Jincheng Li
LGAN: An Efficient High-Order Graph Neural Network via the Line Graph Aggregation
Dec 11, 2025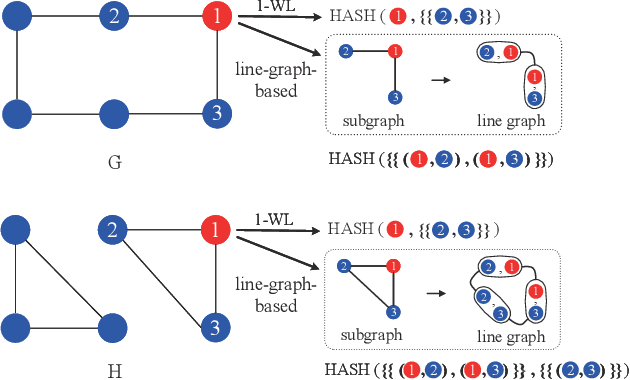
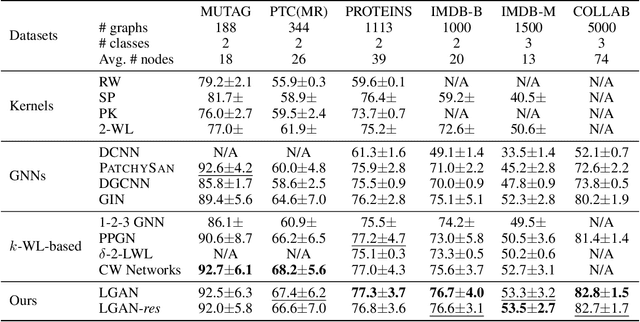
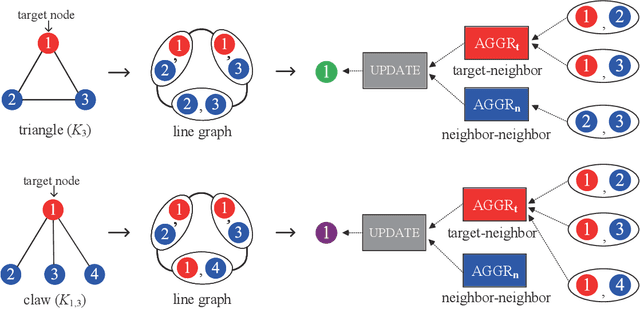
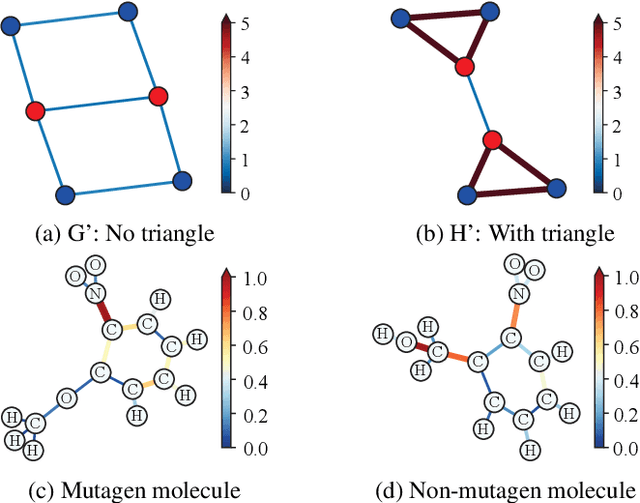
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a dominant paradigm for graph classification. Specifically, most existing GNNs mainly rely on the message passing strategy between neighbor nodes, where the expressivity is limited by the 1-dimensional Weisfeiler-Lehman (1-WL) test. Although a number of k-WL-based GNNs have been proposed to overcome this limitation, their computational cost increases rapidly with k, significantly restricting the practical applicability. Moreover, since the k-WL models mainly operate on node tuples, these k-WL-based GNNs cannot retain fine-grained node- or edge-level semantics required by attribution methods (e.g., Integrated Gradients), leading to the less interpretable problem. To overcome the above shortcomings, in this paper, we propose a novel Line Graph Aggregation Network (LGAN), that constructs a line graph from the induced subgraph centered at each node to perform the higher-order aggregation. We theoretically prove that the LGAN not only possesses the greater expressive power than the 2-WL under injective aggregation assumptions, but also has lower time complexity. Empirical evaluations on benchmarks demonstrate that the LGAN outperforms state-of-the-art k-WL-based GNNs, while offering better interpretability.
FG-CLIP: Fine-Grained Visual and Textual Alignment
May 08, 2025Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) excels in multimodal tasks such as image-text retrieval and zero-shot classification but struggles with fine-grained understanding due to its focus on coarse-grained short captions. To address this, we propose Fine-Grained CLIP (FG-CLIP), which enhances fine-grained understanding through three key innovations. First, we leverage large multimodal models to generate 1.6 billion long caption-image pairs for capturing global-level semantic details. Second, a high-quality dataset is constructed with 12 million images and 40 million region-specific bounding boxes aligned with detailed captions to ensure precise, context-rich representations. Third, 10 million hard fine-grained negative samples are incorporated to improve the model's ability to distinguish subtle semantic differences. Corresponding training methods are meticulously designed for these data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FG-CLIP outperforms the original CLIP and other state-of-the-art methods across various downstream tasks, including fine-grained understanding, open-vocabulary object detection, image-text retrieval, and general multimodal benchmarks. These results highlight FG-CLIP's effectiveness in capturing fine-grained image details and improving overall model performance. The related data, code, and models are available at https://github.com/360CVGroup/FG-CLIP.
Deep Multimodal Collaborative Learning for Polyp Re-Identification
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:Colonoscopic Polyp Re-Identification aims to match the same polyp from a large gallery with images from different views taken using different cameras and plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer in computer-aided diagnosis. However, traditional methods for object ReID directly adopting CNN models trained on the ImageNet dataset usually produce unsatisfactory retrieval performance on colonoscopic datasets due to the large domain gap. Worsely, these solutions typically learn unimodal modal representations on the basis of visual samples, which fails to explore complementary information from different modalities. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Deep Multimodal Collaborative Learning framework named DMCL for polyp re-identification, which can effectively encourage modality collaboration and reinforce generalization capability in medical scenarios. On the basis of it, a dynamic multimodal feature fusion strategy is introduced to leverage the optimized multimodal representations for multimodal fusion via end-to-end training. Experiments on the standard benchmarks show the benefits of the multimodal setting over state-of-the-art unimodal ReID models, especially when combined with the specialized multimodal fusion strategy.
What Makes Good Open-Vocabulary Detector: A Disassembling Perspective
Sep 01, 2023



Abstract:Open-vocabulary detection (OVD) is a new object detection paradigm, aiming to localize and recognize unseen objects defined by an unbounded vocabulary. This is challenging since traditional detectors can only learn from pre-defined categories and thus fail to detect and localize objects out of pre-defined vocabulary. To handle the challenge, OVD leverages pre-trained cross-modal VLM, such as CLIP, ALIGN, etc. Previous works mainly focus on the open vocabulary classification part, with less attention on the localization part. We argue that for a good OVD detector, both classification and localization should be parallelly studied for the novel object categories. We show in this work that improving localization as well as cross-modal classification complement each other, and compose a good OVD detector jointly. We analyze three families of OVD methods with different design emphases. We first propose a vanilla method,i.e., cropping a bounding box obtained by a localizer and resizing it into the CLIP. We next introduce another approach, which combines a standard two-stage object detector with CLIP. A two-stage object detector includes a visual backbone, a region proposal network (RPN), and a region of interest (RoI) head. We decouple RPN and ROI head (DRR) and use RoIAlign to extract meaningful features. In this case, it avoids resizing objects. To further accelerate the training time and reduce the model parameters, we couple RPN and ROI head (CRR) as the third approach. We conduct extensive experiments on these three types of approaches in different settings. On the OVD-COCO benchmark, DRR obtains the best performance and achieves 35.8 Novel AP$_{50}$, an absolute 2.8 gain over the previous state-of-the-art (SOTA). For OVD-LVIS, DRR surpasses the previous SOTA by 1.9 AP$_{50}$ in rare categories. We also provide an object detection dataset called PID and provide a baseline on PID.
Zero and R2D2: A Large-scale Chinese Cross-modal Benchmark and A Vision-Language Framework
May 08, 2022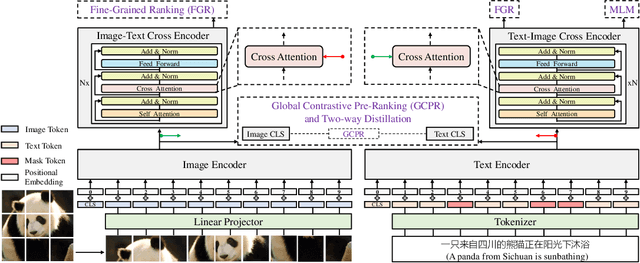
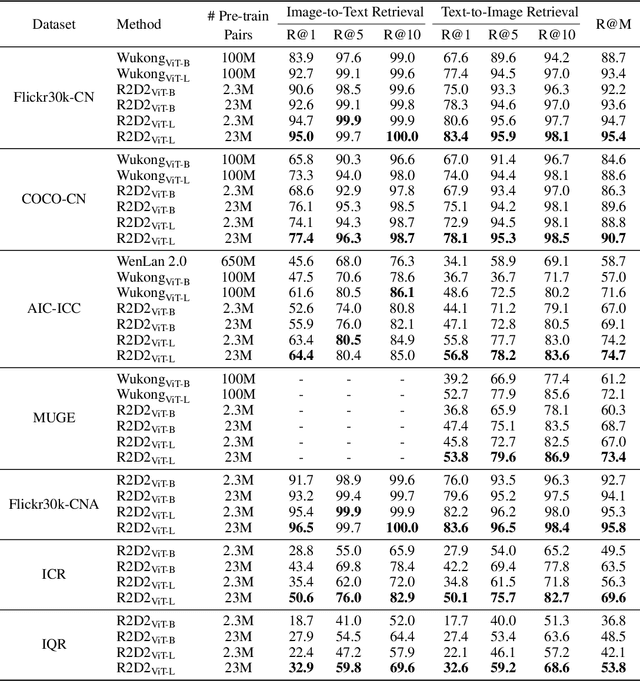
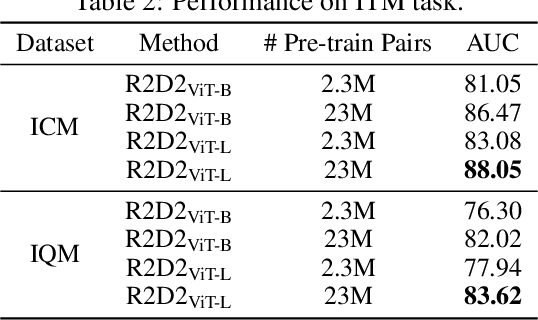
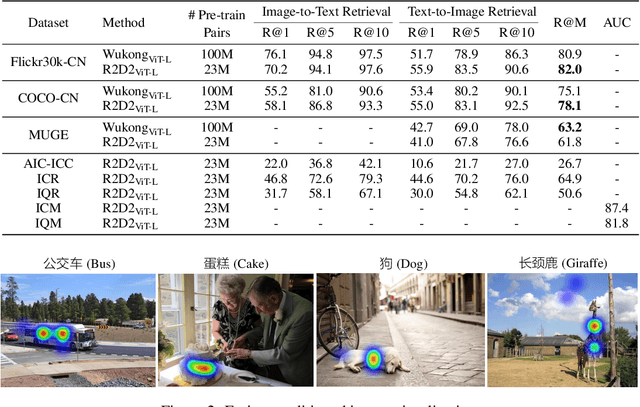
Abstract:Vision-language pre-training (VLP) relying on large-scale pre-training datasets has shown premier performance on various downstream tasks. In this sense, a complete and fair benchmark (i.e., including large-scale pre-training datasets and a variety of downstream datasets) is essential for VLP. But how to construct such a benchmark in Chinese remains a critical problem. To this end, we develop a large-scale Chinese cross-modal benchmark called Zero for AI researchers to fairly compare VLP models. We release two pre-training datasets and five fine-tuning datasets for downstream tasks. Furthermore, we propose a novel pre-training framework of pre-Ranking + Ranking for cross-modal learning. Specifically, we apply global contrastive pre-ranking to learn the individual representations of images and Chinese texts, respectively. We then fuse the representations in a fine-grained ranking manner via an image-text cross encoder and a text-image cross encoder. To further enhance the capability of the model, we propose a two-way distillation strategy consisting of target-guided Distillation and feature-guided Distillation. For simplicity, we call our model R2D2. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on four public cross-modal datasets and our five downstream datasets. The datasets, models and codes will be made available.
Internal Wasserstein Distance for Adversarial Attack and Defense
Mar 13, 2021



Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial examples that can trigger misclassification of DNNs but may be imperceptible to human perception. Adversarial attack has been an important way to evaluate the robustness of DNNs. Existing attack methods on the construction of adversarial examples use such $\ell_p$ distance as a similarity metric to perturb samples. However, this kind of metric is incompatible with the underlying real-world image formation and human visual perception. In this paper, we first propose an internal Wasserstein distance (IWD) to measure image similarity between a sample and its adversarial example. We apply IWD to perform adversarial attack and defense. Specifically, we develop a novel attack method by capturing the distribution of patches in original samples. In this case, our approach is able to generate semantically similar but diverse adversarial examples that are more difficult to defend by existing defense methods. Relying on IWD, we also build a new defense method that seeks to learn robust models to defend against unseen adversarial examples. We provide both thorough theoretical and empirical evidence to support our methods.
Learning Defense Transformers for Counterattacking Adversarial Examples
Mar 13, 2021



Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial examples with small perturbations. Adversarial defense thus has been an important means which improves the robustness of DNNs by defending against adversarial examples. Existing defense methods focus on some specific types of adversarial examples and may fail to defend well in real-world applications. In practice, we may face many types of attacks where the exact type of adversarial examples in real-world applications can be even unknown. In this paper, motivated by that adversarial examples are more likely to appear near the classification boundary, we study adversarial examples from a new perspective that whether we can defend against adversarial examples by pulling them back to the original clean distribution. We theoretically and empirically verify the existence of defense affine transformations that restore adversarial examples. Relying on this, we learn a defense transformer to counterattack the adversarial examples by parameterizing the affine transformations and exploiting the boundary information of DNNs. Extensive experiments on both toy and real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our defense transformer.
Fair Meta-Learning For Few-Shot Classification
Sep 23, 2020



Abstract:Artificial intelligence nowadays plays an increasingly prominent role in our life since decisions that were once made by humans are now delegated to automated systems. A machine learning algorithm trained based on biased data, however, tends to make unfair predictions. Developing classification algorithms that are fair with respect to protected attributes of the data thus becomes an important problem. Motivated by concerns surrounding the fairness effects of sharing and few-shot machine learning tools, such as the Model Agnostic Meta-Learning framework, we propose a novel fair fast-adapted few-shot meta-learning approach that efficiently mitigates biases during meta-train by ensuring controlling the decision boundary covariance that between the protected variable and the signed distance from the feature vectors to the decision boundary. Through extensive experiments on two real-world image benchmarks over three state-of-the-art meta-learning algorithms, we empirically demonstrate that our proposed approach efficiently mitigates biases on model output and generalizes both accuracy and fairness to unseen tasks with a limited amount of training samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge