Rohit Sharma
READ: Reinforcement-based Adversarial Learning for Text Classification with Limited Labeled Data
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained transformer models such as BERT have shown massive gains across many text classification tasks. However, these models usually need enormous labeled data to achieve impressive performances. Obtaining labeled data is often expensive and time-consuming, whereas collecting unlabeled data using some heuristics is relatively much cheaper for any task. Therefore, this paper proposes a method that encapsulates reinforcement learning-based text generation and semi-supervised adversarial learning approaches in a novel way to improve the model's performance. Our method READ, Reinforcement-based Adversarial learning, utilizes an unlabeled dataset to generate diverse synthetic text through reinforcement learning, improving the model's generalization capability using adversarial learning. Our experimental results show that READ outperforms the existing state-of-art methods on multiple datasets.
Optimizing Gastrointestinal Diagnostics: A CNN-Based Model for VCE Image Classification
Nov 03, 2024Abstract:In recent years, the diagnosis of gastrointestinal (GI) diseases has advanced greatly with the advent of high-tech video capsule endoscopy (VCE) technology, which allows for non-invasive observation of the digestive system. The MisaHub Capsule Vision Challenge encourages the development of vendor-independent artificial intelligence models that can autonomously classify GI anomalies from VCE images. This paper presents CNN architecture designed specifically for multiclass classification of ten gut pathologies, including angioectasia, bleeding, erosion, erythema, foreign bodies, lymphangiectasia, polyps, ulcers, and worms as well as their normal state.
ULTRA: A Data-driven Approach for Recommending Team Formation in Response to Proposal Calls
Jan 13, 2022
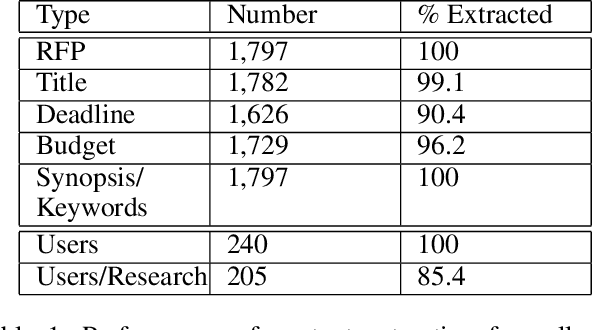

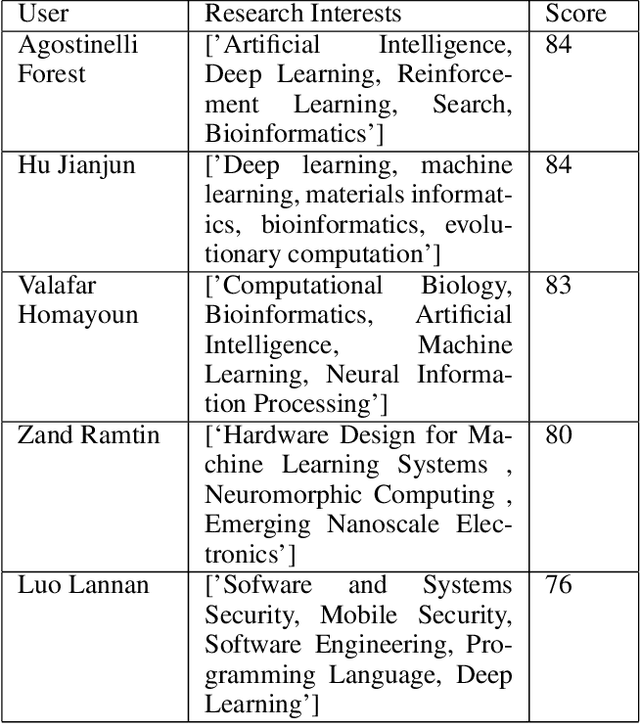
Abstract:We introduce an emerging AI-based approach and prototype system for assisting team formation when researchers respond to calls for proposals from funding agencies. This is an instance of the general problem of building teams when demand opportunities come periodically and potential members may vary over time. The novelties of our approach are that we: (a) extract technical skills needed about researchers and calls from multiple data sources and normalize them using Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, (b) build a prototype solution based on matching and teaming based on constraints, (c) describe initial feedback about system from researchers at a University to deploy, and (d) create and publish a dataset that others can use.
Opportunistic Self Organizing Migrating Algorithm for Real-Time Dynamic Traveling Salesman Problem
Sep 12, 2017



Abstract:Self Organizing Migrating Algorithm (SOMA) is a meta-heuristic algorithm based on the self-organizing behavior of individuals in a simulated social environment. SOMA performs iterative computations on a population of potential solutions in the given search space to obtain an optimal solution. In this paper, an Opportunistic Self Organizing Migrating Algorithm (OSOMA) has been proposed that introduces a novel strategy to generate perturbations effectively. This strategy allows the individual to span across more possible solutions and thus, is able to produce better solutions. A comprehensive analysis of OSOMA on multi-dimensional unconstrained benchmark test functions is performed. OSOMA is then applied to solve real-time Dynamic Traveling Salesman Problem (DTSP). The problem of real-time DTSP has been stipulated and simulated using real-time data from Google Maps with a varying cost-metric between any two cities. Although DTSP is a very common and intuitive model in the real world, its presence in literature is still very limited. OSOMA performs exceptionally well on the problems mentioned above. To substantiate this claim, the performance of OSOMA is compared with SOMA, Differential Evolution and Particle Swarm Optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge