Huayi Tang
Sparsity is Combinatorial Depth: Quantifying MoE Expressivity via Tropical Geometry
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures define the state-of-the-art, their theoretical success is often attributed to heuristic efficiency rather than geometric expressivity. In this work, we present the first analysis of MoE through the lens of tropical geometry, establishing that the Top-$k$ routing mechanism is algebraically isomorphic to the $k$-th elementary symmetric tropical polynomial. This isomorphism partitions the input space into the Normal Fan of a Hypersimplex, revealing that \textbf{sparsity is combinatorial depth} which scales geometric capacity by the binomial coefficient $\binom{N}{k}$. Moving beyond ambient bounds, we introduce the concept of \textit{Effective Capacity} under the Manifold Hypothesis. We prove that while dense networks suffer from capacity collapse on low-dimensional data, MoE architectures exhibit \textit{Combinatorial Resilience}, maintaining high expressivity via the transversality of routing cones. In this study, our framework unifies the discrete geometry of the Hypersimplex with the continuous geometry of neural functions, offering a rigorous theoretical justification for the topological supremacy of conditional computation.
Effective Frontiers: A Unification of Neural Scaling Laws
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Neural scaling laws govern the prediction power-law improvement of test loss with respect to model capacity ($N$), datasize ($D$), and compute ($C$). However, existing theoretical explanations often rely on specific architectures or complex kernel methods, lacking intuitive universality. In this paper, we propose a unified framework that abstracts general learning tasks as the progressive coverage of patterns from a long-tail (Zipfian) distribution. We introduce the Effective Frontier ($k_\star$), a threshold in the pattern rank space that separates learned knowledge from the unlearned tail. We prove that reducible loss is asymptotically determined by the probability mass of the tail a resource-dependent frontier truncation. Based on our framework, we derive the precise scaling laws for $N$, $D$, and $C$, attributing them to capacity, coverage, and optimization bottlenecks, respectively. Furthermore, we unify these mechanisms via a Max-Bottleneck principle, demonstrating that the Kaplan and Chinchilla scaling laws are not contradictory, but equilibrium solutions to the same constrained optimization problem under different active bottlenecks.
Beyond the Black Box: Theory and Mechanism of Large Language Models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:The rapid emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has precipitated a profound paradigm shift in Artificial Intelligence, delivering monumental engineering successes that increasingly impact modern society. However, a critical paradox persists within the current field: despite the empirical efficacy, our theoretical understanding of LLMs remains disproportionately nascent, forcing these systems to be treated largely as ``black boxes''. To address this theoretical fragmentation, this survey proposes a unified lifecycle-based taxonomy that organizes the research landscape into six distinct stages: Data Preparation, Model Preparation, Training, Alignment, Inference, and Evaluation. Within this framework, we provide a systematic review of the foundational theories and internal mechanisms driving LLM performance. Specifically, we analyze core theoretical issues such as the mathematical justification for data mixtures, the representational limits of various architectures, and the optimization dynamics of alignment algorithms. Moving beyond current best practices, we identify critical frontier challenges, including the theoretical limits of synthetic data self-improvement, the mathematical bounds of safety guarantees, and the mechanistic origins of emergent intelligence. By connecting empirical observations with rigorous scientific inquiry, this work provides a structured roadmap for transitioning LLM development from engineering heuristics toward a principled scientific discipline.
Towards Auto-Regressive Next-Token Prediction: In-Context Learning Emerges from Generalization
Feb 24, 2025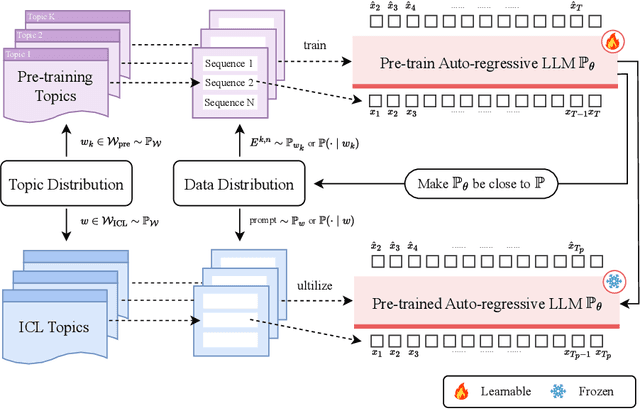



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable in-context learning (ICL) abilities. However, existing theoretical analysis of ICL primarily exhibits two limitations: (a) Limited i.i.d. Setting. Most studies focus on supervised function learning tasks where prompts are constructed with i.i.d. input-label pairs. This i.i.d. assumption diverges significantly from real language learning scenarios where prompt tokens are interdependent. (b) Lack of Emergence Explanation. Most literature answers what ICL does from an implicit optimization perspective but falls short in elucidating how ICL emerges and the impact of pre-training phase on ICL. In our paper, to extend (a), we adopt a more practical paradigm, auto-regressive next-token prediction (AR-NTP), which closely aligns with the actual training of language models. Specifically, within AR-NTP, we emphasize prompt token-dependency, which involves predicting each subsequent token based on the preceding sequence. To address (b), we formalize a systematic pre-training and ICL framework, highlighting the layer-wise structure of sequences and topics, alongside a two-level expectation. In conclusion, we present data-dependent, topic-dependent and optimization-dependent PAC-Bayesian generalization bounds for pre-trained LLMs, investigating that ICL emerges from the generalization of sequences and topics. Our theory is supported by experiments on numerical linear dynamic systems, synthetic GINC and real-world language datasets.
Understanding Model Ensemble in Transferable Adversarial Attack
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Model ensemble adversarial attack has become a powerful method for generating transferable adversarial examples that can target even unknown models, but its theoretical foundation remains underexplored. To address this gap, we provide early theoretical insights that serve as a roadmap for advancing model ensemble adversarial attack. We first define transferability error to measure the error in adversarial transferability, alongside concepts of diversity and empirical model ensemble Rademacher complexity. We then decompose the transferability error into vulnerability, diversity, and a constant, which rigidly explains the origin of transferability error in model ensemble attack: the vulnerability of an adversarial example to ensemble components, and the diversity of ensemble components. Furthermore, we apply the latest mathematical tools in information theory to bound the transferability error using complexity and generalization terms, contributing to three practical guidelines for reducing transferability error: (1) incorporating more surrogate models, (2) increasing their diversity, and (3) reducing their complexity in cases of overfitting. Finally, extensive experiments with 54 models validate our theoretical framework, representing a significant step forward in understanding transferable model ensemble adversarial attacks.
Information-Theoretic Generalization Bounds for Transductive Learning and its Applications
Nov 08, 2023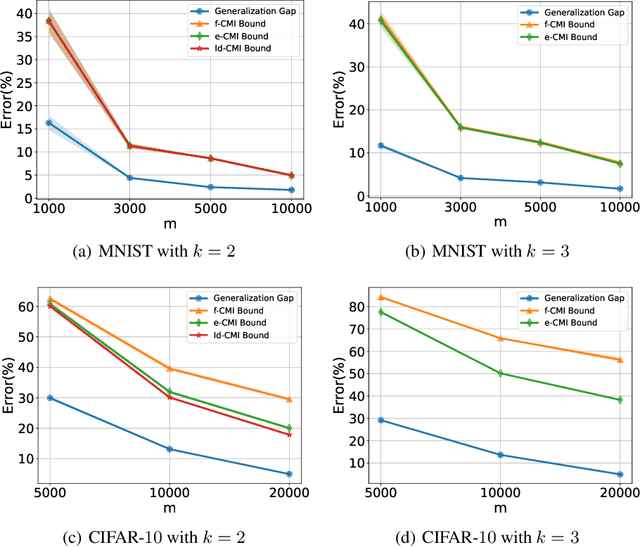
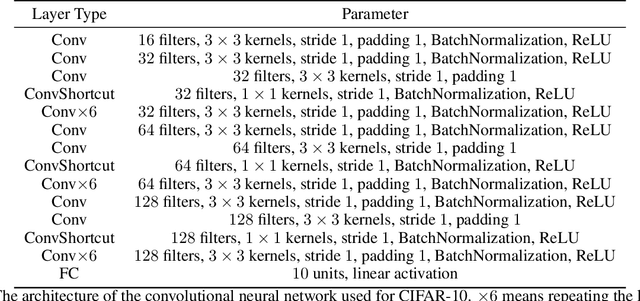
Abstract:In this paper, we develop data-dependent and algorithm-dependent generalization bounds for transductive learning algorithms in the context of information theory for the first time. We show that the generalization gap of transductive learning algorithms can be bounded by the mutual information between training labels and hypothesis. By innovatively proposing the concept of transductive supersamples, we go beyond the inductive learning setting and establish upper bounds in terms of various information measures. Furthermore, we derive novel PAC-Bayesian bounds and build the connection between generalization and loss landscape flatness under the transductive learning setting. Finally, we present the upper bounds for adaptive optimization algorithms and demonstrate the applications of results on semi-supervised learning and graph learning scenarios. Our theoretic results are validated on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Perfect Alignment May be Poisonous to Graph Contrastive Learning
Oct 06, 2023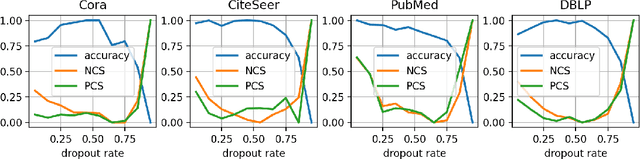
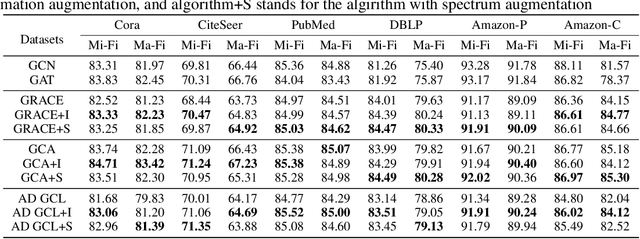
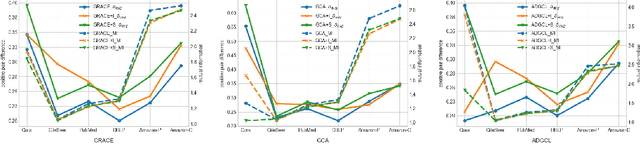
Abstract:Graph Contrastive Learning (GCL) aims to learn node representations by aligning positive pairs and separating negative ones. However, limited research has been conducted on the inner law behind specific augmentations used in graph-based learning. What kind of augmentation will help downstream performance, how does contrastive learning actually influence downstream tasks, and why the magnitude of augmentation matters? This paper seeks to address these questions by establishing a connection between augmentation and downstream performance, as well as by investigating the generalization of contrastive learning. Our findings reveal that GCL contributes to downstream tasks mainly by separating different classes rather than gathering nodes of the same class. So perfect alignment and augmentation overlap which draw all intra-class samples the same can not explain the success of contrastive learning. Then in order to comprehend how augmentation aids the contrastive learning process, we conduct further investigations into its generalization, finding that perfect alignment that draw positive pair the same could help contrastive loss but is poisonous to generalization, on the contrary, imperfect alignment enhances the model's generalization ability. We analyse the result by information theory and graph spectrum theory respectively, and propose two simple but effective methods to verify the theories. The two methods could be easily applied to various GCL algorithms and extensive experiments are conducted to prove its effectiveness.
DCPT: Darkness Clue-Prompted Tracking in Nighttime UAVs
Sep 19, 2023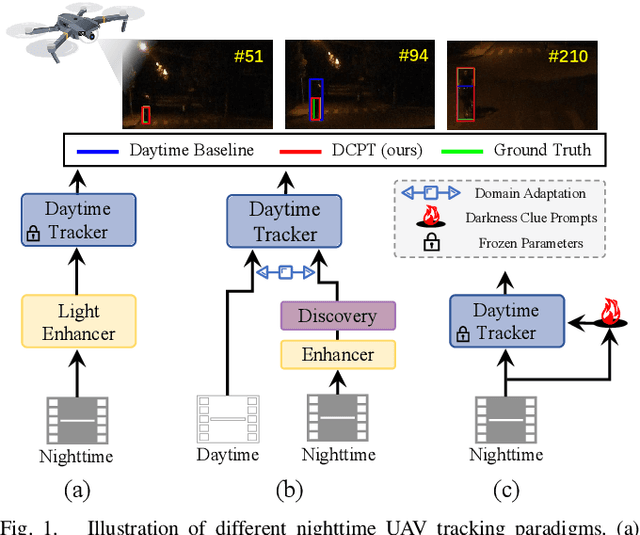
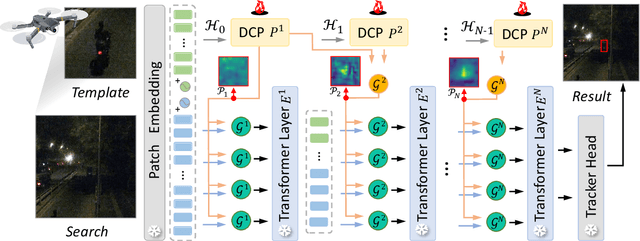
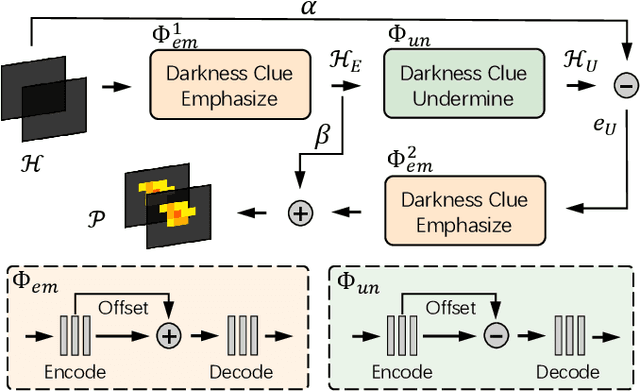
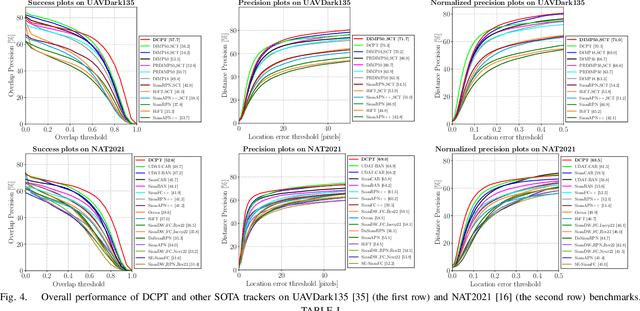
Abstract:Existing nighttime unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) trackers follow an "Enhance-then-Track" architecture - first using a light enhancer to brighten the nighttime video, then employing a daytime tracker to locate the object. This separate enhancement and tracking fails to build an end-to-end trainable vision system. To address this, we propose a novel architecture called Darkness Clue-Prompted Tracking (DCPT) that achieves robust UAV tracking at night by efficiently learning to generate darkness clue prompts. Without a separate enhancer, DCPT directly encodes anti-dark capabilities into prompts using a darkness clue prompter (DCP). Specifically, DCP iteratively learns emphasizing and undermining projections for darkness clues. It then injects these learned visual prompts into a daytime tracker with fixed parameters across transformer layers. Moreover, a gated feature aggregation mechanism enables adaptive fusion between prompts and between prompts and the base model. Extensive experiments show state-of-the-art performance for DCPT on multiple dark scenario benchmarks. The unified end-to-end learning of enhancement and tracking in DCPT enables a more trainable system. The darkness clue prompting efficiently injects anti-dark knowledge without extra modules. Code and models will be released.
Can Large Language Models Empower Molecular Property Prediction?
Jul 14, 2023



Abstract:Molecular property prediction has gained significant attention due to its transformative potential in multiple scientific disciplines. Conventionally, a molecule graph can be represented either as a graph-structured data or a SMILES text. Recently, the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized the field of NLP. Although it is natural to utilize LLMs to assist in understanding molecules represented by SMILES, the exploration of how LLMs will impact molecular property prediction is still in its early stage. In this work, we advance towards this objective through two perspectives: zero/few-shot molecular classification, and using the new explanations generated by LLMs as representations of molecules. To be specific, we first prompt LLMs to do in-context molecular classification and evaluate their performance. After that, we employ LLMs to generate semantically enriched explanations for the original SMILES and then leverage that to fine-tune a small-scale LM model for multiple downstream tasks. The experimental results highlight the superiority of text explanations as molecular representations across multiple benchmark datasets, and confirm the immense potential of LLMs in molecular property prediction tasks. Codes are available at \url{https://github.com/ChnQ/LLM4Mol}.
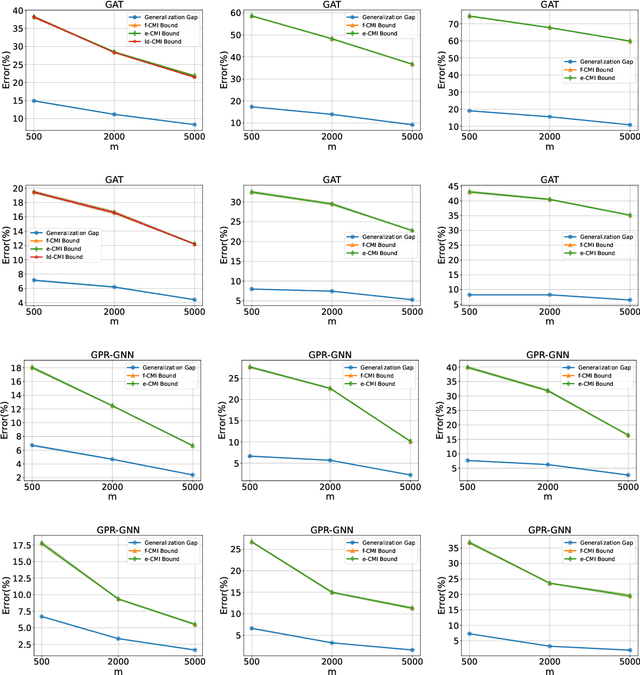
Towards Understanding the Generalization of Graph Neural Networks
May 14, 2023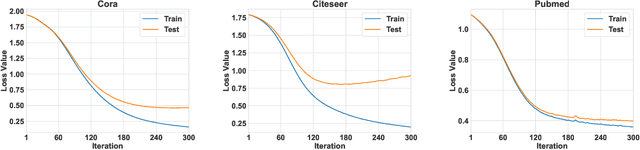
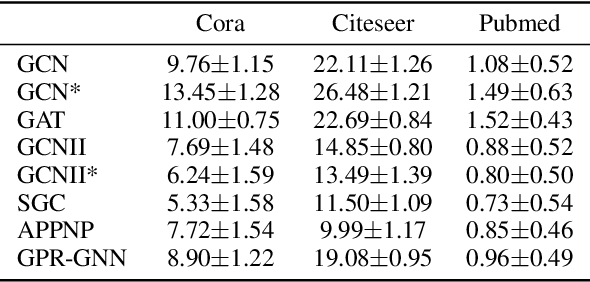
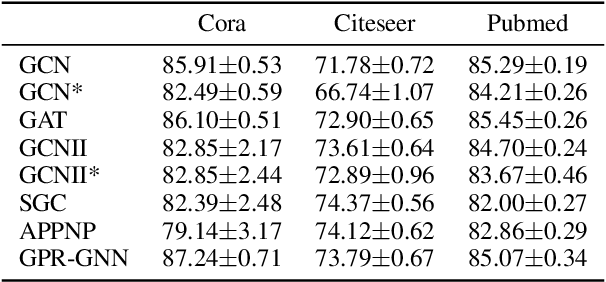
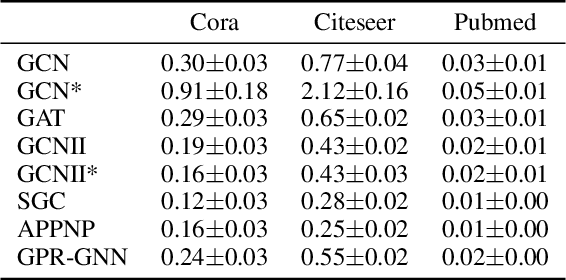
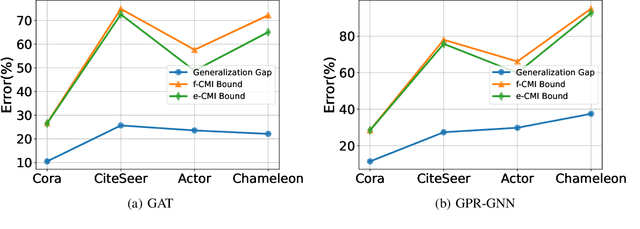
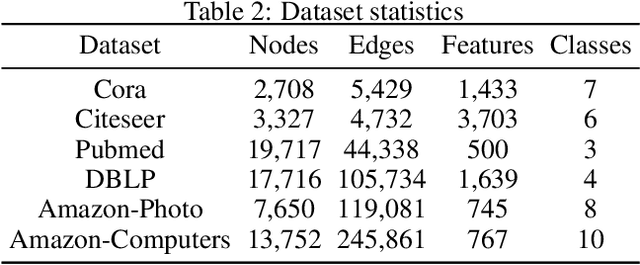
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) are the most widely adopted model in graph-structured data oriented learning and representation. Despite their extraordinary success in real-world applications, understanding their working mechanism by theory is still on primary stage. In this paper, we move towards this goal from the perspective of generalization. To be specific, we first establish high probability bounds of generalization gap and gradients in transductive learning with consideration of stochastic optimization. After that, we provide high probability bounds of generalization gap for popular GNNs. The theoretical results reveal the architecture specific factors affecting the generalization gap. Experimental results on benchmark datasets show the consistency between theoretical results and empirical evidence. Our results provide new insights in understanding the generalization of GNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge