Junjie Xie
CogFlow: Bridging Perception and Reasoning through Knowledge Internalization for Visual Mathematical Problem Solving
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Despite significant progress, multimodal large language models continue to struggle with visual mathematical problem solving. Some recent works recognize that visual perception is a bottleneck in visual mathematical reasoning, but their solutions are limited to improving the extraction and interpretation of visual inputs. Notably, they all ignore the key issue of whether the extracted visual cues are faithfully integrated and properly utilized in subsequent reasoning. Motivated by this, we present CogFlow, a novel cognitive-inspired three-stage framework that incorporates a knowledge internalization stage, explicitly simulating the hierarchical flow of human reasoning: perception$\Rightarrow$internalization$\Rightarrow$reasoning. Inline with this hierarchical flow, we holistically enhance all its stages. We devise Synergistic Visual Rewards to boost perception capabilities in parametric and semantic spaces, jointly improving visual information extraction from symbols and diagrams. To guarantee faithful integration of extracted visual cues into subsequent reasoning, we introduce a Knowledge Internalization Reward model in the internalization stage, bridging perception and reasoning. Moreover, we design a Visual-Gated Policy Optimization algorithm to further enforce the reasoning is grounded with the visual knowledge, preventing models seeking shortcuts that appear coherent but are visually ungrounded reasoning chains. Moreover, we contribute a new dataset MathCog for model training, which contains samples with over 120K high-quality perception-reasoning aligned annotations. Comprehensive experiments and analysis on commonly used visual mathematical reasoning benchmarks validate the superiority of the proposed CogFlow.
A 3D pocket-aware and affinity-guided diffusion model for lead optimization
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Molecular optimization, aimed at improving binding affinity or other molecular properties, is a crucial task in drug discovery that often relies on the expertise of medicinal chemists. Recently, deep learning-based 3D generative models showed promise in enhancing the efficiency of molecular optimization. However, these models often struggle to adequately consider binding affinities with protein targets during lead optimization. Herein, we propose a 3D pocket-aware and affinity-guided diffusion model, named Diffleop, to optimize molecules with enhanced binding affinity. The model explicitly incorporates the knowledge of protein-ligand binding affinity to guide the denoising sampling for molecule generation with high affinity. The comprehensive evaluations indicated that Diffleop outperforms baseline models across multiple metrics, especially in terms of binding affinity.
LARR: Large Language Model Aided Real-time Scene Recommendation with Semantic Understanding
Aug 21, 2024

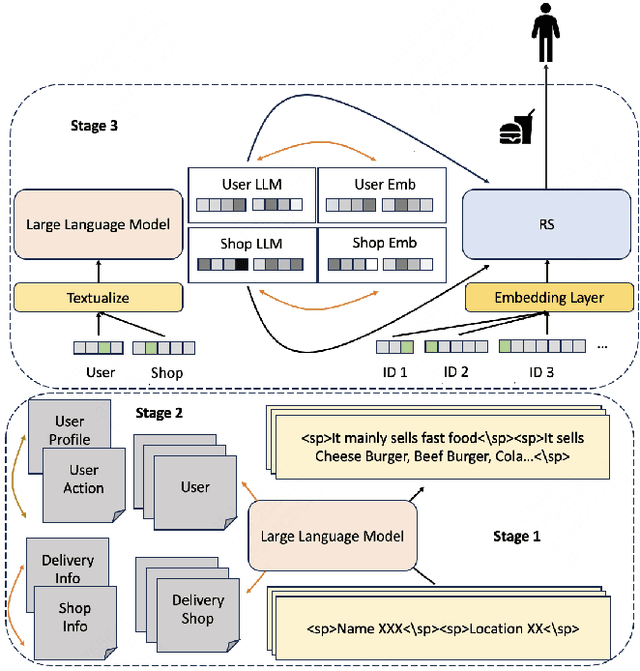

Abstract:Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction is crucial for Recommendation System(RS), aiming to provide personalized recommendation services for users in many aspects such as food delivery, e-commerce and so on. However, traditional RS relies on collaborative signals, which lacks semantic understanding to real-time scenes. We also noticed that a major challenge in utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) for practical recommendation purposes is their efficiency in dealing with long text input. To break through the problems above, we propose Large Language Model Aided Real-time Scene Recommendation(LARR), adopt LLMs for semantic understanding, utilizing real-time scene information in RS without requiring LLM to process the entire real-time scene text directly, thereby enhancing the efficiency of LLM-based CTR modeling. Specifically, recommendation domain-specific knowledge is injected into LLM and then RS employs an aggregation encoder to build real-time scene information from separate LLM's outputs. Firstly, a LLM is continual pretrained on corpus built from recommendation data with the aid of special tokens. Subsequently, the LLM is fine-tuned via contrastive learning on three kinds of sample construction strategies. Through this step, LLM is transformed into a text embedding model. Finally, LLM's separate outputs for different scene features are aggregated by an encoder, aligning to collaborative signals in RS, enhancing the performance of recommendation model.
You Do Not Need Additional Priors in Camouflage Object Detection
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:Camouflage object detection (COD) poses a significant challenge due to the high resemblance between camouflaged objects and their surroundings. Although current deep learning methods have made significant progress in detecting camouflaged objects, many of them heavily rely on additional prior information. However, acquiring such additional prior information is both expensive and impractical in real-world scenarios. Therefore, there is a need to develop a network for camouflage object detection that does not depend on additional priors. In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive feature aggregation method that effectively combines multi-layer feature information to generate guidance information. In contrast to previous approaches that rely on edge or ranking priors, our method directly leverages information extracted from image features to guide model training. Through extensive experimental results, we demonstrate that our proposed method achieves comparable or superior performance when compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
Heterogeneous Knowledge Fusion: A Novel Approach for Personalized Recommendation via LLM
Aug 18, 2023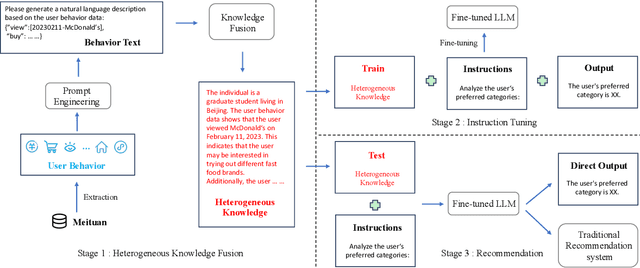
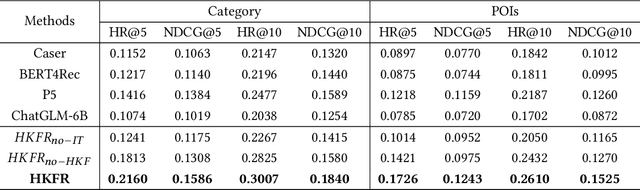
Abstract:The analysis and mining of user heterogeneous behavior are of paramount importance in recommendation systems. However, the conventional approach of incorporating various types of heterogeneous behavior into recommendation models leads to feature sparsity and knowledge fragmentation issues. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach for personalized recommendation via Large Language Model (LLM), by extracting and fusing heterogeneous knowledge from user heterogeneous behavior information. In addition, by combining heterogeneous knowledge and recommendation tasks, instruction tuning is performed on LLM for personalized recommendations. The experimental results demonstrate that our method can effectively integrate user heterogeneous behavior and significantly improve recommendation performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge