Xiaorong Pu
Efficient Medical Image Restoration via Reliability Guided Learning in Frequency Domain
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:Medical image restoration tasks aim to recover high-quality images from degraded observations, exhibiting emergent desires in many clinical scenarios, such as low-dose CT image denoising, MRI super-resolution, and MRI artifact removal. Despite the success achieved by existing deep learning-based restoration methods with sophisticated modules, they struggle with rendering computationally-efficient reconstruction results. Moreover, they usually ignore the reliability of the restoration results, which is much more urgent in medical systems. To alleviate these issues, we present LRformer, a Lightweight Transformer-based method via Reliability-guided learning in the frequency domain. Specifically, inspired by the uncertainty quantification in Bayesian neural networks (BNNs), we develop a Reliable Lesion-Semantic Prior Producer (RLPP). RLPP leverages Monte Carlo (MC) estimators with stochastic sampling operations to generate sufficiently-reliable priors by performing multiple inferences on the foundational medical image segmentation model, MedSAM. Additionally, instead of directly incorporating the priors in the spatial domain, we decompose the cross-attention (CA) mechanism into real symmetric and imaginary anti-symmetric parts via fast Fourier transform (FFT), resulting in the design of the Guided Frequency Cross-Attention (GFCA) solver. By leveraging the conjugated symmetric property of FFT, GFCA reduces the computational complexity of naive CA by nearly half. Extensive experimental results in various tasks demonstrate the superiority of the proposed LRformer in both effectiveness and efficiency.
Dual-Optimized Adaptive Graph Reconstruction for Multi-View Graph Clustering
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:Multi-view clustering is an important machine learning task for multi-media data, encompassing various domains such as images, videos, and texts. Moreover, with the growing abundance of graph data, the significance of multi-view graph clustering (MVGC) has become evident. Most existing methods focus on graph neural networks (GNNs) to extract information from both graph structure and feature data to learn distinguishable node representations. However, traditional GNNs are designed with the assumption of homophilous graphs, making them unsuitable for widely prevalent heterophilous graphs. Several techniques have been introduced to enhance GNNs for heterophilous graphs. While these methods partially mitigate the heterophilous graph issue, they often neglect the advantages of traditional GNNs, such as their simplicity, interpretability, and efficiency. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-view graph clustering method based on dual-optimized adaptive graph reconstruction, named DOAGC. It mainly aims to reconstruct the graph structure adapted to traditional GNNs to deal with heterophilous graph issues while maintaining the advantages of traditional GNNs. Specifically, we first develop an adaptive graph reconstruction mechanism that accounts for node correlation and original structural information. To further optimize the reconstruction graph, we design a dual optimization strategy and demonstrate the feasibility of our optimization strategy through mutual information theory. Numerous experiments demonstrate that DOAGC effectively mitigates the heterophilous graph problem.
Bridging Gaps: Federated Multi-View Clustering in Heterogeneous Hybrid Views
Oct 12, 2024



Abstract:Recently, federated multi-view clustering (FedMVC) has emerged to explore cluster structures in multi-view data distributed on multiple clients. Existing approaches often assume that clients are isomorphic and all of them belong to either single-view clients or multi-view clients. Despite their success, these methods also present limitations when dealing with practical FedMVC scenarios involving heterogeneous hybrid views, where a mixture of both single-view and multi-view clients exhibit varying degrees of heterogeneity. In this paper, we propose a novel FedMVC framework, which concurrently addresses two challenges associated with heterogeneous hybrid views, i.e., client gap and view gap. To address the client gap, we design a local-synergistic contrastive learning approach that helps single-view clients and multi-view clients achieve consistency for mitigating heterogeneity among all clients. To address the view gap, we develop a global-specific weighting aggregation method, which encourages global models to learn complementary features from hybrid views. The interplay between local-synergistic contrastive learning and global-specific weighting aggregation mutually enhances the exploration of the data cluster structures distributed on multiple clients. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can handle the heterogeneous hybrid views in FedMVC and outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/5Martina5/FMCSC}.
Homophily-Related: Adaptive Hybrid Graph Filter for Multi-View Graph Clustering
Jan 05, 2024Abstract:Recently there is a growing focus on graph data, and multi-view graph clustering has become a popular area of research interest. Most of the existing methods are only applicable to homophilous graphs, yet the extensive real-world graph data can hardly fulfill the homophily assumption, where the connected nodes tend to belong to the same class. Several studies have pointed out that the poor performance on heterophilous graphs is actually due to the fact that conventional graph neural networks (GNNs), which are essentially low-pass filters, discard information other than the low-frequency information on the graph. Nevertheless, on certain graphs, particularly heterophilous ones, neglecting high-frequency information and focusing solely on low-frequency information impedes the learning of node representations. To break this limitation, our motivation is to perform graph filtering that is closely related to the homophily degree of the given graph, with the aim of fully leveraging both low-frequency and high-frequency signals to learn distinguishable node embedding. In this work, we propose Adaptive Hybrid Graph Filter for Multi-View Graph Clustering (AHGFC). Specifically, a graph joint process and graph joint aggregation matrix are first designed by using the intrinsic node features and adjacency relationship, which makes the low and high-frequency signals on the graph more distinguishable. Then we design an adaptive hybrid graph filter that is related to the homophily degree, which learns the node embedding based on the graph joint aggregation matrix. After that, the node embedding of each view is weighted and fused into a consensus embedding for the downstream task. Experimental results show that our proposed model performs well on six datasets containing homophilous and heterophilous graphs.
A Novel Approach for Effective Multi-View Clustering with Information-Theoretic Perspective
Sep 25, 2023



Abstract:Multi-view clustering (MVC) is a popular technique for improving clustering performance using various data sources. However, existing methods primarily focus on acquiring consistent information while often neglecting the issue of redundancy across multiple views. This study presents a new approach called Sufficient Multi-View Clustering (SUMVC) that examines the multi-view clustering framework from an information-theoretic standpoint. Our proposed method consists of two parts. Firstly, we develop a simple and reliable multi-view clustering method SCMVC (simple consistent multi-view clustering) that employs variational analysis to generate consistent information. Secondly, we propose a sufficient representation lower bound to enhance consistent information and minimise unnecessary information among views. The proposed SUMVC method offers a promising solution to the problem of multi-view clustering and provides a new perspective for analyzing multi-view data. To verify the effectiveness of our model, we conducted a theoretical analysis based on the Bayes Error Rate, and experiments on multiple multi-view datasets demonstrate the superior performance of SUMVC.
Federated Deep Multi-View Clustering with Global Self-Supervision
Sep 24, 2023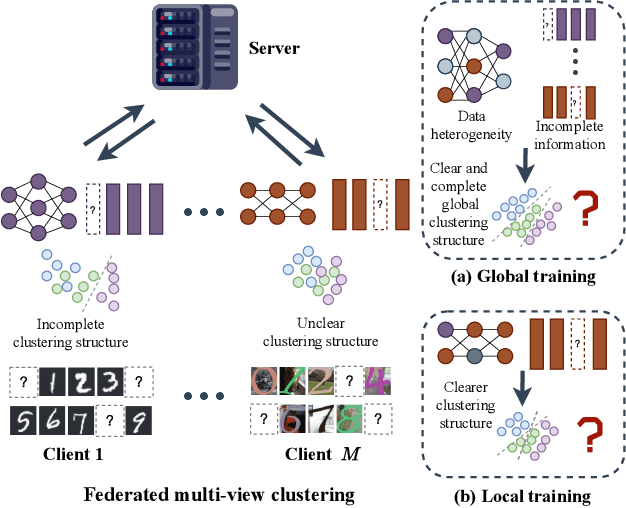
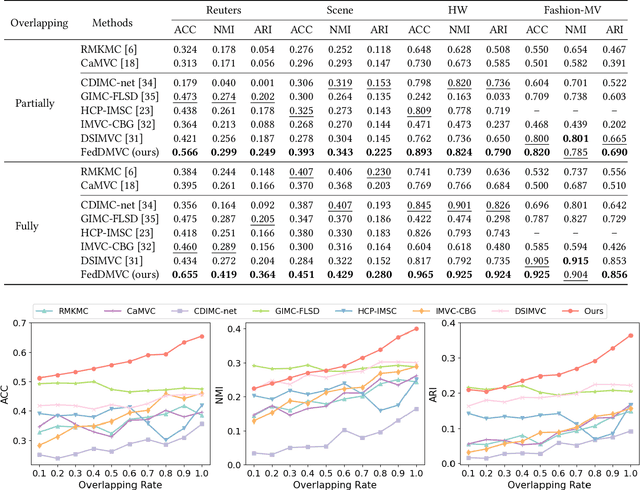
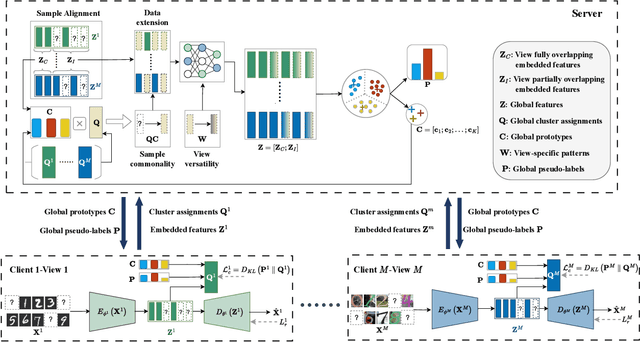
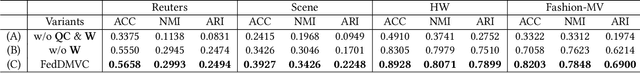
Abstract:Federated multi-view clustering has the potential to learn a global clustering model from data distributed across multiple devices. In this setting, label information is unknown and data privacy must be preserved, leading to two major challenges. First, views on different clients often have feature heterogeneity, and mining their complementary cluster information is not trivial. Second, the storage and usage of data from multiple clients in a distributed environment can lead to incompleteness of multi-view data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel federated deep multi-view clustering method that can mine complementary cluster structures from multiple clients, while dealing with data incompleteness and privacy concerns. Specifically, in the server environment, we propose sample alignment and data extension techniques to explore the complementary cluster structures of multiple views. The server then distributes global prototypes and global pseudo-labels to each client as global self-supervised information. In the client environment, multiple clients use the global self-supervised information and deep autoencoders to learn view-specific cluster assignments and embedded features, which are then uploaded to the server for refining the global self-supervised information. Finally, the results of our extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method exhibits superior performance in addressing the challenges of incomplete multi-view data in distributed environments.
Deep Multi-View Subspace Clustering with Anchor Graph
May 11, 2023



Abstract:Deep multi-view subspace clustering (DMVSC) has recently attracted increasing attention due to its promising performance. However, existing DMVSC methods still have two issues: (1) they mainly focus on using autoencoders to nonlinearly embed the data, while the embedding may be suboptimal for clustering because the clustering objective is rarely considered in autoencoders, and (2) existing methods typically have a quadratic or even cubic complexity, which makes it challenging to deal with large-scale data. To address these issues, in this paper we propose a novel deep multi-view subspace clustering method with anchor graph (DMCAG). To be specific, DMCAG firstly learns the embedded features for each view independently, which are used to obtain the subspace representations. To significantly reduce the complexity, we construct an anchor graph with small size for each view. Then, spectral clustering is performed on an integrated anchor graph to obtain pseudo-labels. To overcome the negative impact caused by suboptimal embedded features, we use pseudo-labels to refine the embedding process to make it more suitable for the clustering task. Pseudo-labels and embedded features are updated alternately. Furthermore, we design a strategy to keep the consistency of the labels based on contrastive learning to enhance the clustering performance. Empirical studies on real-world datasets show that our method achieves superior clustering performance over other state-of-the-art methods.
Self-Paced Neutral Expression-Disentangled Learning for Facial Expression Recognition
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:The accuracy of facial expression recognition is typically affected by the following factors: high similarities across different expressions, disturbing factors, and micro-facial movement of rapid and subtle changes. One potentially viable solution for addressing these barriers is to exploit the neutral information concealed in neutral expression images. To this end, in this paper we propose a self-Paced Neutral Expression-Disentangled Learning (SPNDL) model. SPNDL disentangles neutral information from facial expressions, making it easier to extract key and deviation features. Specifically, it allows to capture discriminative information among similar expressions and perceive micro-facial movements. In order to better learn these neutral expression-disentangled features (NDFs) and to alleviate the non-convex optimization problem, a self-paced learning (SPL) strategy based on NDFs is proposed in the training stage. SPL learns samples from easy to complex by increasing the number of samples selected into the training process, which enables to effectively suppress the negative impacts introduced by low-quality samples and inconsistently distributed NDFs. Experiments on three popular databases (i.e., CK+, Oulu-CASIA, and RAF-DB) show the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Deep Learning and Medical Imaging for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 13, 2023
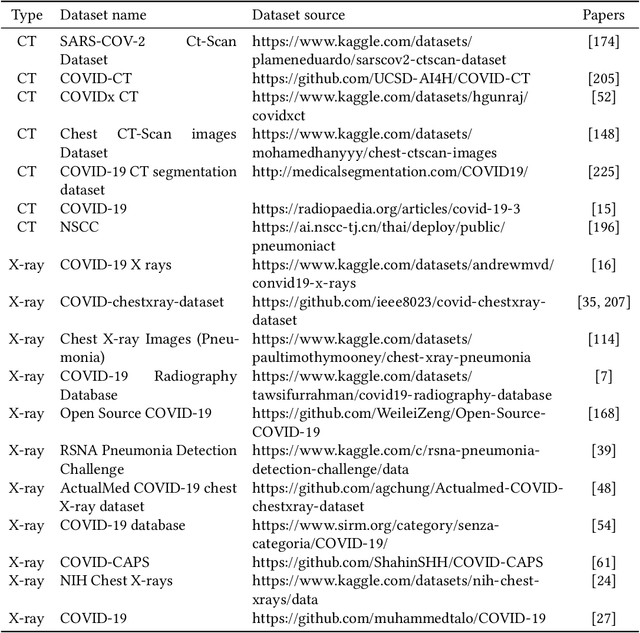


Abstract:COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease 2019) has been quickly spreading since its outbreak, impacting financial markets and healthcare systems globally. Countries all around the world have adopted a number of extraordinary steps to restrict the spreading virus, where early COVID-19 diagnosis is essential. Medical images such as X-ray images and Computed Tomography scans are becoming one of the main diagnostic tools to combat COVID-19 with the aid of deep learning-based systems. In this survey, we investigate the main contributions of deep learning applications using medical images in fighting against COVID-19 from the aspects of image classification, lesion localization, and severity quantification, and review different deep learning architectures and some image preprocessing techniques for achieving a preciser diagnosis. We also provide a summary of the X-ray and CT image datasets used in various studies for COVID-19 detection. The key difficulties and potential applications of deep learning in fighting against COVID-19 are finally discussed. This work summarizes the latest methods of deep learning using medical images to diagnose COVID-19, highlighting the challenges and inspiring more studies to keep utilizing the advantages of deep learning to combat COVID-19.
Variational Graph Generator for Multi-View Graph Clustering
Oct 13, 2022



Abstract:Multi-view graph clustering (MGC) methods are increasingly being studied due to the rising of multi-view data with graph structural information. The critical point of MGC is to better utilize the view-specific and view-common information in features and graphs of multiple views. However, existing works have an inherent limitation that they are unable to concurrently utilize the consensus graph information across multiple graphs and the view-specific feature information. To address this issue, we propose Variational Graph Generator for Multi-View Graph Clustering (VGMGC). Specifically, a novel variational graph generator is proposed to infer a reliable variational consensus graph based on a priori assumption over multiple graphs. Then a simple yet effective graph encoder in conjunction with the multi-view clustering objective is presented to learn the desired graph embeddings for clustering, which embeds the consensus and view-specific graphs together with features. Finally, theoretical results illustrate the rationality of VGMGC by analyzing the uncertainty of the inferred consensus graph with information bottleneck principle. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our VGMGC over SOTAs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge