Irwan Bello
Designing Effective Sparse Expert Models
Feb 17, 2022
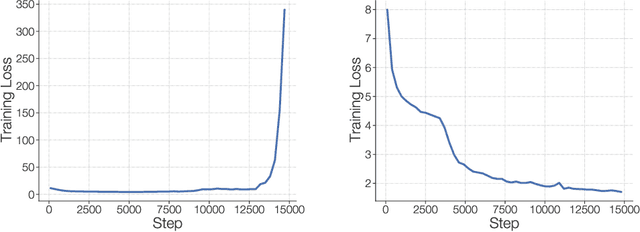

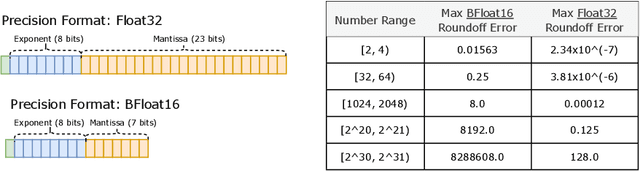
Abstract:Scale has opened new frontiers in natural language processing -- but at a high cost. In response, Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) and Switch Transformers have been proposed as an energy efficient path to even larger and more capable language models. But advancing the state-of-the-art across a broad set of natural language tasks has been hindered by training instabilities and uncertain quality during fine-tuning. Our work focuses on these issues and acts as a design guide. We conclude by scaling a sparse model to 269B parameters, with a computational cost comparable to a 32B dense encoder-decoder Transformer (Stable and Transferable Mixture-of-Experts or ST-MoE-32B). For the first time, a sparse model achieves state-of-the-art performance in transfer learning, across a diverse set of tasks including reasoning (SuperGLUE, ARC Easy, ARC Challenge), summarization (XSum, CNN-DM), closed book question answering (WebQA, Natural Questions), and adversarially constructed tasks (Winogrande, ANLI R3).
Revisiting 3D ResNets for Video Recognition
Sep 03, 2021



Abstract:A recent work from Bello shows that training and scaling strategies may be more significant than model architectures for visual recognition. This short note studies effective training and scaling strategies for video recognition models. We propose a simple scaling strategy for 3D ResNets, in combination with improved training strategies and minor architectural changes. The resulting models, termed 3D ResNet-RS, attain competitive performance of 81.0 on Kinetics-400 and 83.8 on Kinetics-600 without pre-training. When pre-trained on a large Web Video Text dataset, our best model achieves 83.5 and 84.3 on Kinetics-400 and Kinetics-600. The proposed scaling rule is further evaluated in a self-supervised setup using contrastive learning, demonstrating improved performance. Code is available at: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official.
Revisiting ResNets: Improved Training and Scaling Strategies
Mar 13, 2021



Abstract:Novel computer vision architectures monopolize the spotlight, but the impact of the model architecture is often conflated with simultaneous changes to training methodology and scaling strategies. Our work revisits the canonical ResNet (He et al., 2015) and studies these three aspects in an effort to disentangle them. Perhaps surprisingly, we find that training and scaling strategies may matter more than architectural changes, and further, that the resulting ResNets match recent state-of-the-art models. We show that the best performing scaling strategy depends on the training regime and offer two new scaling strategies: (1) scale model depth in regimes where overfitting can occur (width scaling is preferable otherwise); (2) increase image resolution more slowly than previously recommended (Tan & Le, 2019). Using improved training and scaling strategies, we design a family of ResNet architectures, ResNet-RS, which are 1.7x - 2.7x faster than EfficientNets on TPUs, while achieving similar accuracies on ImageNet. In a large-scale semi-supervised learning setup, ResNet-RS achieves 86.2% top-1 ImageNet accuracy, while being 4.7x faster than EfficientNet NoisyStudent. The training techniques improve transfer performance on a suite of downstream tasks (rivaling state-of-the-art self-supervised algorithms) and extend to video classification on Kinetics-400. We recommend practitioners use these simple revised ResNets as baselines for future research.
LambdaNetworks: Modeling Long-Range Interactions Without Attention
Feb 17, 2021



Abstract:We present lambda layers -- an alternative framework to self-attention -- for capturing long-range interactions between an input and structured contextual information (e.g. a pixel surrounded by other pixels). Lambda layers capture such interactions by transforming available contexts into linear functions, termed lambdas, and applying these linear functions to each input separately. Similar to linear attention, lambda layers bypass expensive attention maps, but in contrast, they model both content and position-based interactions which enables their application to large structured inputs such as images. The resulting neural network architectures, LambdaNetworks, significantly outperform their convolutional and attentional counterparts on ImageNet classification, COCO object detection and COCO instance segmentation, while being more computationally efficient. Additionally, we design LambdaResNets, a family of hybrid architectures across different scales, that considerably improves the speed-accuracy tradeoff of image classification models. LambdaResNets reach excellent accuracies on ImageNet while being 3.2 - 4.4x faster than the popular EfficientNets on modern machine learning accelerators. When training with an additional 130M pseudo-labeled images, LambdaResNets achieve up to a 9.5x speed-up over the corresponding EfficientNet checkpoints.
Global Self-Attention Networks for Image Recognition
Oct 14, 2020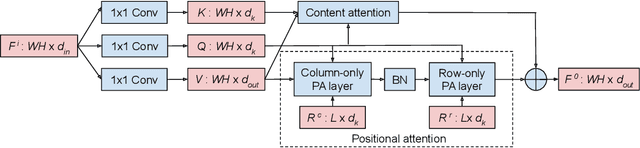
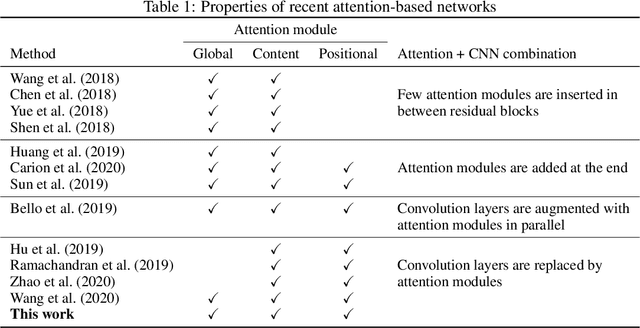
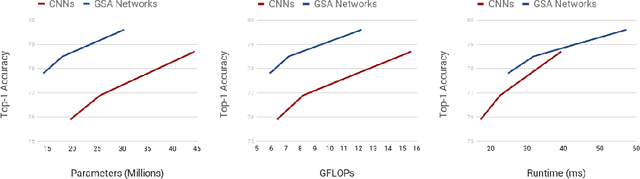
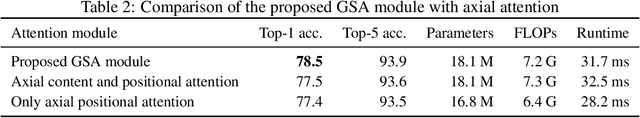
Abstract:Recently, a series of works in computer vision have shown promising results on various image and video understanding tasks using self-attention. However, due to the quadratic computational and memory complexities of self-attention, these works either apply attention only to low-resolution feature maps in later stages of a deep network or restrict the receptive field of attention in each layer to a small local region. To overcome these limitations, this work introduces a new global self-attention module, referred to as the GSA module, which is efficient enough to serve as the backbone component of a deep network. This module consists of two parallel layers: a content attention layer that attends to pixels based only on their content and a positional attention layer that attends to pixels based on their spatial locations. The output of this module is the sum of the outputs of the two layers. Based on the proposed GSA module, we introduce new standalone global attention-based deep networks that use GSA modules instead of convolutions to model pixel interactions. Due to the global extent of the proposed GSA module, a GSA network has the ability to model long-range pixel interactions throughout the network. Our experimental results show that GSA networks outperform the corresponding convolution-based networks significantly on the CIFAR-100 and ImageNet datasets while using less parameters and computations. The proposed GSA networks also outperform various existing attention-based networks on the ImageNet dataset.
Stand-Alone Self-Attention in Vision Models
Jun 13, 2019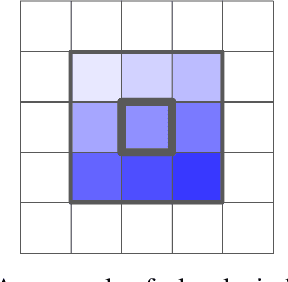
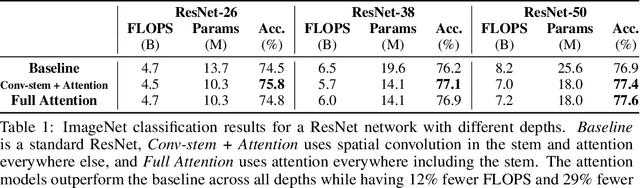
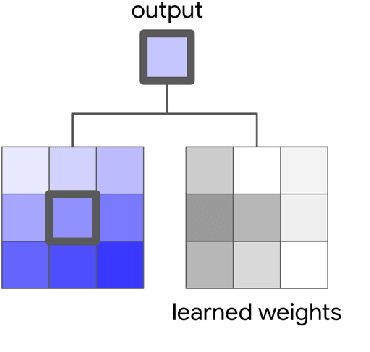
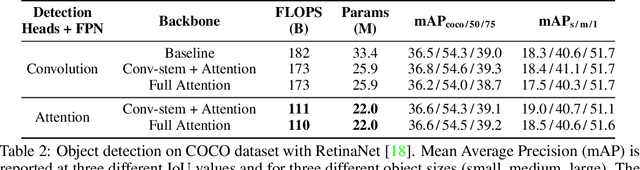
Abstract:Convolutions are a fundamental building block of modern computer vision systems. Recent approaches have argued for going beyond convolutions in order to capture long-range dependencies. These efforts focus on augmenting convolutional models with content-based interactions, such as self-attention and non-local means, to achieve gains on a number of vision tasks. The natural question that arises is whether attention can be a stand-alone primitive for vision models instead of serving as just an augmentation on top of convolutions. In developing and testing a pure self-attention vision model, we verify that self-attention can indeed be an effective stand-alone layer. A simple procedure of replacing all instances of spatial convolutions with a form of self-attention applied to ResNet model produces a fully self-attentional model that outperforms the baseline on ImageNet classification with 12% fewer FLOPS and 29% fewer parameters. On COCO object detection, a pure self-attention model matches the mAP of a baseline RetinaNet while having 39% fewer FLOPS and 34% fewer parameters. Detailed ablation studies demonstrate that self-attention is especially impactful when used in later layers. These results establish that stand-alone self-attention is an important addition to the vision practitioner's toolbox.
Attention Augmented Convolutional Networks
Apr 22, 2019



Abstract:Convolutional networks have been the paradigm of choice in many computer vision applications. The convolution operation however has a significant weakness in that it only operates on a local neighborhood, thus missing global information. Self-attention, on the other hand, has emerged as a recent advance to capture long range interactions, but has mostly been applied to sequence modeling and generative modeling tasks. In this paper, we consider the use of self-attention for discriminative visual tasks as an alternative to convolutions. We introduce a novel two-dimensional relative self-attention mechanism that proves competitive in replacing convolutions as a stand-alone computational primitive for image classification. We find in control experiments that the best results are obtained when combining both convolutions and self-attention. We therefore propose to augment convolutional operators with this self-attention mechanism by concatenating convolutional feature maps with a set of feature maps produced via self-attention. Extensive experiments show that Attention Augmentation leads to consistent improvements in image classification on ImageNet and object detection on COCO across many different models and scales, including ResNets and a state-of-the art mobile constrained network, while keeping the number of parameters similar. In particular, our method achieves a $1.3\%$ top-1 accuracy improvement on ImageNet classification over a ResNet50 baseline and outperforms other attention mechanisms for images such as Squeeze-and-Excitation. It also achieves an improvement of 1.4 mAP in COCO Object Detection on top of a RetinaNet baseline.
Seq2Slate: Re-ranking and Slate Optimization with RNNs
Oct 04, 2018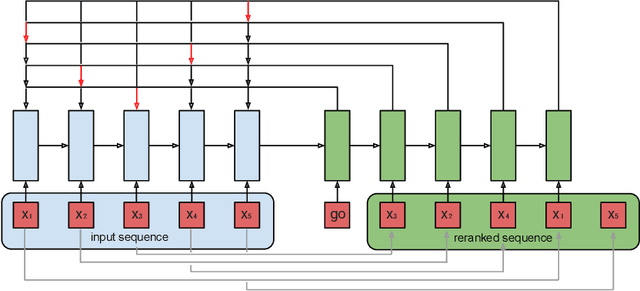



Abstract:Ranking is a central task in machine learning and information retrieval. In this task, it is especially important to present the user with a slate of items that is appealing as a whole. This in turn requires taking into account interactions between items, since intuitively, placing an item on the slate affects the decision of which other items should be placed alongside it. In this work, we propose a sequence-to-sequence model for ranking called seq2slate. At each step, the model predicts the next item to place on the slate given the items already selected. The recurrent nature of the model allows complex dependencies between items to be captured directly in a flexible and scalable way. We show how to learn the model end-to-end from weak supervision in the form of easily obtained click-through data. We further demonstrate the usefulness of our approach in experiments on standard ranking benchmarks as well as in a real-world recommendation system.
Backprop Evolution
Aug 08, 2018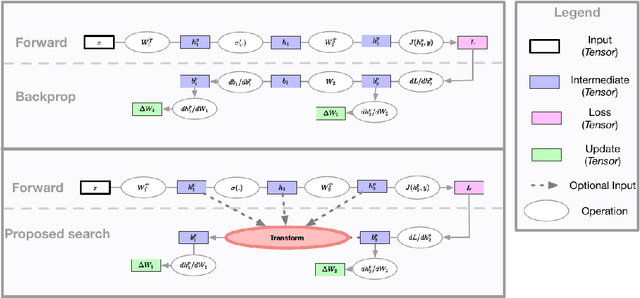
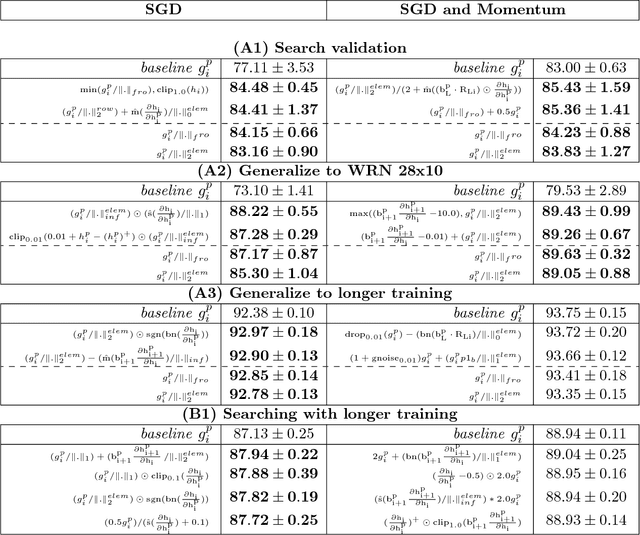
Abstract:The back-propagation algorithm is the cornerstone of deep learning. Despite its importance, few variations of the algorithm have been attempted. This work presents an approach to discover new variations of the back-propagation equation. We use a domain specific lan- guage to describe update equations as a list of primitive functions. An evolution-based method is used to discover new propagation rules that maximize the generalization per- formance after a few epochs of training. We find several update equations that can train faster with short training times than standard back-propagation, and perform similar as standard back-propagation at convergence.
Neural Optimizer Search with Reinforcement Learning
Sep 22, 2017



Abstract:We present an approach to automate the process of discovering optimization methods, with a focus on deep learning architectures. We train a Recurrent Neural Network controller to generate a string in a domain specific language that describes a mathematical update equation based on a list of primitive functions, such as the gradient, running average of the gradient, etc. The controller is trained with Reinforcement Learning to maximize the performance of a model after a few epochs. On CIFAR-10, our method discovers several update rules that are better than many commonly used optimizers, such as Adam, RMSProp, or SGD with and without Momentum on a ConvNet model. We introduce two new optimizers, named PowerSign and AddSign, which we show transfer well and improve training on a variety of different tasks and architectures, including ImageNet classification and Google's neural machine translation system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge