Jiahong Wu
Latent Temporal Discrepancy as Motion Prior: A Loss-Weighting Strategy for Dynamic Fidelity in T2V
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Video generation models have achieved notable progress in static scenarios, yet their performance in motion video generation remains limited, with quality degrading under drastic dynamic changes. This is due to noise disrupting temporal coherence and increasing the difficulty of learning dynamic regions. {Unfortunately, existing diffusion models rely on static loss for all scenarios, constraining their ability to capture complex dynamics.} To address this issue, we introduce Latent Temporal Discrepancy (LTD) as a motion prior to guide loss weighting. LTD measures frame-to-frame variation in the latent space, assigning larger penalties to regions with higher discrepancy while maintaining regular optimization for stable regions. This motion-aware strategy stabilizes training and enables the model to better reconstruct high-frequency dynamics. Extensive experiments on the general benchmark VBench and the motion-focused VMBench show consistent gains, with our method outperforming strong baselines by 3.31% on VBench and 3.58% on VMBench, achieving significant improvements in motion quality.
Ranking-aware Reinforcement Learning for Ordinal Ranking
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Ordinal regression and ranking are challenging due to inherent ordinal dependencies that conventional methods struggle to model. We propose Ranking-Aware Reinforcement Learning (RARL), a novel RL framework that explicitly learns these relationships. At its core, RARL features a unified objective that synergistically integrates regression and Learning-to-Rank (L2R), enabling mutual improvement between the two tasks. This is driven by a ranking-aware verifiable reward that jointly assesses regression precision and ranking accuracy, facilitating direct model updates via policy optimization. To further enhance training, we introduce Response Mutation Operations (RMO), which inject controlled noise to improve exploration and prevent stagnation at saddle points. The effectiveness of RARL is validated through extensive experiments on three distinct benchmarks.
Artifact-Aware Evaluation for High-Quality Video Generation
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement of video generation techniques, evaluating and auditing generated videos has become increasingly crucial. Existing approaches typically offer coarse video quality scores, lacking detailed localization and categorization of specific artifacts. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation protocol focusing on three key aspects affecting human perception: Appearance, Motion, and Camera. We define these axes through a taxonomy of 10 prevalent artifact categories reflecting common generative failures observed in video generation. To enable robust artifact detection and categorization, we introduce GenVID, a large-scale dataset of 80k videos generated by various state-of-the-art video generation models, each carefully annotated for the defined artifact categories. Leveraging GenVID, we develop DVAR, a Dense Video Artifact Recognition framework for fine-grained identification and classification of generative artifacts. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly improves artifact detection accuracy and enables effective filtering of low-quality content.
Taming Preference Mode Collapse via Directional Decoupling Alignment in Diffusion Reinforcement Learning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated significant progress in aligning text-to-image diffusion models with human preference via Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback. However, while existing methods achieve high scores on automated reward metrics, they often lead to Preference Mode Collapse (PMC)-a specific form of reward hacking where models converge on narrow, high-scoring outputs (e.g., images with monolithic styles or pervasive overexposure), severely degrading generative diversity. In this work, we introduce and quantify this phenomenon, proposing DivGenBench, a novel benchmark designed to measure the extent of PMC. We posit that this collapse is driven by over-optimization along the reward model's inherent biases. Building on this analysis, we propose Directional Decoupling Alignment (D$^2$-Align), a novel framework that mitigates PMC by directionally correcting the reward signal. Specifically, our method first learns a directional correction within the reward model's embedding space while keeping the model frozen. This correction is then applied to the reward signal during the optimization process, preventing the model from collapsing into specific modes and thereby maintaining diversity. Our comprehensive evaluation, combining qualitative analysis with quantitative metrics for both quality and diversity, reveals that D$^2$-Align achieves superior alignment with human preference.
Taming Hallucinations: Boosting MLLMs' Video Understanding via Counterfactual Video Generation
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made remarkable progress in video understanding. However, they suffer from a critical vulnerability: an over-reliance on language priors, which can lead to visual ungrounded hallucinations, especially when processing counterfactual videos that defy common sense. This limitation, stemming from the intrinsic data imbalance between text and video, is challenging to address due to the substantial cost of collecting and annotating counterfactual data. To address this, we introduce DualityForge, a novel counterfactual data synthesis framework that employs controllable, diffusion-based video editing to transform real-world videos into counterfactual scenarios. By embedding structured contextual information into the video editing and QA generation processes, the framework automatically produces high-quality QA pairs together with original-edited video pairs for contrastive training. Based on this, we build DualityVidQA, a large-scale video dataset designed to reduce MLLM hallucinations. In addition, to fully exploit the contrastive nature of our paired data, we propose Duality-Normalized Advantage Training (DNA-Train), a two-stage SFT-RL training regime where the RL phase applies pair-wise $\ell_1$ advantage normalization, thereby enabling a more stable and efficient policy optimization. Experiments on DualityVidQA-Test demonstrate that our method substantially reduces model hallucinations on counterfactual videos, yielding a relative improvement of 24.0% over the Qwen2.5-VL-7B baseline. Moreover, our approach achieves significant gains across both hallucination and general-purpose benchmarks, indicating strong generalization capability. We will open-source our dataset and code.
MACE-Dance: Motion-Appearance Cascaded Experts for Music-Driven Dance Video Generation
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:With the rise of online dance-video platforms and rapid advances in AI-generated content (AIGC), music-driven dance generation has emerged as a compelling research direction. Despite substantial progress in related domains such as music-driven 3D dance generation, pose-driven image animation, and audio-driven talking-head synthesis, existing methods cannot be directly adapted to this task. Moreover, the limited studies in this area still struggle to jointly achieve high-quality visual appearance and realistic human motion. Accordingly, we present MACE-Dance, a music-driven dance video generation framework with cascaded Mixture-of-Experts (MoE). The Motion Expert performs music-to-3D motion generation while enforcing kinematic plausibility and artistic expressiveness, whereas the Appearance Expert carries out motion- and reference-conditioned video synthesis, preserving visual identity with spatiotemporal coherence. Specifically, the Motion Expert adopts a diffusion model with a BiMamba-Transformer hybrid architecture and a Guidance-Free Training (GFT) strategy, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in 3D dance generation. The Appearance Expert employs a decoupled kinematic-aesthetic fine-tuning strategy, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in pose-driven image animation. To better benchmark this task, we curate a large-scale and diverse dataset and design a motion-appearance evaluation protocol. Based on this protocol, MACE-Dance also achieves state-of-the-art performance. Project page: https://macedance.github.io/
Advancing End-to-End Pixel Space Generative Modeling via Self-supervised Pre-training
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Pixel-space generative models are often more difficult to train and generally underperform compared to their latent-space counterparts, leaving a persistent performance and efficiency gap. In this paper, we introduce a novel two-stage training framework that closes this gap for pixel-space diffusion and consistency models. In the first stage, we pre-train encoders to capture meaningful semantics from clean images while aligning them with points along the same deterministic sampling trajectory, which evolves points from the prior to the data distribution. In the second stage, we integrate the encoder with a randomly initialized decoder and fine-tune the complete model end-to-end for both diffusion and consistency models. Our training framework demonstrates strong empirical performance on ImageNet dataset. Specifically, our diffusion model reaches an FID of 2.04 on ImageNet-256 and 2.35 on ImageNet-512 with 75 number of function evaluations (NFE), surpassing prior pixel-space methods by a large margin in both generation quality and efficiency while rivaling leading VAE-based models at comparable training cost. Furthermore, on ImageNet-256, our consistency model achieves an impressive FID of 8.82 in a single sampling step, significantly surpassing its latent-space counterpart. To the best of our knowledge, this marks the first successful training of a consistency model directly on high-resolution images without relying on pre-trained VAEs or diffusion models.
Omni-Effects: Unified and Spatially-Controllable Visual Effects Generation
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Visual effects (VFX) are essential visual enhancements fundamental to modern cinematic production. Although video generation models offer cost-efficient solutions for VFX production, current methods are constrained by per-effect LoRA training, which limits generation to single effects. This fundamental limitation impedes applications that require spatially controllable composite effects, i.e., the concurrent generation of multiple effects at designated locations. However, integrating diverse effects into a unified framework faces major challenges: interference from effect variations and spatial uncontrollability during multi-VFX joint training. To tackle these challenges, we propose Omni-Effects, a first unified framework capable of generating prompt-guided effects and spatially controllable composite effects. The core of our framework comprises two key innovations: (1) LoRA-based Mixture of Experts (LoRA-MoE), which employs a group of expert LoRAs, integrating diverse effects within a unified model while effectively mitigating cross-task interference. (2) Spatial-Aware Prompt (SAP) incorporates spatial mask information into the text token, enabling precise spatial control. Furthermore, we introduce an Independent-Information Flow (IIF) module integrated within the SAP, isolating the control signals corresponding to individual effects to prevent any unwanted blending. To facilitate this research, we construct a comprehensive VFX dataset Omni-VFX via a novel data collection pipeline combining image editing and First-Last Frame-to-Video (FLF2V) synthesis, and introduce a dedicated VFX evaluation framework for validating model performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Omni-Effects achieves precise spatial control and diverse effect generation, enabling users to specify both the category and location of desired effects.
VMBench: A Benchmark for Perception-Aligned Video Motion Generation
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Video generation has advanced rapidly, improving evaluation methods, yet assessing video's motion remains a major challenge. Specifically, there are two key issues: 1) current motion metrics do not fully align with human perceptions; 2) the existing motion prompts are limited. Based on these findings, we introduce VMBench--a comprehensive Video Motion Benchmark that has perception-aligned motion metrics and features the most diverse types of motion. VMBench has several appealing properties: 1) Perception-Driven Motion Evaluation Metrics, we identify five dimensions based on human perception in motion video assessment and develop fine-grained evaluation metrics, providing deeper insights into models' strengths and weaknesses in motion quality. 2) Meta-Guided Motion Prompt Generation, a structured method that extracts meta-information, generates diverse motion prompts with LLMs, and refines them through human-AI validation, resulting in a multi-level prompt library covering six key dynamic scene dimensions. 3) Human-Aligned Validation Mechanism, we provide human preference annotations to validate our benchmarks, with our metrics achieving an average 35.3% improvement in Spearman's correlation over baseline methods. This is the first time that the quality of motion in videos has been evaluated from the perspective of human perception alignment. Additionally, we will soon release VMBench at https://github.com/GD-AIGC/VMBench, setting a new standard for evaluating and advancing motion generation models.
EVLM: An Efficient Vision-Language Model for Visual Understanding
Jul 19, 2024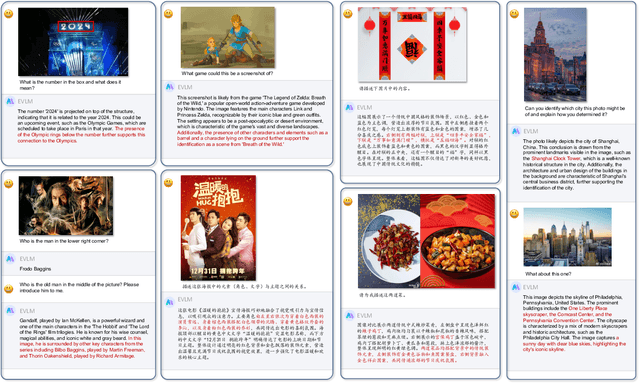
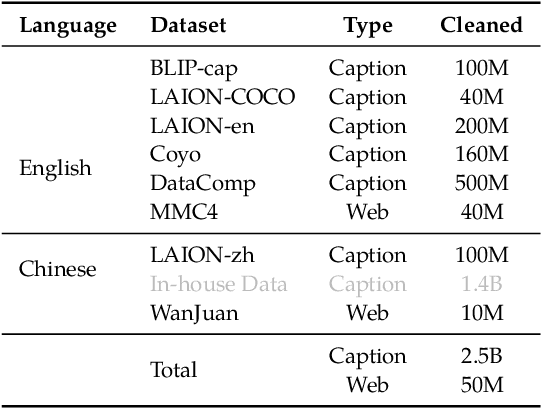
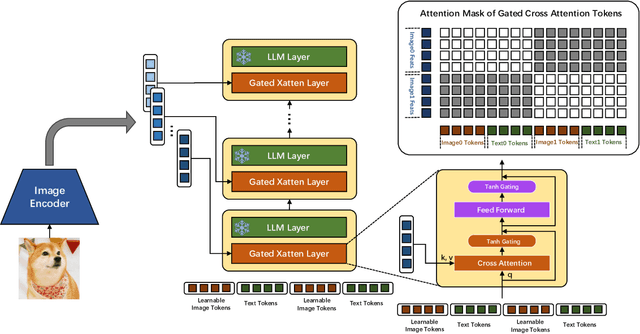

Abstract:In the field of multi-modal language models, the majority of methods are built on an architecture similar to LLaVA. These models use a single-layer ViT feature as a visual prompt, directly feeding it into the language models alongside textual tokens. However, when dealing with long sequences of visual signals or inputs such as videos, the self-attention mechanism of language models can lead to significant computational overhead. Additionally, using single-layer ViT features makes it challenging for large language models to perceive visual signals fully. This paper proposes an efficient multi-modal language model to minimize computational costs while enabling the model to perceive visual signals as comprehensively as possible. Our method primarily includes: (1) employing cross-attention to image-text interaction similar to Flamingo. (2) utilize hierarchical ViT features. (3) introduce the Mixture of Experts (MoE) mechanism to enhance model effectiveness. Our model achieves competitive scores on public multi-modal benchmarks and performs well in tasks such as image captioning and video captioning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge