Jessy Lin
Learning to Model the World with Language
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:To interact with humans in the world, agents need to understand the diverse types of language that people use, relate them to the visual world, and act based on them. While current agents learn to execute simple language instructions from task rewards, we aim to build agents that leverage diverse language that conveys general knowledge, describes the state of the world, provides interactive feedback, and more. Our key idea is that language helps agents predict the future: what will be observed, how the world will behave, and which situations will be rewarded. This perspective unifies language understanding with future prediction as a powerful self-supervised learning objective. We present Dynalang, an agent that learns a multimodal world model that predicts future text and image representations and learns to act from imagined model rollouts. Unlike traditional agents that use language only to predict actions, Dynalang acquires rich language understanding by using past language also to predict future language, video, and rewards. In addition to learning from online interaction in an environment, Dynalang can be pretrained on datasets of text, video, or both without actions or rewards. From using language hints in grid worlds to navigating photorealistic scans of homes, Dynalang utilizes diverse types of language to improve task performance, including environment descriptions, game rules, and instructions.
Decision-Oriented Dialogue for Human-AI Collaboration
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:We describe a class of tasks called decision-oriented dialogues, in which AI assistants must collaborate with one or more humans via natural language to help them make complex decisions. We formalize three domains in which users face everyday decisions: (1) choosing an assignment of reviewers to conference papers, (2) planning a multi-step itinerary in a city, and (3) negotiating travel plans for a group of friends. In each of these settings, AI assistants and users have disparate abilities that they must combine to arrive at the best decision: assistants can access and process large amounts of information, while users have preferences and constraints external to the system. For each task, we build a dialogue environment where agents receive a reward based on the quality of the final decision they reach. Using these environments, we collect human-human dialogues with humans playing the role of assistant. To compare how current AI assistants communicate in these settings, we present baselines using large language models in self-play. Finally, we highlight a number of challenges models face in decision-oriented dialogues, ranging from efficient communication to reasoning and optimization, and release our environments as a testbed for future modeling work.
UniMASK: Unified Inference in Sequential Decision Problems
Nov 20, 2022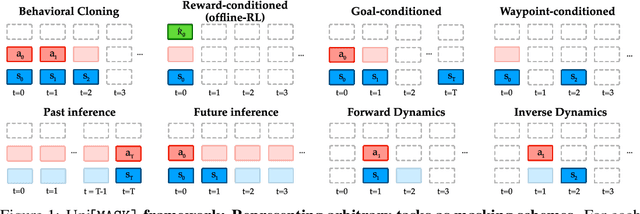
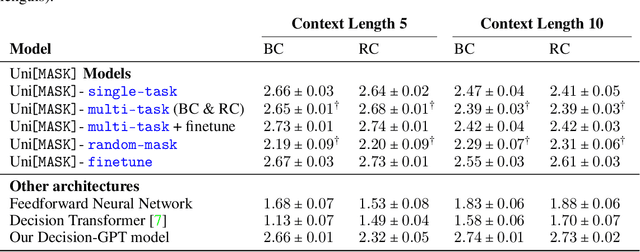
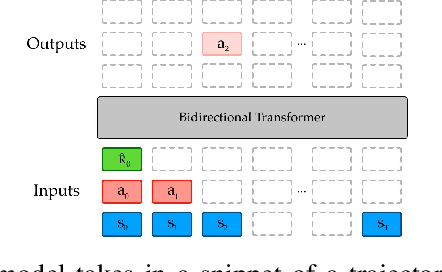
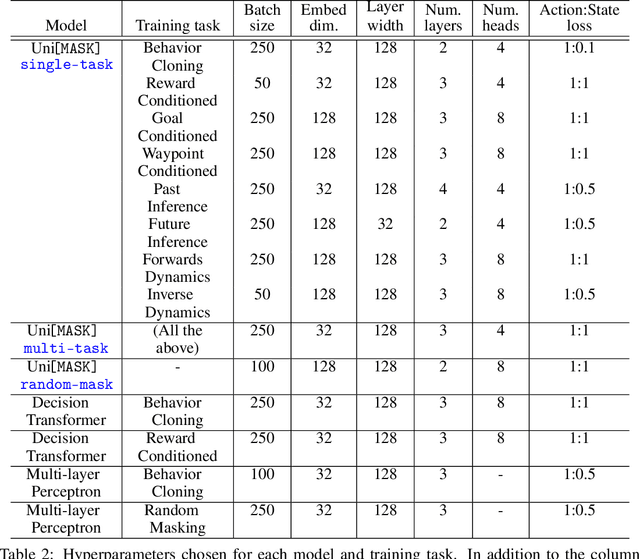
Abstract:Randomly masking and predicting word tokens has been a successful approach in pre-training language models for a variety of downstream tasks. In this work, we observe that the same idea also applies naturally to sequential decision-making, where many well-studied tasks like behavior cloning, offline reinforcement learning, inverse dynamics, and waypoint conditioning correspond to different sequence maskings over a sequence of states, actions, and returns. We introduce the UniMASK framework, which provides a unified way to specify models which can be trained on many different sequential decision-making tasks. We show that a single UniMASK model is often capable of carrying out many tasks with performance similar to or better than single-task models. Additionally, after fine-tuning, our UniMASK models consistently outperform comparable single-task models. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/micahcarroll/uniMASK.
Automatic Correction of Human Translations
Jun 17, 2022
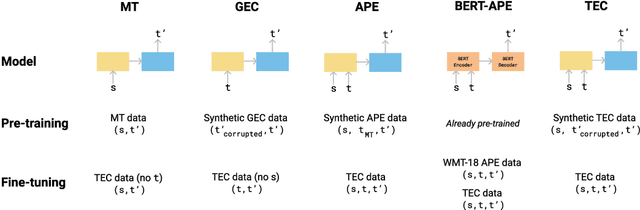
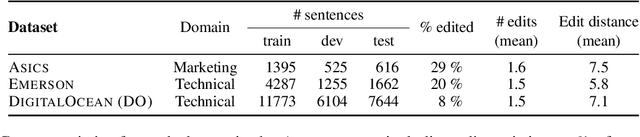

Abstract:We introduce translation error correction (TEC), the task of automatically correcting human-generated translations. Imperfections in machine translations (MT) have long motivated systems for improving translations post-hoc with automatic post-editing. In contrast, little attention has been devoted to the problem of automatically correcting human translations, despite the intuition that humans make distinct errors that machines would be well-suited to assist with, from typos to inconsistencies in translation conventions. To investigate this, we build and release the Aced corpus with three TEC datasets. We show that human errors in TEC exhibit a more diverse range of errors and far fewer translation fluency errors than the MT errors in automatic post-editing datasets, suggesting the need for dedicated TEC models that are specialized to correct human errors. We show that pre-training instead on synthetic errors based on human errors improves TEC F-score by as much as 5.1 points. We conducted a human-in-the-loop user study with nine professional translation editors and found that the assistance of our TEC system led them to produce significantly higher quality revised translations.
Towards Flexible Inference in Sequential Decision Problems via Bidirectional Transformers
Apr 28, 2022



Abstract:Randomly masking and predicting word tokens has been a successful approach in pre-training language models for a variety of downstream tasks. In this work, we observe that the same idea also applies naturally to sequential decision making, where many well-studied tasks like behavior cloning, offline RL, inverse dynamics, and waypoint conditioning correspond to different sequence maskings over a sequence of states, actions, and returns. We introduce the FlexiBiT framework, which provides a unified way to specify models which can be trained on many different sequential decision making tasks. We show that a single FlexiBiT model is simultaneously capable of carrying out many tasks with performance similar to or better than specialized models. Additionally, we show that performance can be further improved by fine-tuning our general model on specific tasks of interest.
InCoder: A Generative Model for Code Infilling and Synthesis
Apr 17, 2022



Abstract:Code is seldom written in a single left-to-right pass and is instead repeatedly edited and refined. We introduce InCoder, a unified generative model that can perform program synthesis (via left-to-right generation) as well as editing (via infilling). InCoder is trained to generate code files from a large corpus of permissively licensed code, where regions of code have been randomly masked and moved to the end of each file, allowing code infilling with bidirectional context. Our model is the first generative model that is able to directly perform zero-shot code infilling, which we evaluate on challenging tasks such as type inference, comment generation, and variable re-naming. We find that the ability to condition on bidirectional context substantially improves performance on these tasks, while still performing comparably on standard program synthesis benchmarks in comparison to left-to-right only models pretrained at similar scale. The InCoder models and code are publicly released. https://sites.google.com/view/incoder-code-models
Inferring Rewards from Language in Context
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:In classic instruction following, language like "I'd like the JetBlue flight" maps to actions (e.g., selecting that flight). However, language also conveys information about a user's underlying reward function (e.g., a general preference for JetBlue), which can allow a model to carry out desirable actions in new contexts. We present a model that infers rewards from language pragmatically: reasoning about how speakers choose utterances not only to elicit desired actions, but also to reveal information about their preferences. On a new interactive flight-booking task with natural language, our model more accurately infers rewards and predicts optimal actions in unseen environments, in comparison to past work that first maps language to actions (instruction following) and then maps actions to rewards (inverse reinforcement learning).
Black-box Adversarial Attacks with Limited Queries and Information
Jul 11, 2018



Abstract:Current neural network-based classifiers are susceptible to adversarial examples even in the black-box setting, where the attacker only has query access to the model. In practice, the threat model for real-world systems is often more restrictive than the typical black-box model where the adversary can observe the full output of the network on arbitrarily many chosen inputs. We define three realistic threat models that more accurately characterize many real-world classifiers: the query-limited setting, the partial-information setting, and the label-only setting. We develop new attacks that fool classifiers under these more restrictive threat models, where previous methods would be impractical or ineffective. We demonstrate that our methods are effective against an ImageNet classifier under our proposed threat models. We also demonstrate a targeted black-box attack against a commercial classifier, overcoming the challenges of limited query access, partial information, and other practical issues to break the Google Cloud Vision API.
Query-Efficient Black-box Adversarial Examples (superceded)
Apr 06, 2018

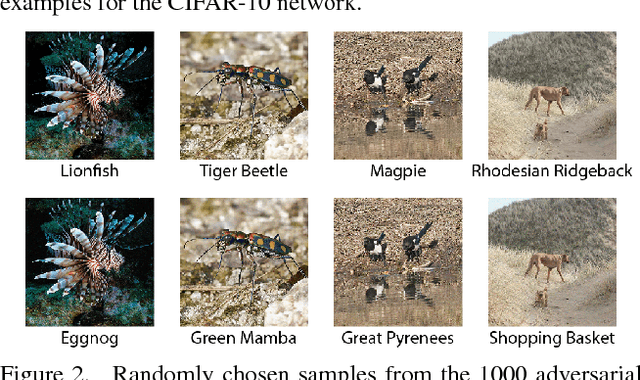
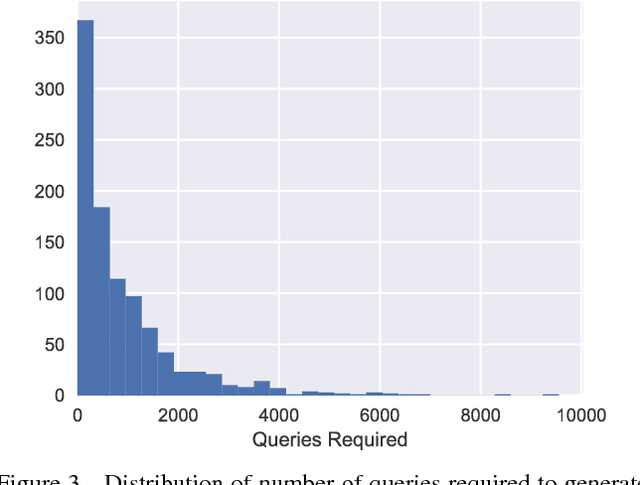
Abstract:Note that this paper is superceded by "Black-Box Adversarial Attacks with Limited Queries and Information." Current neural network-based image classifiers are susceptible to adversarial examples, even in the black-box setting, where the attacker is limited to query access without access to gradients. Previous methods --- substitute networks and coordinate-based finite-difference methods --- are either unreliable or query-inefficient, making these methods impractical for certain problems. We introduce a new method for reliably generating adversarial examples under more restricted, practical black-box threat models. First, we apply natural evolution strategies to perform black-box attacks using two to three orders of magnitude fewer queries than previous methods. Second, we introduce a new algorithm to perform targeted adversarial attacks in the partial-information setting, where the attacker only has access to a limited number of target classes. Using these techniques, we successfully perform the first targeted adversarial attack against a commercially deployed machine learning system, the Google Cloud Vision API, in the partial information setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge