Sunyam Bagga
EWEK-QA: Enhanced Web and Efficient Knowledge Graph Retrieval for Citation-based Question Answering Systems
Jun 14, 2024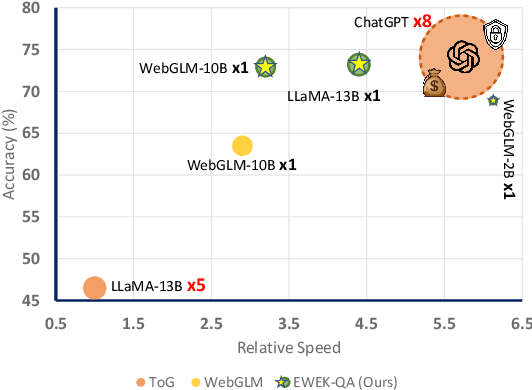
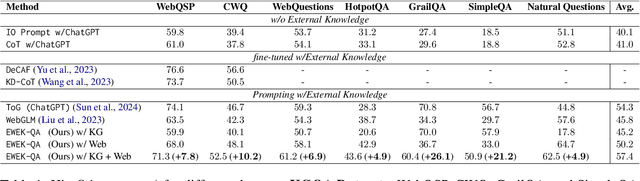
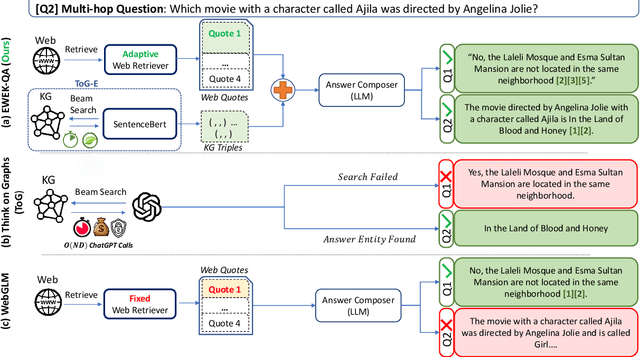
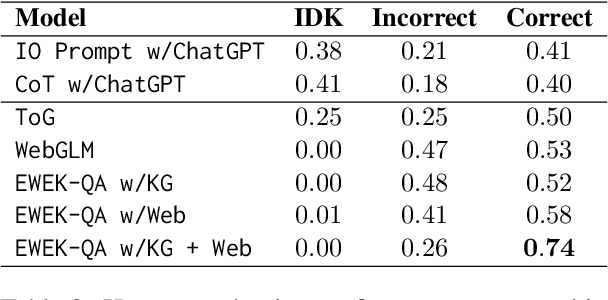
Abstract:The emerging citation-based QA systems are gaining more attention especially in generative AI search applications. The importance of extracted knowledge provided to these systems is vital from both accuracy (completeness of information) and efficiency (extracting the information in a timely manner). In this regard, citation-based QA systems are suffering from two shortcomings. First, they usually rely only on web as a source of extracted knowledge and adding other external knowledge sources can hamper the efficiency of the system. Second, web-retrieved contents are usually obtained by some simple heuristics such as fixed length or breakpoints which might lead to splitting information into pieces. To mitigate these issues, we propose our enhanced web and efficient knowledge graph (KG) retrieval solution (EWEK-QA) to enrich the content of the extracted knowledge fed to the system. This has been done through designing an adaptive web retriever and incorporating KGs triples in an efficient manner. We demonstrate the effectiveness of EWEK-QA over the open-source state-of-the-art (SoTA) web-based and KG baseline models using a comprehensive set of quantitative and human evaluation experiments. Our model is able to: first, improve the web-retriever baseline in terms of extracting more relevant passages (>20\%), the coverage of answer span (>25\%) and self containment (>35\%); second, obtain and integrate KG triples into its pipeline very efficiently (by avoiding any LLM calls) to outperform the web-only and KG-only SoTA baselines significantly in 7 quantitative QA tasks and our human evaluation.
Revisiting Pre-trained Language Models and their Evaluation for Arabic Natural Language Understanding
May 21, 2022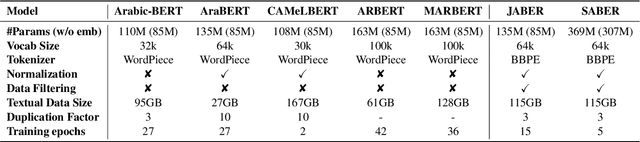
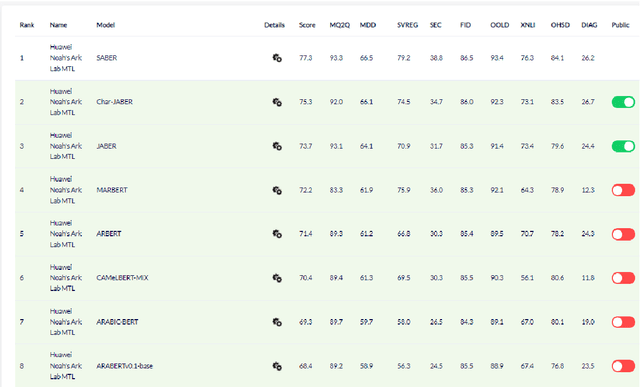

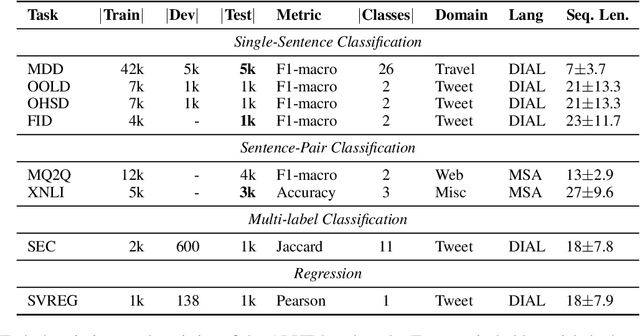
Abstract:There is a growing body of work in recent years to develop pre-trained language models (PLMs) for the Arabic language. This work concerns addressing two major problems in existing Arabic PLMs which constraint progress of the Arabic NLU and NLG fields.First, existing Arabic PLMs are not well-explored and their pre-trainig can be improved significantly using a more methodical approach. Second, there is a lack of systematic and reproducible evaluation of these models in the literature. In this work, we revisit both the pre-training and evaluation of Arabic PLMs. In terms of pre-training, we explore improving Arabic LMs from three perspectives: quality of the pre-training data, size of the model, and incorporating character-level information. As a result, we release three new Arabic BERT-style models ( JABER, Char-JABER, and SABER), and two T5-style models (AT5S and AT5B). In terms of evaluation, we conduct a comprehensive empirical study to systematically evaluate the performance of existing state-of-the-art models on ALUE that is a leaderboard-powered benchmark for Arabic NLU tasks, and on a subset of the ARGEN benchmark for Arabic NLG tasks. We show that our models significantly outperform existing Arabic PLMs and achieve a new state-of-the-art performance on discriminative and generative Arabic NLU and NLG tasks. Our models and source code to reproduce of results will be made available shortly.
Opportunistic Self Organizing Migrating Algorithm for Real-Time Dynamic Traveling Salesman Problem
Sep 12, 2017



Abstract:Self Organizing Migrating Algorithm (SOMA) is a meta-heuristic algorithm based on the self-organizing behavior of individuals in a simulated social environment. SOMA performs iterative computations on a population of potential solutions in the given search space to obtain an optimal solution. In this paper, an Opportunistic Self Organizing Migrating Algorithm (OSOMA) has been proposed that introduces a novel strategy to generate perturbations effectively. This strategy allows the individual to span across more possible solutions and thus, is able to produce better solutions. A comprehensive analysis of OSOMA on multi-dimensional unconstrained benchmark test functions is performed. OSOMA is then applied to solve real-time Dynamic Traveling Salesman Problem (DTSP). The problem of real-time DTSP has been stipulated and simulated using real-time data from Google Maps with a varying cost-metric between any two cities. Although DTSP is a very common and intuitive model in the real world, its presence in literature is still very limited. OSOMA performs exceptionally well on the problems mentioned above. To substantiate this claim, the performance of OSOMA is compared with SOMA, Differential Evolution and Particle Swarm Optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge