Koushik Biswas
Hyperspectral Image Land Cover Captioning Dataset for Vision Language Models
May 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce HyperCap, the first large-scale hyperspectral captioning dataset designed to enhance model performance and effectiveness in remote sensing applications. Unlike traditional hyperspectral imaging (HSI) datasets that focus solely on classification tasks, HyperCap integrates spectral data with pixel-wise textual annotations, enabling deeper semantic understanding of hyperspectral imagery. This dataset enhances model performance in tasks like classification and feature extraction, providing a valuable resource for advanced remote sensing applications. HyperCap is constructed from four benchmark datasets and annotated through a hybrid approach combining automated and manual methods to ensure accuracy and consistency. Empirical evaluations using state-of-the-art encoders and diverse fusion techniques demonstrate significant improvements in classification performance. These results underscore the potential of vision-language learning in HSI and position HyperCap as a foundational dataset for future research in the field.
Predicting Risk of Pulmonary Fibrosis Formation in PASC Patients
May 15, 2025Abstract:While the acute phase of the COVID-19 pandemic has subsided, its long-term effects persist through Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), commonly known as Long COVID. There remains substantial uncertainty regarding both its duration and optimal management strategies. PASC manifests as a diverse array of persistent or newly emerging symptoms--ranging from fatigue, dyspnea, and neurologic impairments (e.g., brain fog), to cardiovascular, pulmonary, and musculoskeletal abnormalities--that extend beyond the acute infection phase. This heterogeneous presentation poses substantial challenges for clinical assessment, diagnosis, and treatment planning. In this paper, we focus on imaging findings that may suggest fibrotic damage in the lungs, a critical manifestation characterized by scarring of lung tissue, which can potentially affect long-term respiratory function in patients with PASC. This study introduces a novel multi-center chest CT analysis framework that combines deep learning and radiomics for fibrosis prediction. Our approach leverages convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and interpretable feature extraction, achieving 82.2% accuracy and 85.5% AUC in classification tasks. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Grad-CAM visualization and radiomics-based feature analysis in providing clinically relevant insights for PASC-related lung fibrosis prediction. Our findings highlight the potential of deep learning-driven computational methods for early detection and risk assessment of PASC-related lung fibrosis--presented for the first time in the literature.
Is Long Range Sequential Modeling Necessary For Colorectal Tumor Segmentation?
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Segmentation of colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors in 3D medical imaging is both complex and clinically critical, providing vital support for effective radiation therapy planning and survival outcome assessment. Recently, 3D volumetric segmentation architectures incorporating long-range sequence modeling mechanisms, such as Transformers and Mamba, have gained attention for their capacity to achieve high accuracy in 3D medical image segmentation. In this work, we evaluate the effectiveness of these global token modeling techniques by pitting them against our proposed MambaOutUNet within the context of our newly introduced colorectal tumor segmentation dataset (CTS-204). Our findings suggest that robust local token interactions can outperform long-range modeling techniques in cases where the region of interest is small and anatomically complex, proposing a potential shift in 3D tumor segmentation research.
Uncertainty-Guided Cross Attention Ensemble Mean Teacher for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:This work proposes a novel framework, Uncertainty-Guided Cross Attention Ensemble Mean Teacher (UG-CEMT), for achieving state-of-the-art performance in semi-supervised medical image segmentation. UG-CEMT leverages the strengths of co-training and knowledge distillation by combining a Cross-attention Ensemble Mean Teacher framework (CEMT) inspired by Vision Transformers (ViT) with uncertainty-guided consistency regularization and Sharpness-Aware Minimization emphasizing uncertainty. UG-CEMT improves semi-supervised performance while maintaining a consistent network architecture and task setting by fostering high disparity between sub-networks. Experiments demonstrate significant advantages over existing methods like Mean Teacher and Cross-pseudo Supervision in terms of disparity, domain generalization, and medical image segmentation performance. UG-CEMT achieves state-of-the-art results on multi-center prostate MRI and cardiac MRI datasets, where object segmentation is particularly challenging. Our results show that using only 10\% labeled data, UG-CEMT approaches the performance of fully supervised methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in exploiting unlabeled data for robust medical image segmentation. The code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/Meghnak13/UG-CEMT}
Frequency-Based Federated Domain Generalization for Polyp Segmentation
Oct 02, 2024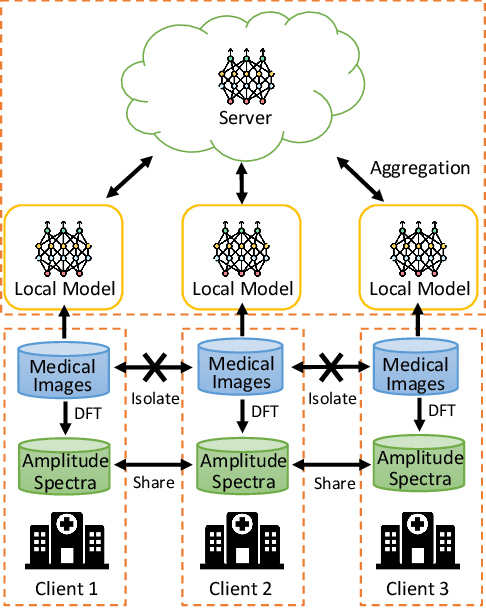
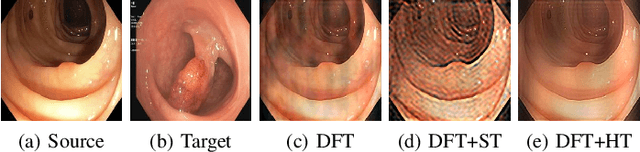
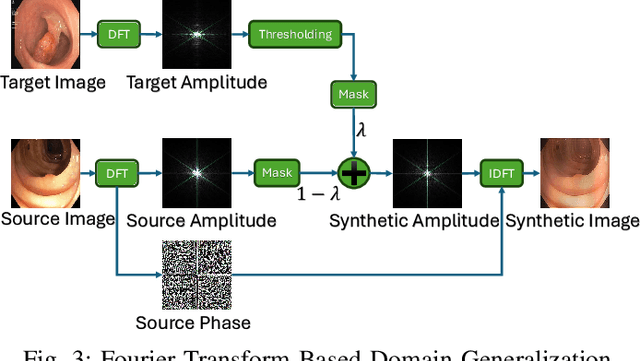

Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) offers a powerful strategy for training machine learning models across decentralized datasets while maintaining data privacy, yet domain shifts among clients can degrade performance, particularly in medical imaging tasks like polyp segmentation. This paper introduces a novel Frequency-Based Domain Generalization (FDG) framework, utilizing soft- and hard-thresholding in the Fourier domain to address these challenges. By applying soft- and hard-thresholding to Fourier coefficients, our method generates new images with reduced background noise and enhances the model's ability to generalize across diverse medical imaging domains. Extensive experiments demonstrate substantial improvements in segmentation accuracy and domain robustness over baseline methods. This innovation integrates frequency domain techniques into FL, presenting a resilient approach to overcoming domain variability in decentralized medical image analysis.
A Novel Momentum-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Image Classification and Segmentation
Aug 11, 2024



Abstract:Accurately segmenting different organs from medical images is a critical prerequisite for computer-assisted diagnosis and intervention planning. This study proposes a deep learning-based approach for segmenting various organs from CT and MRI scans and classifying diseases. Our study introduces a novel technique integrating momentum within residual blocks for enhanced training dynamics in medical image analysis. We applied our method in two distinct tasks: segmenting liver, lung, & colon data and classifying abdominal pelvic CT and MRI scans. The proposed approach has shown promising results, outperforming state-of-the-art methods on publicly available benchmarking datasets. For instance, in the lung segmentation dataset, our approach yielded significant enhancements over the TransNetR model, including a 5.72% increase in dice score, a 5.04% improvement in mean Intersection over Union (mIoU), an 8.02% improvement in recall, and a 4.42% improvement in precision. Hence, incorporating momentum led to state-of-the-art performance in both segmentation and classification tasks, representing a significant advancement in the field of medical imaging.
DCT-Based Decorrelated Attention for Vision Transformers
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Central to the Transformer architectures' effectiveness is the self-attention mechanism, a function that maps queries, keys, and values into a high-dimensional vector space. However, training the attention weights of queries, keys, and values is non-trivial from a state of random initialization. In this paper, we propose two methods. (i) We first address the initialization problem of Vision Transformers by introducing a simple, yet highly innovative, initialization approach utilizing Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) coefficients. Our proposed DCT-based attention initialization marks a significant gain compared to traditional initialization strategies; offering a robust foundation for the attention mechanism. Our experiments reveal that the DCT-based initialization enhances the accuracy of Vision Transformers in classification tasks. (ii) We also recognize that since DCT effectively decorrelates image information in the frequency domain, this decorrelation is useful for compression because it allows the quantization step to discard many of the higher-frequency components. Based on this observation, we propose a novel DCT-based compression technique for the attention function of Vision Transformers. Since high-frequency DCT coefficients usually correspond to noise, we truncate the high-frequency DCT components of the input patches. Our DCT-based compression reduces the size of weight matrices for queries, keys, and values. While maintaining the same level of accuracy, our DCT compressed Swin Transformers obtain a considerable decrease in the computational overhead.
Federated Learning in Healthcare: Model Misconducts, Security, Challenges, Applications, and Future Research Directions -- A Systematic Review
May 22, 2024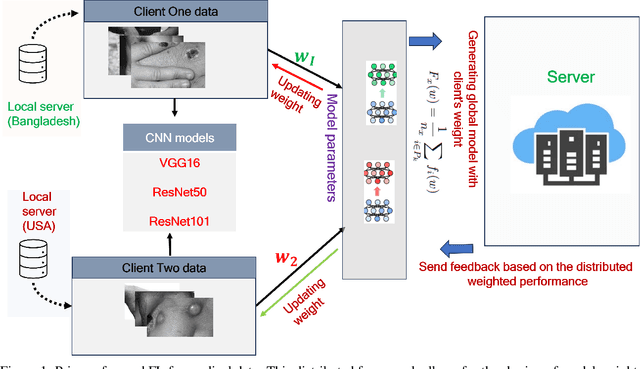
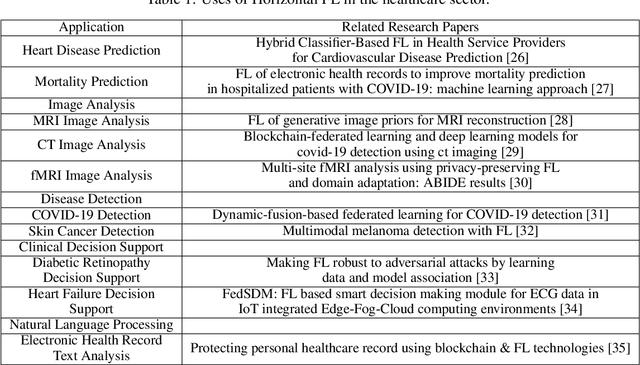
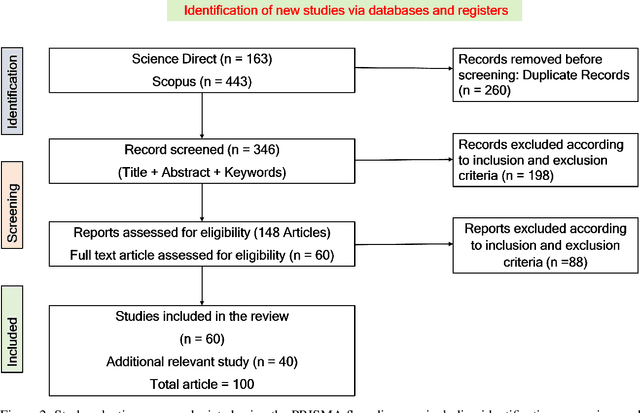
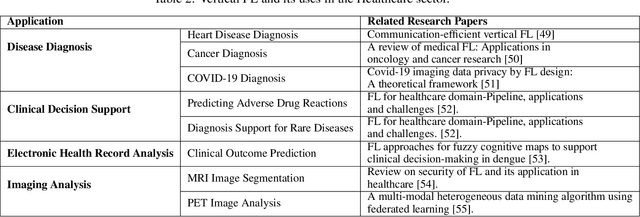
Abstract:Data privacy has become a major concern in healthcare due to the increasing digitization of medical records and data-driven medical research. Protecting sensitive patient information from breaches and unauthorized access is critical, as such incidents can have severe legal and ethical complications. Federated Learning (FL) addresses this concern by enabling multiple healthcare institutions to collaboratively learn from decentralized data without sharing it. FL's scope in healthcare covers areas such as disease prediction, treatment customization, and clinical trial research. However, implementing FL poses challenges, including model convergence in non-IID (independent and identically distributed) data environments, communication overhead, and managing multi-institutional collaborations. A systematic review of FL in healthcare is necessary to evaluate how effectively FL can provide privacy while maintaining the integrity and usability of medical data analysis. In this study, we analyze existing literature on FL applications in healthcare. We explore the current state of model security practices, identify prevalent challenges, and discuss practical applications and their implications. Additionally, the review highlights promising future research directions to refine FL implementations, enhance data security protocols, and expand FL's use to broader healthcare applications, which will benefit future researchers and practitioners.
MDNet: Multi-Decoder Network for Abdominal CT Organs Segmentation
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Accurate segmentation of organs from abdominal CT scans is essential for clinical applications such as diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. To handle challenges of heterogeneity in organ shapes, sizes, and complex anatomical relationships, we propose a \textbf{\textit{\ac{MDNet}}}, an encoder-decoder network that uses the pre-trained \textit{MiT-B2} as the encoder and multiple different decoder networks. Each decoder network is connected to a different part of the encoder via a multi-scale feature enhancement dilated block. With each decoder, we increase the depth of the network iteratively and refine segmentation masks, enriching feature maps by integrating previous decoders' feature maps. To refine the feature map further, we also utilize the predicted masks from the previous decoder to the current decoder to provide spatial attention across foreground and background regions. MDNet effectively refines the segmentation mask with a high dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.9013 and 0.9169 on the Liver Tumor segmentation (LiTS) and MSD Spleen datasets. Additionally, it reduces Hausdorff distance (HD) to 3.79 for the LiTS dataset and 2.26 for the spleen segmentation dataset, underscoring the precision of MDNet in capturing the complex contours. Moreover, \textit{\ac{MDNet}} is more interpretable and robust compared to the other baseline models.
PAM-UNet: Shifting Attention on Region of Interest in Medical Images
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Computer-aided segmentation methods can assist medical personnel in improving diagnostic outcomes. While recent advancements like UNet and its variants have shown promise, they face a critical challenge: balancing accuracy with computational efficiency. Shallow encoder architectures in UNets often struggle to capture crucial spatial features, leading in inaccurate and sparse segmentation. To address this limitation, we propose a novel \underline{P}rogressive \underline{A}ttention based \underline{M}obile \underline{UNet} (\underline{PAM-UNet}) architecture. The inverted residual (IR) blocks in PAM-UNet help maintain a lightweight framework, while layerwise \textit{Progressive Luong Attention} ($\mathcal{PLA}$) promotes precise segmentation by directing attention toward regions of interest during synthesis. Our approach prioritizes both accuracy and speed, achieving a commendable balance with a mean IoU of 74.65 and a dice score of 82.87, while requiring only 1.32 floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) on the Liver Tumor Segmentation Benchmark (LiTS) 2017 dataset. These results highlight the importance of developing efficient segmentation models to accelerate the adoption of AI in clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge