ASR. For different tasks/models, different multichannel data fusion strategies are considered, including channel-level cross-channel attention for MC-FD-SOT, frame-level cross-channel attention for MC-WD-SOT and neural beamforming for MC-TS-ASR. Experimental results on the AliMeeting corpus reveal that our proposed multichannel SA-ASR models can consistently outperform the corresponding single-channel counterparts in terms of the speaker-dependent character error rate (SD-CER).
Robust Data2vec: Noise-robust Speech Representation Learning for ASR by Combining Regression and Improved Contrastive Learning
Oct 27, 2022



Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training methods based on contrastive learning or regression tasks can utilize more unlabeled data to improve the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, the robustness impact of combining the two pre-training tasks and constructing different negative samples for contrastive learning still remains unclear. In this paper, we propose a noise-robust data2vec for self-supervised speech representation learning by jointly optimizing the contrastive learning and regression tasks in the pre-training stage. Furthermore, we present two improved methods to facilitate contrastive learning. More specifically, we first propose to construct patch-based non-semantic negative samples to boost the noise robustness of the pre-training model, which is achieved by dividing the features into patches at different sizes (i.e., so-called negative samples). Second, by analyzing the distribution of positive and negative samples, we propose to remove the easily distinguishable negative samples to improve the discriminative capacity for pre-training models. Experimental results on the CHiME-4 dataset show that our method is able to improve the performance of the pre-trained model in noisy scenarios. We find that joint training of the contrastive learning and regression tasks can avoid the model collapse to some extent compared to only training the regression task.
Joint Training of Speech Enhancement and Self-supervised Model for Noise-robust ASR
May 26, 2022



Abstract:Speech enhancement (SE) is usually required as a front end to improve the speech quality in noisy environments, while the enhanced speech might not be optimal for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems due to speech distortion. On the other hand, it was shown that self-supervised pre-training enables the utilization of a large amount of unlabeled noisy data, which is rather beneficial for the noise robustness of ASR. However, the potential of the (optimal) integration of SE and self-supervised pre-training still remains unclear. In order to find an appropriate combination and reduce the impact of speech distortion caused by SE, in this paper we therefore propose a joint pre-training approach for the SE module and the self-supervised model. First, in the pre-training phase the original noisy waveform or the waveform obtained by SE is fed into the self-supervised model to learn the contextual representation, where the quantified clean speech acts as the target. Second, we propose a dual-attention fusion method to fuse the features of noisy and enhanced speeches, which can compensate the information loss caused by separately using individual modules. Due to the flexible exploitation of clean/noisy/enhanced branches, the proposed method turns out to be a generalization of some existing noise-robust ASR models, e.g., enhanced wav2vec2.0. Finally, experimental results on both synthetic and real noisy datasets show that the proposed joint training approach can improve the ASR performance under various noisy settings, leading to a stronger noise robustness.
A Complementary Joint Training Approach Using Unpaired Speech and Text for Low-Resource Automatic Speech Recognition
Apr 05, 2022
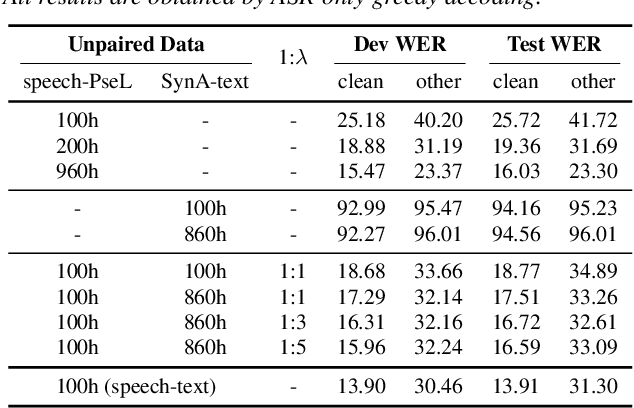
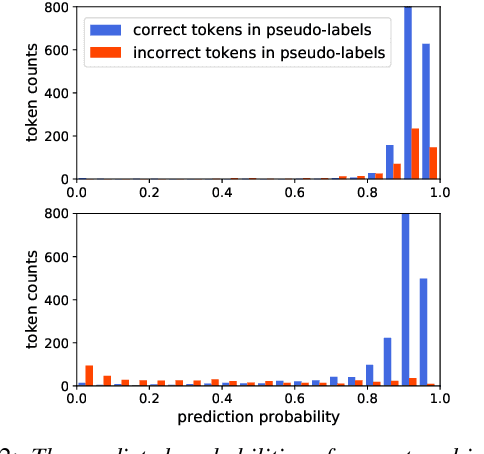
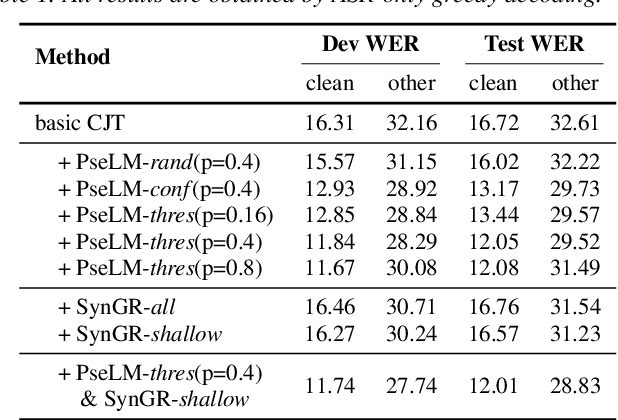
Abstract:Unpaired data has shown to be beneficial for low-resource automatic speech recognition~(ASR), which can be involved in the design of hybrid models with multi-task training or language model dependent pre-training. In this work, we leverage unpaired data to train a general sequence-to-sequence model. Unpaired speech and text are used in the form of data pairs by generating the corresponding missing parts in prior to model training. Inspired by the complementarity of speech-PseudoLabel pair and SynthesizedAudio-text pair in both acoustic features and linguistic features, we propose a complementary joint training~(CJT) method that trains a model alternatively with two data pairs. Furthermore, label masking for pseudo-labels and gradient restriction for synthesized audio are proposed to further cope with the deviations from real data, termed as CJT++. Experimental results show that compared to speech-only training, the proposed basic CJT achieves great performance improvements on clean/other test sets, and the CJT++ re-training yields further performance enhancements. It is also apparent that the proposed method outperforms the wav2vec2.0 model with the same model size and beam size, particularly in extreme low-resource cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge