Khalil Bibi
EWEK-QA: Enhanced Web and Efficient Knowledge Graph Retrieval for Citation-based Question Answering Systems
Jun 14, 2024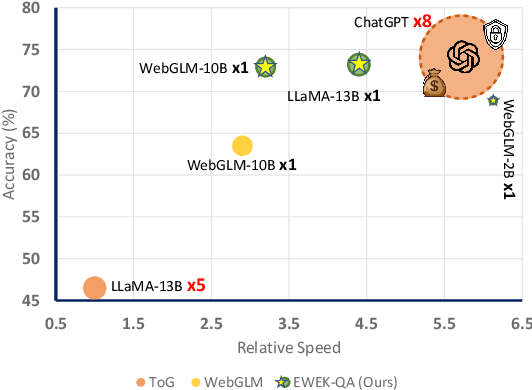
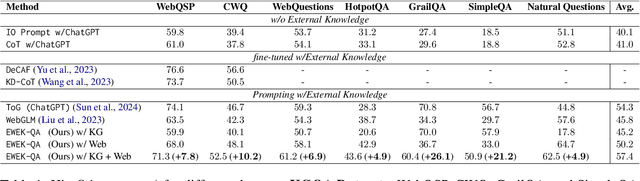
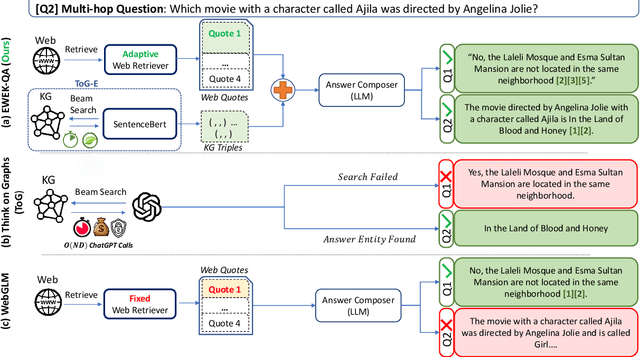
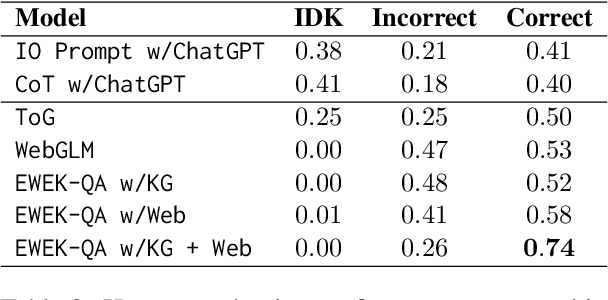
Abstract:The emerging citation-based QA systems are gaining more attention especially in generative AI search applications. The importance of extracted knowledge provided to these systems is vital from both accuracy (completeness of information) and efficiency (extracting the information in a timely manner). In this regard, citation-based QA systems are suffering from two shortcomings. First, they usually rely only on web as a source of extracted knowledge and adding other external knowledge sources can hamper the efficiency of the system. Second, web-retrieved contents are usually obtained by some simple heuristics such as fixed length or breakpoints which might lead to splitting information into pieces. To mitigate these issues, we propose our enhanced web and efficient knowledge graph (KG) retrieval solution (EWEK-QA) to enrich the content of the extracted knowledge fed to the system. This has been done through designing an adaptive web retriever and incorporating KGs triples in an efficient manner. We demonstrate the effectiveness of EWEK-QA over the open-source state-of-the-art (SoTA) web-based and KG baseline models using a comprehensive set of quantitative and human evaluation experiments. Our model is able to: first, improve the web-retriever baseline in terms of extracting more relevant passages (>20\%), the coverage of answer span (>25\%) and self containment (>35\%); second, obtain and integrate KG triples into its pipeline very efficiently (by avoiding any LLM calls) to outperform the web-only and KG-only SoTA baselines significantly in 7 quantitative QA tasks and our human evaluation.
Low-bit Shift Network for End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding
Jul 15, 2022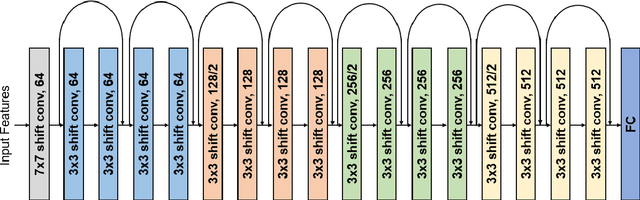
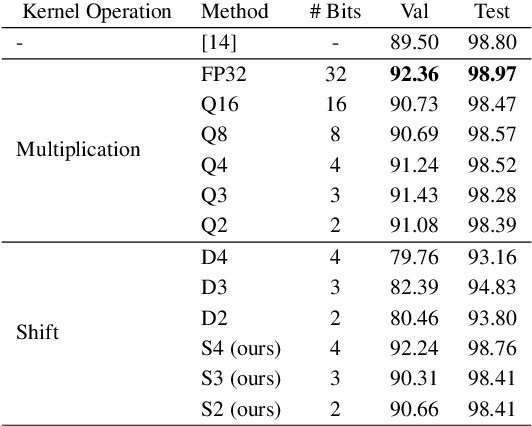
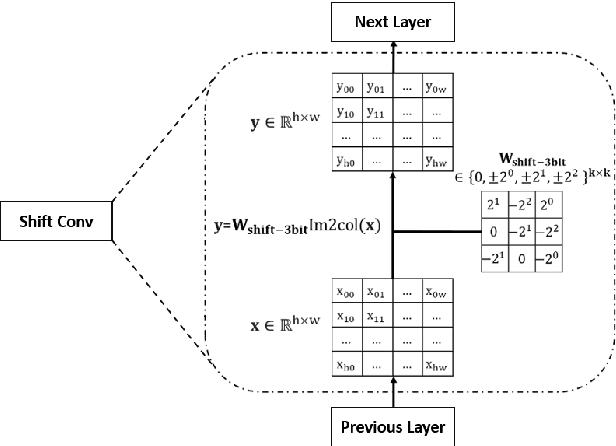
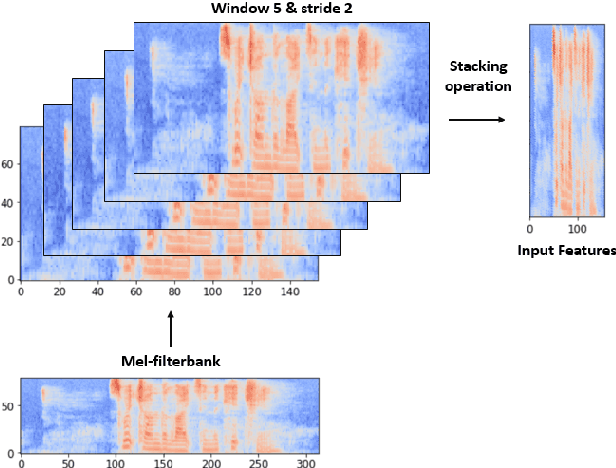
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNN) have achieved impressive success in multiple domains. Over the years, the accuracy of these models has increased with the proliferation of deeper and more complex architectures. Thus, state-of-the-art solutions are often computationally expensive, which makes them unfit to be deployed on edge computing platforms. In order to mitigate the high computation, memory, and power requirements of inferring convolutional neural networks (CNNs), we propose the use of power-of-two quantization, which quantizes continuous parameters into low-bit power-of-two values. This reduces computational complexity by removing expensive multiplication operations and with the use of low-bit weights. ResNet is adopted as the building block of our solution and the proposed model is evaluated on a spoken language understanding (SLU) task. Experimental results show improved performance for shift neural network architectures, with our low-bit quantization achieving 98.76 \% on the test set which is comparable performance to its full-precision counterpart and state-of-the-art solutions.
Revisiting Pre-trained Language Models and their Evaluation for Arabic Natural Language Understanding
May 21, 2022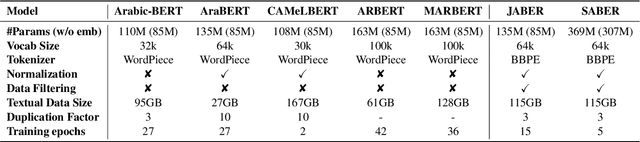
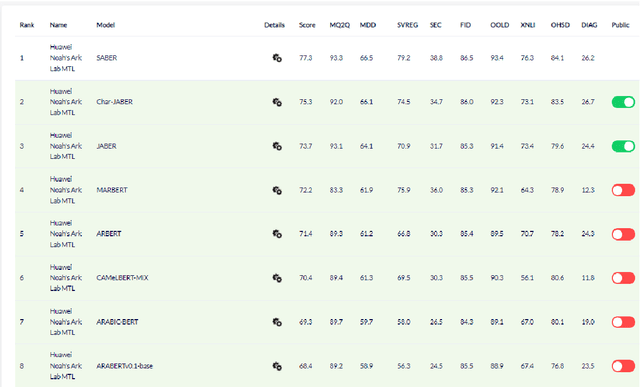

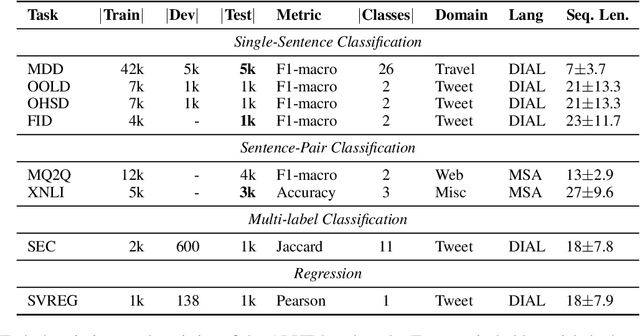
Abstract:There is a growing body of work in recent years to develop pre-trained language models (PLMs) for the Arabic language. This work concerns addressing two major problems in existing Arabic PLMs which constraint progress of the Arabic NLU and NLG fields.First, existing Arabic PLMs are not well-explored and their pre-trainig can be improved significantly using a more methodical approach. Second, there is a lack of systematic and reproducible evaluation of these models in the literature. In this work, we revisit both the pre-training and evaluation of Arabic PLMs. In terms of pre-training, we explore improving Arabic LMs from three perspectives: quality of the pre-training data, size of the model, and incorporating character-level information. As a result, we release three new Arabic BERT-style models ( JABER, Char-JABER, and SABER), and two T5-style models (AT5S and AT5B). In terms of evaluation, we conduct a comprehensive empirical study to systematically evaluate the performance of existing state-of-the-art models on ALUE that is a leaderboard-powered benchmark for Arabic NLU tasks, and on a subset of the ARGEN benchmark for Arabic NLG tasks. We show that our models significantly outperform existing Arabic PLMs and achieve a new state-of-the-art performance on discriminative and generative Arabic NLU and NLG tasks. Our models and source code to reproduce of results will be made available shortly.
CILDA: Contrastive Data Augmentation using Intermediate Layer Knowledge Distillation
Apr 15, 2022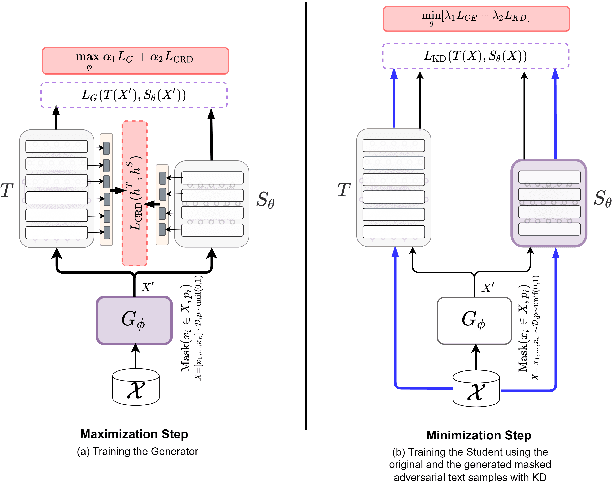
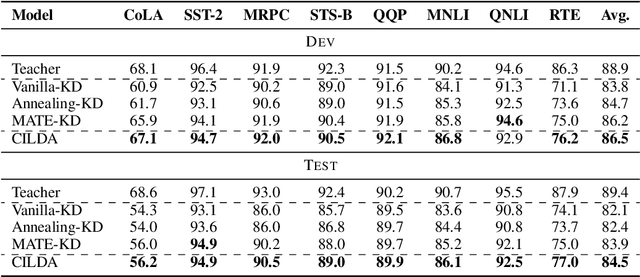
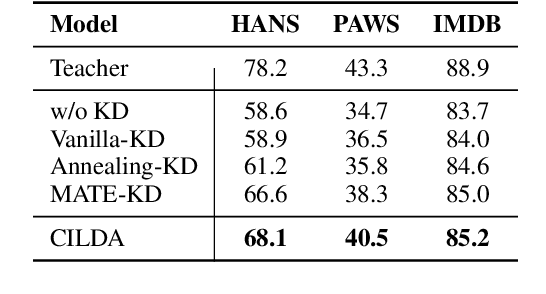
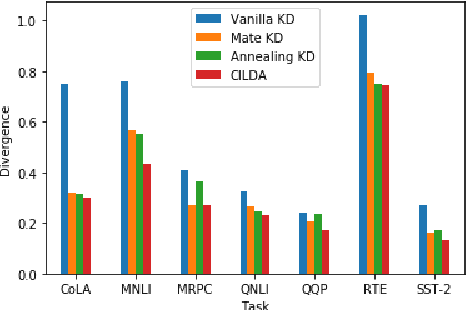
Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) is an efficient framework for compressing large-scale pre-trained language models. Recent years have seen a surge of research aiming to improve KD by leveraging Contrastive Learning, Intermediate Layer Distillation, Data Augmentation, and Adversarial Training. In this work, we propose a learning based data augmentation technique tailored for knowledge distillation, called CILDA. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that intermediate layer representations of the main task are used in improving the quality of augmented samples. More precisely, we introduce an augmentation technique for KD based on intermediate layer matching using contrastive loss to improve masked adversarial data augmentation. CILDA outperforms existing state-of-the-art KD approaches on the GLUE benchmark, as well as in an out-of-domain evaluation.
JABER and SABER: Junior and Senior Arabic BERt
Jan 09, 2022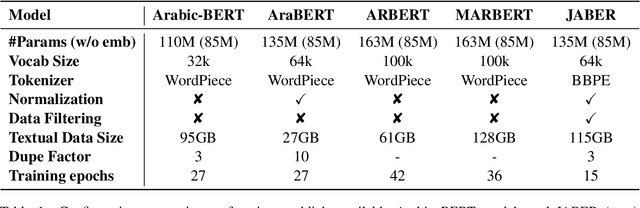
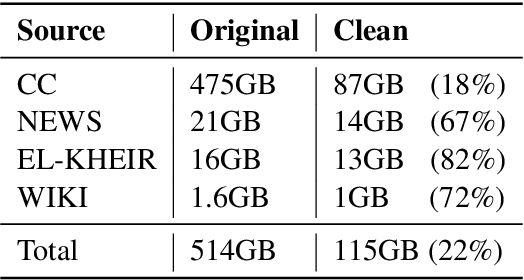
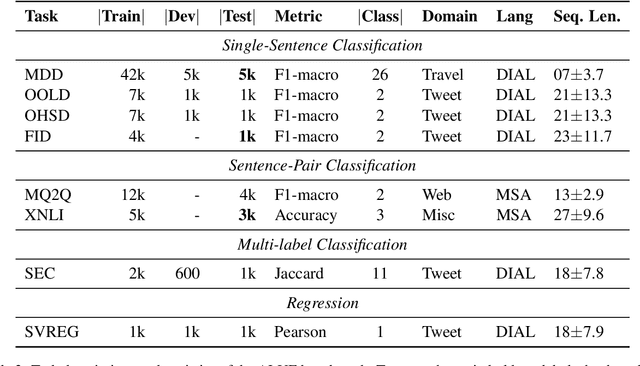
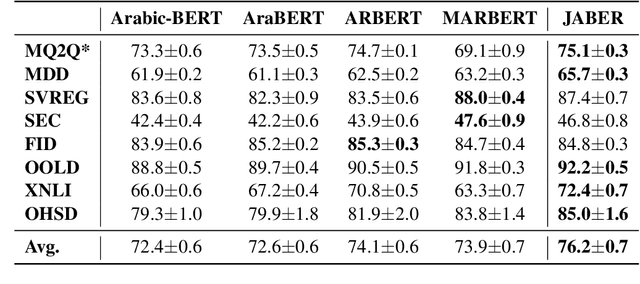
Abstract:Language-specific pre-trained models have proven to be more accurate than multilingual ones in a monolingual evaluation setting, Arabic is no exception. However, we found that previously released Arabic BERT models were significantly under-trained. In this technical report, we present JABER and SABER, Junior and Senior Arabic BERt respectively, our pre-trained language model prototypes dedicated for Arabic. We conduct an empirical study to systematically evaluate the performance of models across a diverse set of existing Arabic NLU tasks. Experimental results show that JABER and SABER achieve state-of-the-art performances on ALUE, a new benchmark for Arabic Language Understanding Evaluation, as well as on a well-established NER benchmark.
Knowledge Distillation with Noisy Labels for Natural Language Understanding
Sep 21, 2021


Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) is extensively used to compress and deploy large pre-trained language models on edge devices for real-world applications. However, one neglected area of research is the impact of noisy (corrupted) labels on KD. We present, to the best of our knowledge, the first study on KD with noisy labels in Natural Language Understanding (NLU). We document the scope of the problem and present two methods to mitigate the impact of label noise. Experiments on the GLUE benchmark show that our methods are effective even under high noise levels. Nevertheless, our results indicate that more research is necessary to cope with label noise under the KD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge