Ruizhuo Xu
Skeleton2vec: A Self-supervised Learning Framework with Contextualized Target Representations for Skeleton Sequence
Jan 01, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training paradigms have been extensively explored in the field of skeleton-based action recognition. In particular, methods based on masked prediction have pushed the performance of pre-training to a new height. However, these methods take low-level features, such as raw joint coordinates or temporal motion, as prediction targets for the masked regions, which is suboptimal. In this paper, we show that using high-level contextualized features as prediction targets can achieve superior performance. Specifically, we propose Skeleton2vec, a simple and efficient self-supervised 3D action representation learning framework, which utilizes a transformer-based teacher encoder taking unmasked training samples as input to create latent contextualized representations as prediction targets. Benefiting from the self-attention mechanism, the latent representations generated by the teacher encoder can incorporate the global context of the entire training samples, leading to a richer training task. Additionally, considering the high temporal correlations in skeleton sequences, we propose a motion-aware tube masking strategy which divides the skeleton sequence into several tubes and performs persistent masking within each tube based on motion priors, thus forcing the model to build long-range spatio-temporal connections and focus on action-semantic richer regions. Extensive experiments on NTU-60, NTU-120, and PKU-MMD datasets demonstrate that our proposed Skeleton2vec outperforms previous methods and achieves state-of-the-art results.
Depth Map Denoising Network and Lightweight Fusion Network for Enhanced 3D Face Recognition
Jan 01, 2024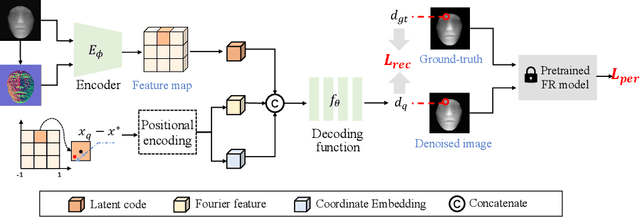
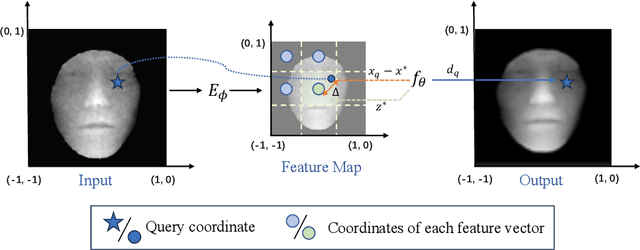
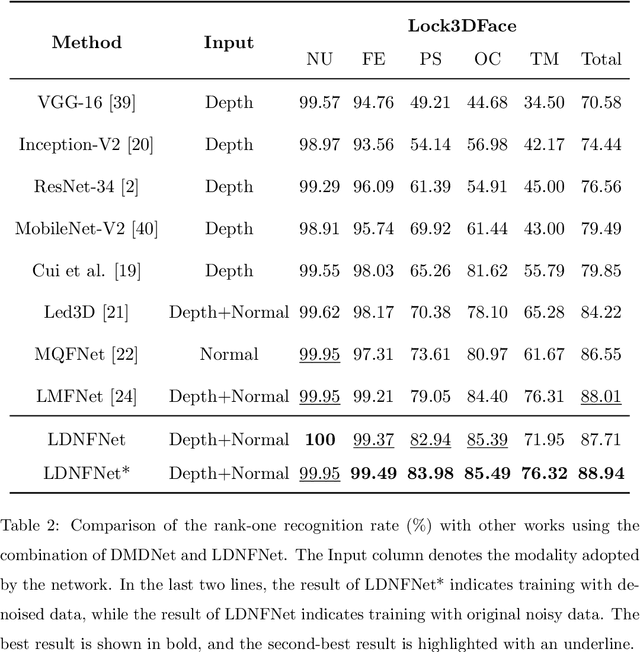
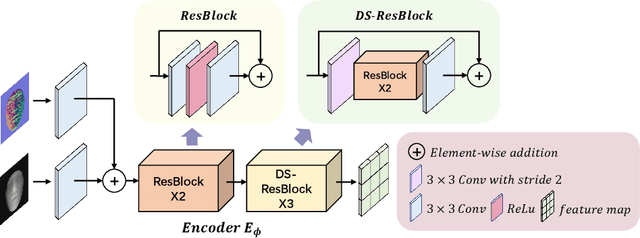
Abstract:With the increasing availability of consumer depth sensors, 3D face recognition (FR) has attracted more and more attention. However, the data acquired by these sensors are often coarse and noisy, making them impractical to use directly. In this paper, we introduce an innovative Depth map denoising network (DMDNet) based on the Denoising Implicit Image Function (DIIF) to reduce noise and enhance the quality of facial depth images for low-quality 3D FR. After generating clean depth faces using DMDNet, we further design a powerful recognition network called Lightweight Depth and Normal Fusion network (LDNFNet), which incorporates a multi-branch fusion block to learn unique and complementary features between different modalities such as depth and normal images. Comprehensive experiments conducted on four distinct low-quality databases demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed methods. Furthermore, when combining DMDNet and LDNFNet, we achieve state-of-the-art results on the Lock3DFace database.
WaBERT: A Low-resource End-to-end Model for Spoken Language Understanding and Speech-to-BERT Alignment
Apr 22, 2022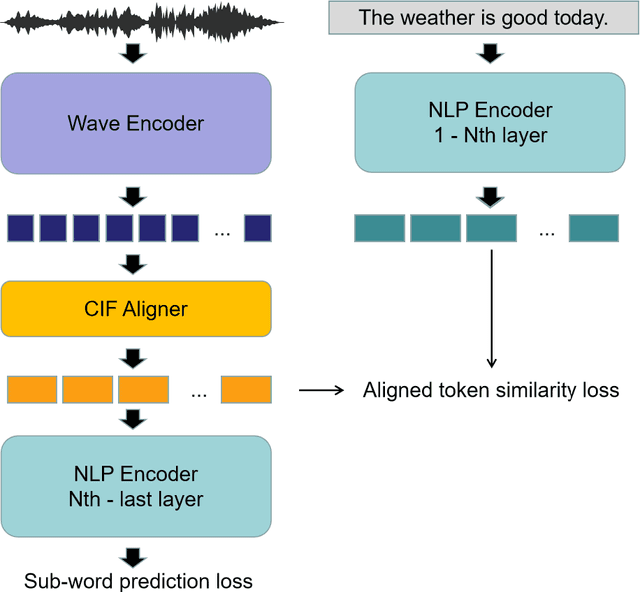

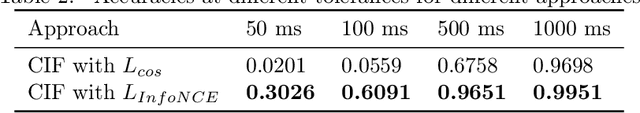
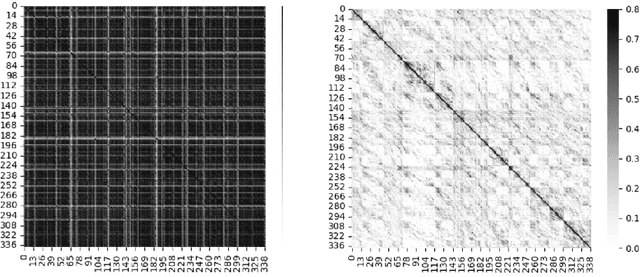
Abstract:Historically lower-level tasks such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speaker identification are the main focus in the speech field. Interest has been growing in higher-level spoken language understanding (SLU) tasks recently, like sentiment analysis (SA). However, improving performances on SLU tasks remains a big challenge. Basically, there are two main methods for SLU tasks: (1) Two-stage method, which uses a speech model to transfer speech to text, then uses a language model to get the results of downstream tasks; (2) One-stage method, which just fine-tunes a pre-trained speech model to fit in the downstream tasks. The first method loses emotional cues such as intonation, and causes recognition errors during ASR process, and the second one lacks necessary language knowledge. In this paper, we propose the Wave BERT (WaBERT), a novel end-to-end model combining the speech model and the language model for SLU tasks. WaBERT is based on the pre-trained speech and language model, hence training from scratch is not needed. We also set most parameters of WaBERT frozen during training. By introducing WaBERT, audio-specific information and language knowledge are integrated in the short-time and low-resource training process to improve results on the dev dataset of SLUE SA tasks by 1.15% of recall score and 0.82% of F1 score. Additionally, we modify the serial Continuous Integrate-and-Fire (CIF) mechanism to achieve the monotonic alignment between the speech and text modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge