Jianfei Song
AAVDiff: Experimental Validation of Enhanced Viability and Diversity in Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Capsids through Diffusion Generation
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors have revolutionized gene therapy, but their broad tropism and suboptimal transduction efficiency limit their clinical applications. To overcome these limitations, researchers have focused on designing and screening capsid libraries to identify improved vectors. However, the large sequence space and limited resources present challenges in identifying viable capsid variants. In this study, we propose an end-to-end diffusion model to generate capsid sequences with enhanced viability. Using publicly available AAV2 data, we generated 38,000 diverse AAV2 viral protein (VP) sequences, and evaluated 8,000 for viral selection. The results attested the superiority of our model compared to traditional methods. Additionally, in the absence of AAV9 capsid data, apart from one wild-type sequence, we used the same model to directly generate a number of viable sequences with up to 9 mutations. we transferred the remaining 30,000 samples to the AAV9 domain. Furthermore, we conducted mutagenesis on AAV9 VP hypervariable regions VI and V, contributing to the continuous improvement of the AAV9 VP sequence. This research represents a significant advancement in the design and functional validation of rAAV vectors, offering innovative solutions to enhance specificity and transduction efficiency in gene therapy applications.
Zero and R2D2: A Large-scale Chinese Cross-modal Benchmark and A Vision-Language Framework
May 08, 2022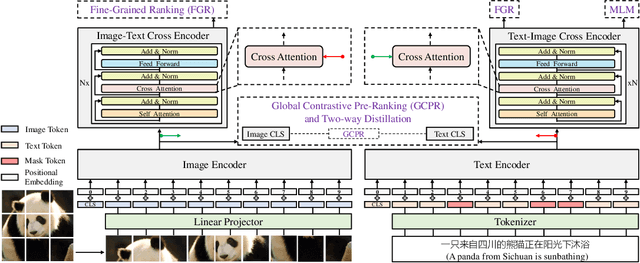
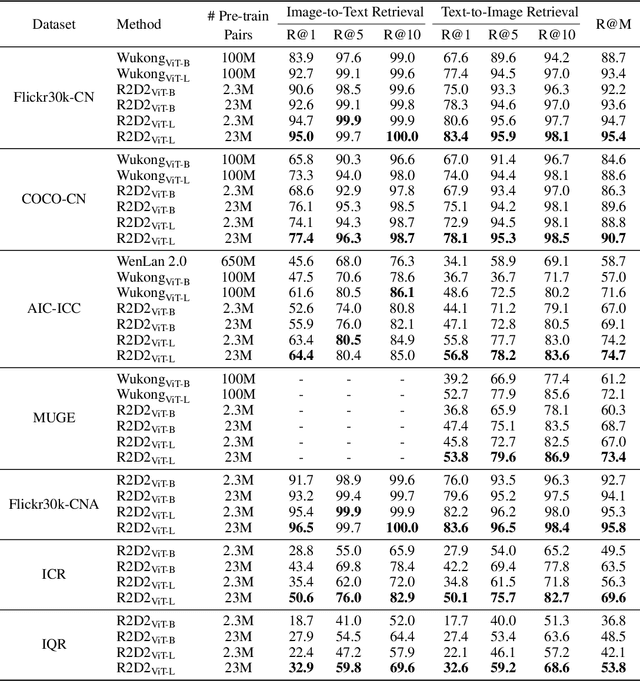
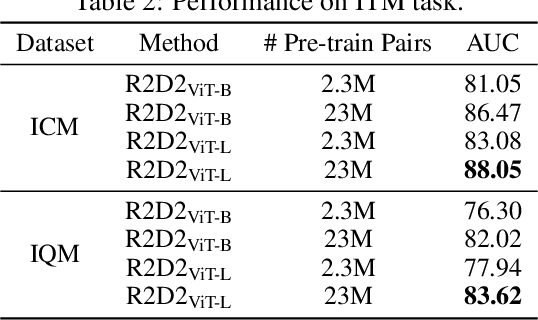
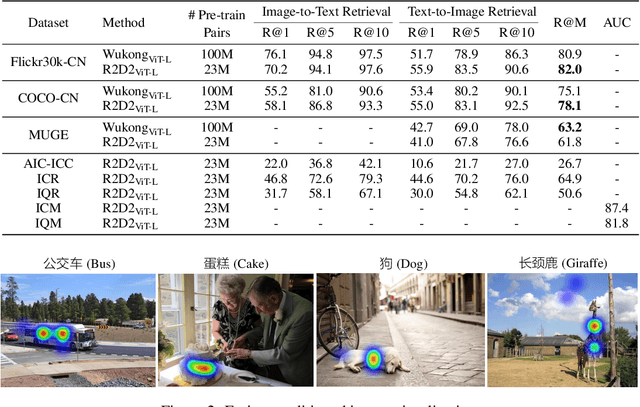
Abstract:Vision-language pre-training (VLP) relying on large-scale pre-training datasets has shown premier performance on various downstream tasks. In this sense, a complete and fair benchmark (i.e., including large-scale pre-training datasets and a variety of downstream datasets) is essential for VLP. But how to construct such a benchmark in Chinese remains a critical problem. To this end, we develop a large-scale Chinese cross-modal benchmark called Zero for AI researchers to fairly compare VLP models. We release two pre-training datasets and five fine-tuning datasets for downstream tasks. Furthermore, we propose a novel pre-training framework of pre-Ranking + Ranking for cross-modal learning. Specifically, we apply global contrastive pre-ranking to learn the individual representations of images and Chinese texts, respectively. We then fuse the representations in a fine-grained ranking manner via an image-text cross encoder and a text-image cross encoder. To further enhance the capability of the model, we propose a two-way distillation strategy consisting of target-guided Distillation and feature-guided Distillation. For simplicity, we call our model R2D2. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on four public cross-modal datasets and our five downstream datasets. The datasets, models and codes will be made available.
WaBERT: A Low-resource End-to-end Model for Spoken Language Understanding and Speech-to-BERT Alignment
Apr 22, 2022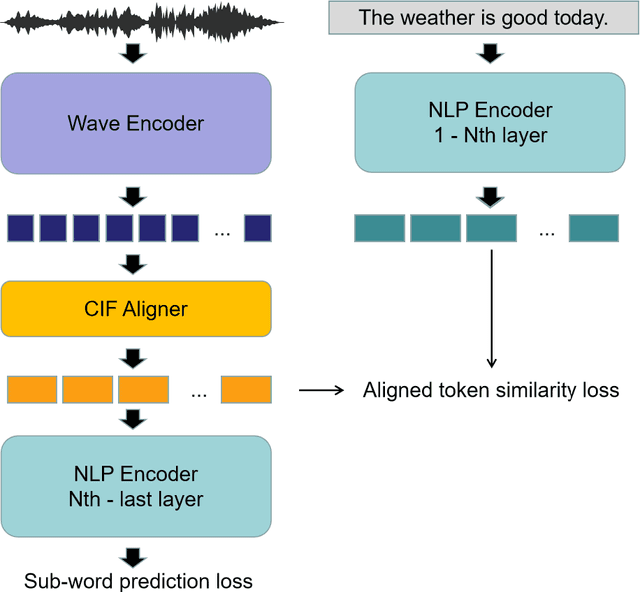

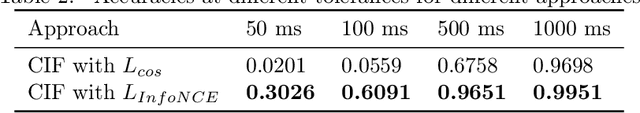
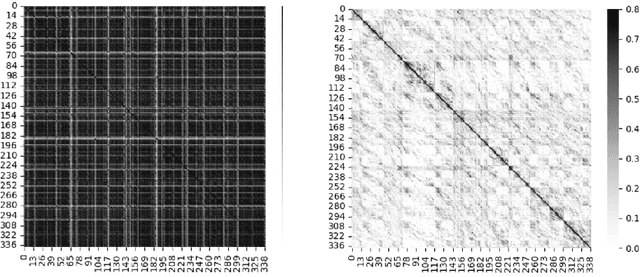
Abstract:Historically lower-level tasks such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speaker identification are the main focus in the speech field. Interest has been growing in higher-level spoken language understanding (SLU) tasks recently, like sentiment analysis (SA). However, improving performances on SLU tasks remains a big challenge. Basically, there are two main methods for SLU tasks: (1) Two-stage method, which uses a speech model to transfer speech to text, then uses a language model to get the results of downstream tasks; (2) One-stage method, which just fine-tunes a pre-trained speech model to fit in the downstream tasks. The first method loses emotional cues such as intonation, and causes recognition errors during ASR process, and the second one lacks necessary language knowledge. In this paper, we propose the Wave BERT (WaBERT), a novel end-to-end model combining the speech model and the language model for SLU tasks. WaBERT is based on the pre-trained speech and language model, hence training from scratch is not needed. We also set most parameters of WaBERT frozen during training. By introducing WaBERT, audio-specific information and language knowledge are integrated in the short-time and low-resource training process to improve results on the dev dataset of SLUE SA tasks by 1.15% of recall score and 0.82% of F1 score. Additionally, we modify the serial Continuous Integrate-and-Fire (CIF) mechanism to achieve the monotonic alignment between the speech and text modalities.
AinnoSeg: Panoramic Segmentation with High Perfomance
Jul 21, 2020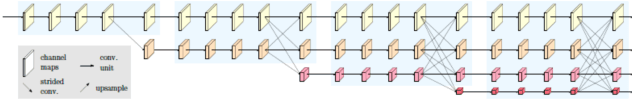
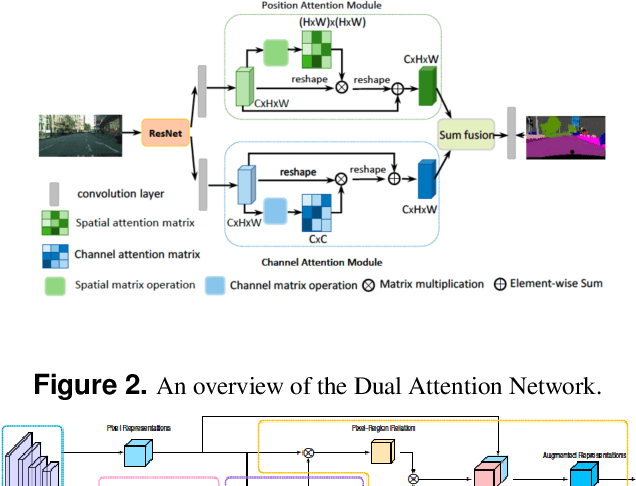
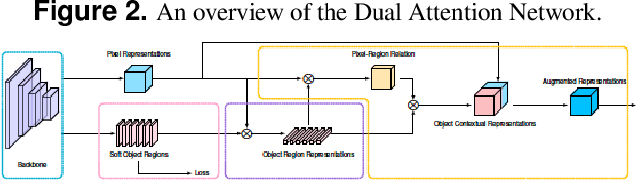

Abstract:Panoramic segmentation is a scene where image segmentation tasks is more difficult. With the development of CNN networks, panoramic segmentation tasks have been sufficiently developed.However, the current panoramic segmentation algorithms are more concerned with context semantics, but the details of image are not processed enough. Moreover, they cannot solve the problems which contains the accuracy of occluded object segmentation,little object segmentation,boundary pixel in object segmentation etc. Aiming to address these issues, this paper presents some useful tricks. (a) By changing the basic segmentation model, the model can take into account the large objects and the boundary pixel classification of image details. (b) Modify the loss function so that it can take into account the boundary pixels of multiple objects in the image. (c) Use a semi-supervised approach to regain control of the training process. (d) Using multi-scale training and reasoning. All these operations named AinnoSeg, AinnoSeg can achieve state-of-art performance on the well-known dataset ADE20K.
Accurate Face Detection for High Performance
May 24, 2019


Abstract:Face detection has witnessed significant progress due to the advances of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Its central issue in recent years is how to improve the detection performance of tiny faces. To this end, many recent works propose some specific strategies, redesign the architecture and introduce new loss functions for tiny object detection. In this report, we start from the popular one-stage RetinaNet approach and apply some recent tricks to obtain a high performance face detector. Specifically, we apply the Intersection over Union (IoU) loss function for regression, employ the two-step classification and regression for detection, revisit the data augmentation based on data-anchor-sampling for training, utilize the max-out operation for classification and use the multi-scale testing strategy for inference. As a consequence, the proposed face detection method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the most popular and challenging face detection benchmark WIDER FACE dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge