Jiecheng Guo
Long-Term Individual Causal Effect Estimation via Identifiable Latent Representation Learning
May 08, 2025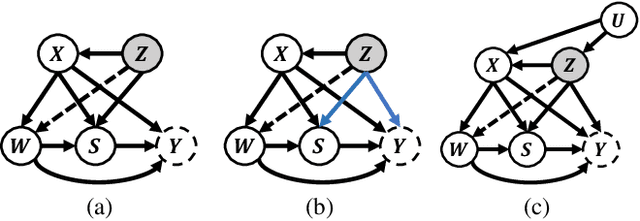
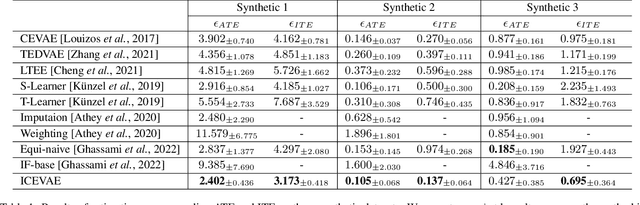
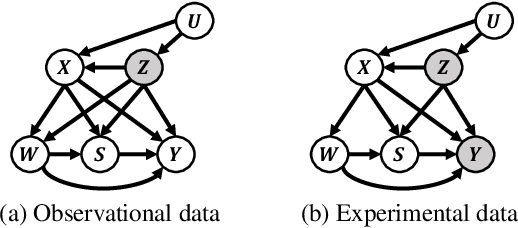
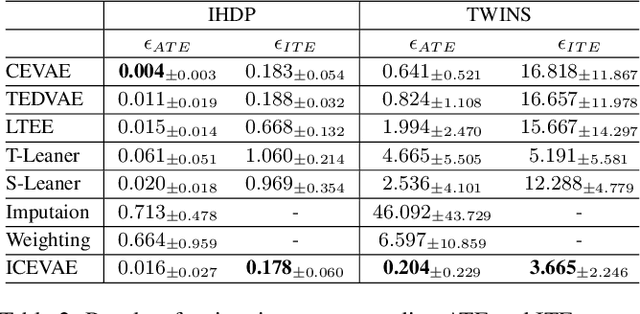
Abstract:Estimating long-term causal effects by combining long-term observational and short-term experimental data is a crucial but challenging problem in many real-world scenarios. In existing methods, several ideal assumptions, e.g. latent unconfoundedness assumption or additive equi-confounding bias assumption, are proposed to address the latent confounder problem raised by the observational data. However, in real-world applications, these assumptions are typically violated which limits their practical effectiveness. In this paper, we tackle the problem of estimating the long-term individual causal effects without the aforementioned assumptions. Specifically, we propose to utilize the natural heterogeneity of data, such as data from multiple sources, to identify latent confounders, thereby significantly avoiding reliance on idealized assumptions. Practically, we devise a latent representation learning-based estimator of long-term causal effects. Theoretically, we establish the identifiability of latent confounders, with which we further achieve long-term effect identification. Extensive experimental studies, conducted on multiple synthetic and semi-synthetic datasets, demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
The Estimation of Continual Causal Effect for Dataset Shifting Streams
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Causal effect estimation has been widely used in marketing optimization. The framework of an uplift model followed by a constrained optimization algorithm is popular in practice. To enhance performance in the online environment, the framework needs to be improved to address the complexities caused by temporal dataset shift. This paper focuses on capturing the dataset shift from user behavior and domain distribution changing over time. We propose an Incremental Causal Effect with Proxy Knowledge Distillation (ICE-PKD) framework to tackle this challenge. The ICE-PKD framework includes two components: (i) a multi-treatment uplift network that eliminates confounding bias using counterfactual regression; (ii) an incremental training strategy that adapts to the temporal dataset shift by updating with the latest data and protects generalization via replay-based knowledge distillation. We also revisit the uplift modeling metrics and introduce a novel metric for more precise online evaluation in multiple treatment scenarios. Extensive experiments on both simulated and online datasets show that the proposed framework achieves better performance. The ICE-PKD framework has been deployed in the marketing system of Huaxiaozhu, a ride-hailing platform in China.
Treatment Effect Estimation for Exponential Family Outcomes using Neural Networks with Targeted Regularization
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Neural Networks (NNs) have became a natural choice for treatment effect estimation due to their strong approximation capabilities. Nevertheless, how to design NN-based estimators with desirable properties, such as low bias and doubly robustness, still remains a significant challenge. A common approach to address this is targeted regularization, which modifies the objective function of NNs. However, existing works on targeted regularization are limited to Gaussian-distributed outcomes, significantly restricting their applicability in real-world scenarios. In this work, we aim to bridge this blank by extending this framework to the boarder exponential family outcomes. Specifically, we first derive the von-Mises expansion of the Average Dose function of Canonical Functions (ADCF), which inspires us how to construct a doubly robust estimator with good properties. Based on this, we develop a NN-based estimator for ADCF by generalizing functional targeted regularization to exponential families, and provide the corresponding theoretical convergence rate. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model.
DFF: Decision-Focused Fine-tuning for Smarter Predict-then-Optimize with Limited Data
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Decision-focused learning (DFL) offers an end-to-end approach to the predict-then-optimize (PO) framework by training predictive models directly on decision loss (DL), enhancing decision-making performance within PO contexts. However, the implementation of DFL poses distinct challenges. Primarily, DL can result in deviation from the physical significance of the predictions under limited data. Additionally, some predictive models are non-differentiable or black-box, which cannot be adjusted using gradient-based methods. To tackle the above challenges, we propose a novel framework, Decision-Focused Fine-tuning (DFF), which embeds the DFL module into the PO pipeline via a novel bias correction module. DFF is formulated as a constrained optimization problem that maintains the proximity of the DL-enhanced model to the original predictive model within a defined trust region. We theoretically prove that DFF strictly confines prediction bias within a predetermined upper bound, even with limited datasets, thereby substantially reducing prediction shifts caused by DL under limited data. Furthermore, the bias correction module can be integrated into diverse predictive models, enhancing adaptability to a broad range of PO tasks. Extensive evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets, including network flow, portfolio optimization, and resource allocation problems with different predictive models, demonstrate that DFF not only improves decision performance but also adheres to fine-tuning constraints, showcasing robust adaptability across various scenarios.
Estimating Long-term Heterogeneous Dose-response Curve: Generalization Bound Leveraging Optimal Transport Weights
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Long-term causal effect estimation is a significant but challenging problem in many applications. Existing methods rely on ideal assumptions to estimate long-term average effects, e.g., no unobserved confounders or a binary treatment,while in numerous real-world applications, these assumptions could be violated and average effects are unable to provide individual-level suggestions.In this paper,we address a more general problem of estimating the long-term heterogeneous dose-response curve (HDRC) while accounting for unobserved confounders. Specifically, to remove unobserved confounding in observational data, we introduce an optimal transport weighting framework to align the observational data to the experimental data with theoretical guarantees. Furthermore,to accurately predict the heterogeneous effects of continuous treatment, we establish a generalization bound on counterfactual prediction error by leveraging the reweighted distribution induced by optimal transport. Finally, we develop an HDRC estimator building upon the above theoretical foundations. Extensive experimental studies conducted on multiple synthetic and semi-synthetic datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Contrastive Balancing Representation Learning for Heterogeneous Dose-Response Curves Estimation
Mar 21, 2024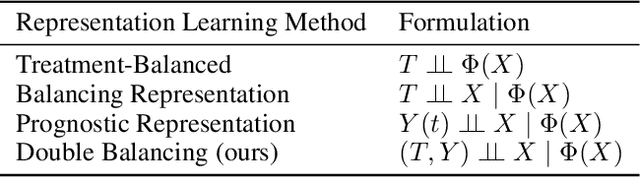
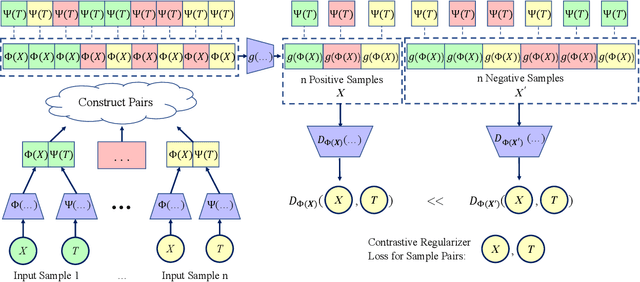
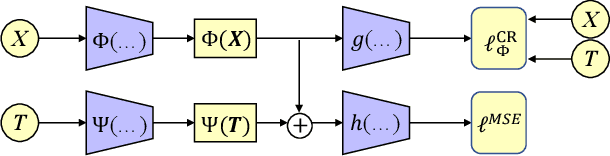
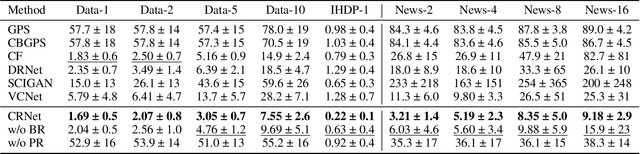
Abstract:Estimating the individuals' potential response to varying treatment doses is crucial for decision-making in areas such as precision medicine and management science. Most recent studies predict counterfactual outcomes by learning a covariate representation that is independent of the treatment variable. However, such independence constraints neglect much of the covariate information that is useful for counterfactual prediction, especially when the treatment variables are continuous. To tackle the above issue, in this paper, we first theoretically demonstrate the importance of the balancing and prognostic representations for unbiased estimation of the heterogeneous dose-response curves, that is, the learned representations are constrained to satisfy the conditional independence between the covariates and both of the treatment variables and the potential responses. Based on this, we propose a novel Contrastive balancing Representation learning Network using a partial distance measure, called CRNet, for estimating the heterogeneous dose-response curves without losing the continuity of treatments. Extensive experiments are conducted on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrating that our proposal significantly outperforms previous methods.
Long-term Causal Effects Estimation via Latent Surrogates Representation Learning
Aug 09, 2022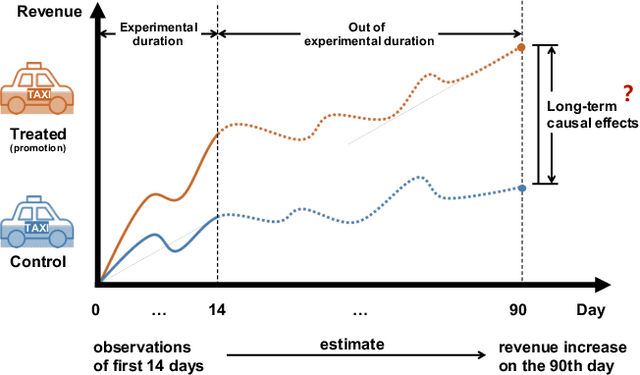
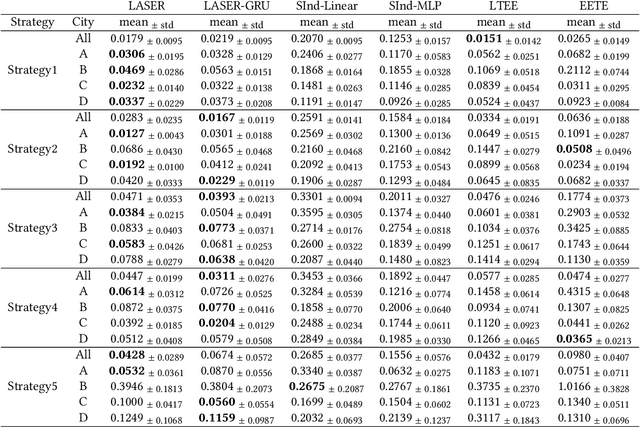
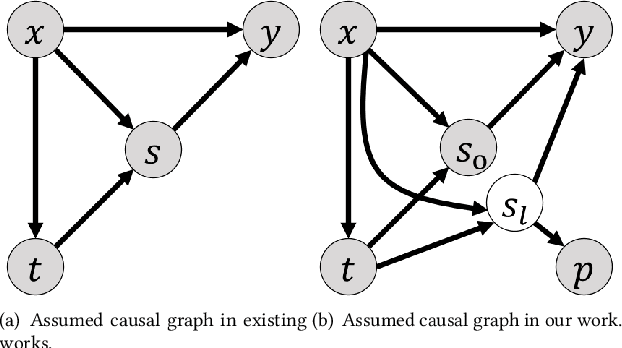
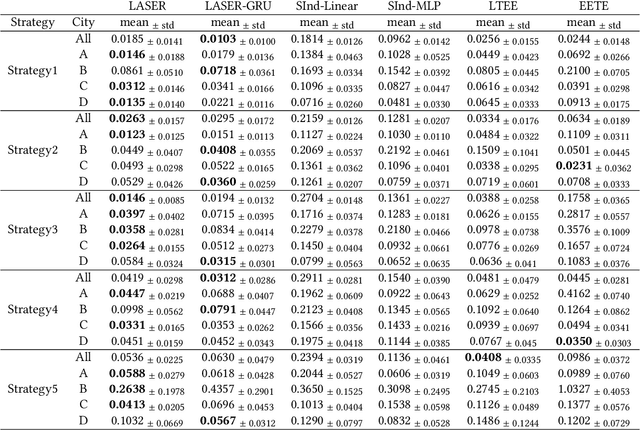
Abstract:Estimating long-term causal effects based on short-term surrogates is a significant but challenging problem in many real-world applications, e.g., marketing and medicine. Despite its success in certain domains, most existing methods estimate causal effects in an idealistic and simplistic way - ignoring the causal structure among short-term outcomes and treating all of them as surrogates. However, such methods cannot be well applied to real-world scenarios, in which the partially observed surrogates are mixed with their proxies among short-term outcomes. To this end, we develop our flexible method, Laser, to estimate long-term causal effects in the more realistic situation that the surrogates are observed or have observed proxies.Given the indistinguishability between the surrogates and proxies, we utilize identifiable variational auto-encoder (iVAE) to recover the whole valid surrogates on all the surrogates candidates without the need of distinguishing the observed surrogates or the proxies of latent surrogates. With the help of the recovered surrogates, we further devise an unbiased estimation of long-term causal effects. Extensive experimental results on the real-world and semi-synthetic datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
GCF: Generalized Causal Forest for Heterogeneous Treatment Effect Estimation in Online Marketplace
Mar 21, 2022
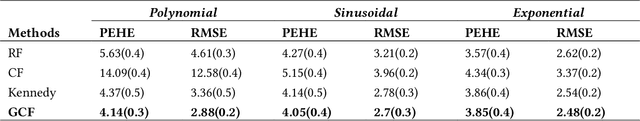
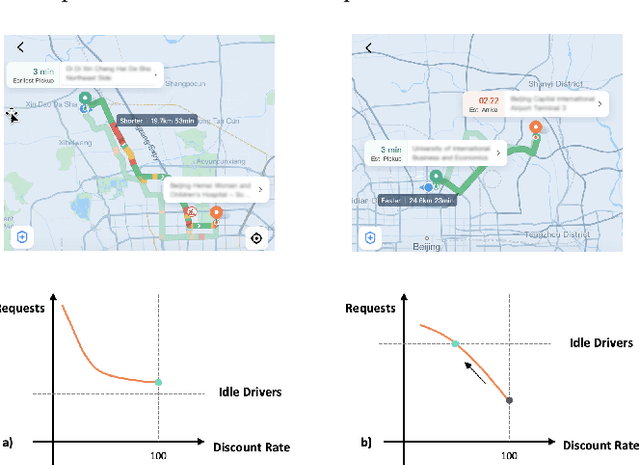
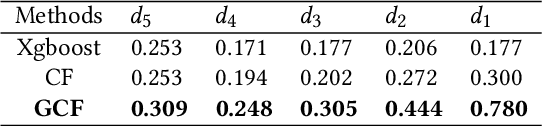
Abstract:Uplift modeling is a rapidly growing approach that utilizes machine learning and causal inference methods to estimate the heterogeneous treatment effects. It has been widely adopted and applied to online marketplaces to assist large-scale decision-making in recent years. The existing popular methods, like forest-based modeling, either work only for discrete treatments or make partially linear or parametric assumptions that may suffer from model misspecification. To alleviate these problems, we extend causal forest (CF) with non-parametric dose-response functions (DRFs) that can be estimated locally using a kernel-based doubly robust estimator. Moreover, we propose a distance-based splitting criterion in the functional space of conditional DRFs to capture the heterogeneity for the continuous treatments. We call the proposed algorithm generalized causal forest (GCF) as it generalizes the use case of CF to a much broader setup. We show the effectiveness of GCF by comparing it to popular uplift modeling models on both synthetic and real-world datasets. We implement GCF in Spark and successfully deploy it into DiDi's real-time pricing system. Online A/B testing results further validate the superiority of GCF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge