Hongmin Wang
FEANet: Feature-Enhanced Attention Network for RGB-Thermal Real-time Semantic Segmentation
Oct 18, 2021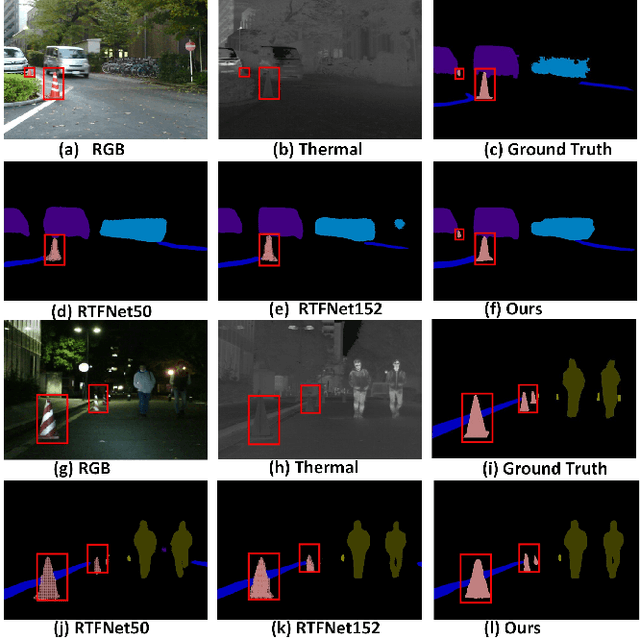
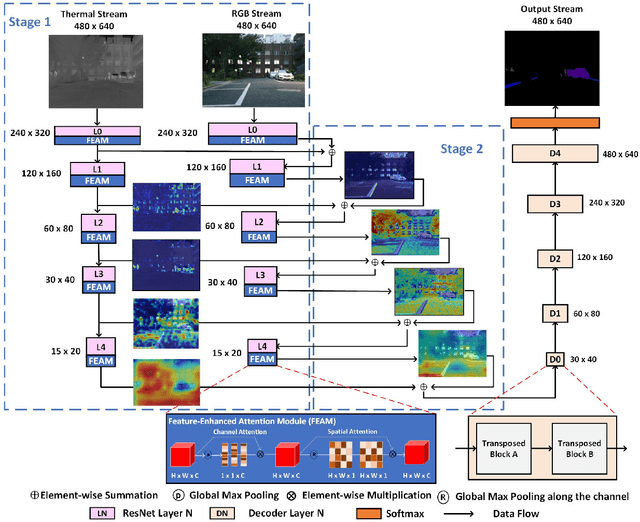
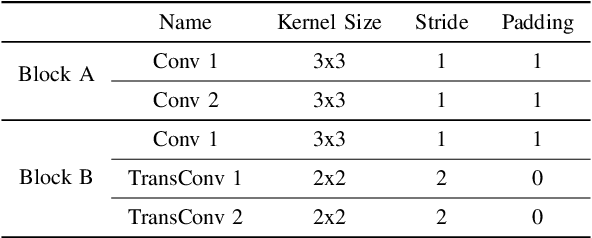
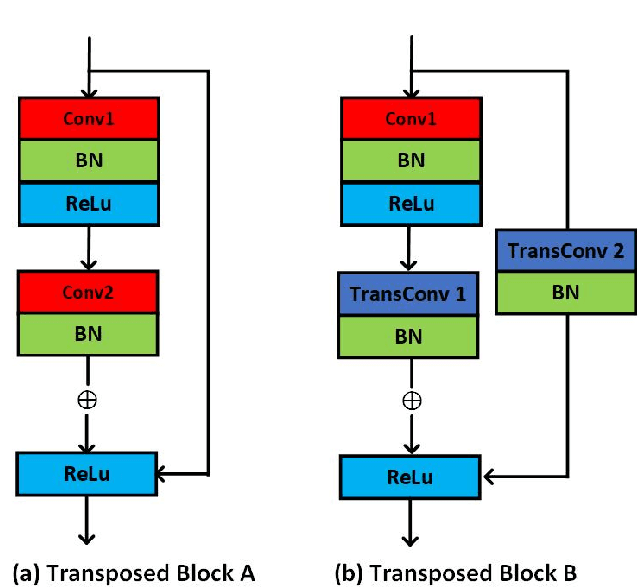
Abstract:The RGB-Thermal (RGB-T) information for semantic segmentation has been extensively explored in recent years. However, most existing RGB-T semantic segmentation usually compromises spatial resolution to achieve real-time inference speed, which leads to poor performance. To better extract detail spatial information, we propose a two-stage Feature-Enhanced Attention Network (FEANet) for the RGB-T semantic segmentation task. Specifically, we introduce a Feature-Enhanced Attention Module (FEAM) to excavate and enhance multi-level features from both the channel and spatial views. Benefited from the proposed FEAM module, our FEANet can preserve the spatial information and shift more attention to high-resolution features from the fused RGB-T images. Extensive experiments on the urban scene dataset demonstrate that our FEANet outperforms other state-of-the-art (SOTA) RGB-T methods in terms of objective metrics and subjective visual comparison (+2.6% in global mAcc and +0.8% in global mIoU). For the 480 x 640 RGB-T test images, our FEANet can run with a real-time speed on an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti card.
Revisiting Challenges in Data-to-Text Generation with Fact Grounding
Jan 12, 2020
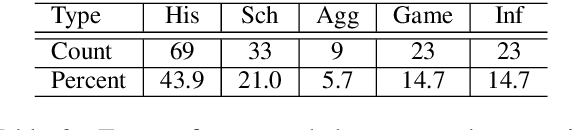
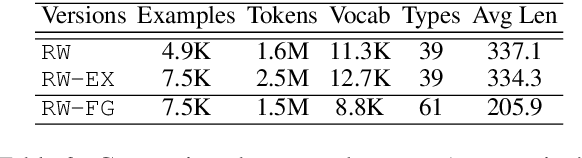
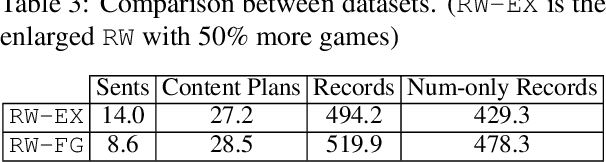
Abstract:Data-to-text generation models face challenges in ensuring data fidelity by referring to the correct input source. To inspire studies in this area, Wiseman et al. (2017) introduced the RotoWire corpus on generating NBA game summaries from the box- and line-score tables. However, limited attempts have been made in this direction and the challenges remain. We observe a prominent bottleneck in the corpus where only about 60% of the summary contents can be grounded to the boxscore records. Such information deficiency tends to misguide a conditioned language model to produce unconditioned random facts and thus leads to factual hallucinations. In this work, we restore the information balance and revamp this task to focus on fact-grounded data-to-text generation. We introduce a purified and larger-scale dataset, RotoWire-FG (Fact-Grounding), with 50% more data from the year 2017-19 and enriched input tables, hoping to attract more research focuses in this direction. Moreover, we achieve improved data fidelity over the state-of-the-art models by integrating a new form of table reconstruction as an auxiliary task to boost the generation quality.
TabFact: A Large-scale Dataset for Table-based Fact Verification
Oct 08, 2019



Abstract:The problem of verifying whether a textual hypothesis holds based on the given evidence, also known as fact verification, plays an important role in the study of natural language understanding and semantic representation. However, existing studies are mainly restricted to dealing with unstructured evidence (e.g., natural language sentences and documents, news, etc), while verification under structured evidence, such as tables, graphs, and databases, remains unexplored. This paper specifically aims to study the fact verification given semi-structured data as evidence. To this end, we construct a large-scale dataset called TabFact with 16k Wikipedia tables as the evidence for 118k human-annotated natural language statements, which are labeled as either ENTAILED or REFUTED. TabFact is challenging since it involves both soft linguistic reasoning and hard symbolic reasoning. To address these reasoning challenges, we design two different models: Table-BERT and Latent Program Algorithm (LPA). Table-BERT leverages the state-of-the-art pre-trained language model to encode the linearized tables and statements into continuous vectors for verification. LPA parses statements into LISP-like programs and executes them against the tables to obtain the returned binary value for verification. Both methods achieve similar accuracy but still lag far behind human performance. We also perform a comprehensive analysis to demonstrate great future opportunities. The data and code of the dataset are provided in \url{https://github.com/wenhuchen/Table-Fact-Checking}.
Look Before You Leap: Bridging Model-Free and Model-Based Reinforcement Learning for Planned-Ahead Vision-and-Language Navigation
Jul 26, 2018
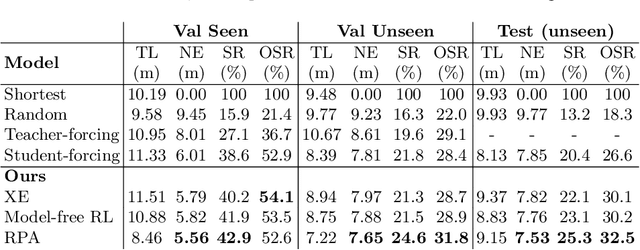
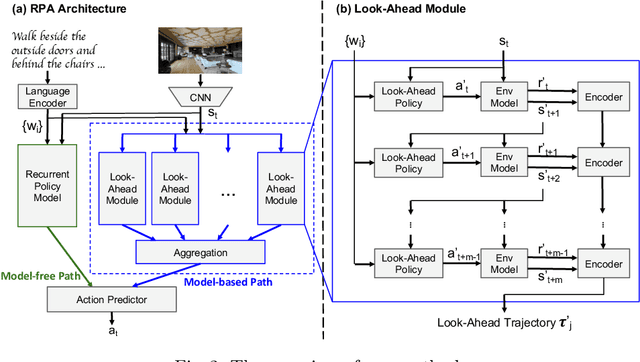
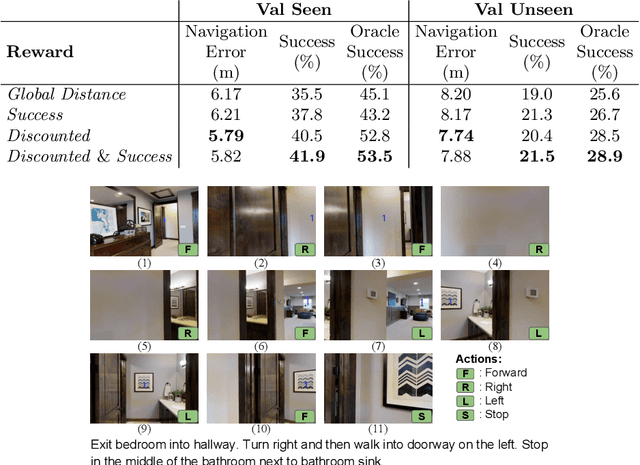
Abstract:Existing research studies on vision and language grounding for robot navigation focus on improving model-free deep reinforcement learning (DRL) models in synthetic environments. However, model-free DRL models do not consider the dynamics in the real-world environments, and they often fail to generalize to new scenes. In this paper, we take a radical approach to bridge the gap between synthetic studies and real-world practices---We propose a novel, planned-ahead hybrid reinforcement learning model that combines model-free and model-based reinforcement learning to solve a real-world vision-language navigation task. Our look-ahead module tightly integrates a look-ahead policy model with an environment model that predicts the next state and the reward. Experimental results suggest that our proposed method significantly outperforms the baselines and achieves the best on the real-world Room-to-Room dataset. Moreover, our scalable method is more generalizable when transferring to unseen environments.
A Rank-Based Similarity Metric for Word Embeddings
May 04, 2018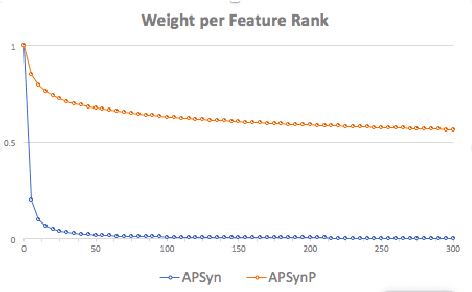
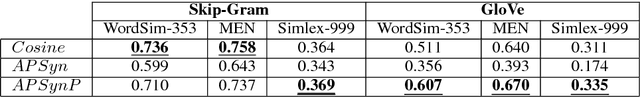
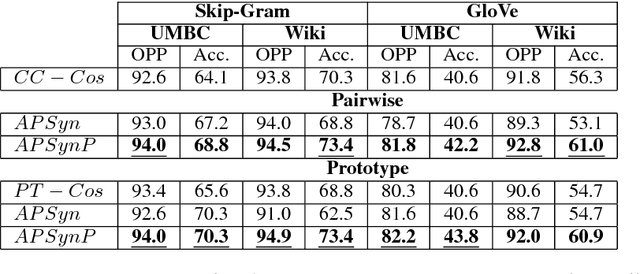
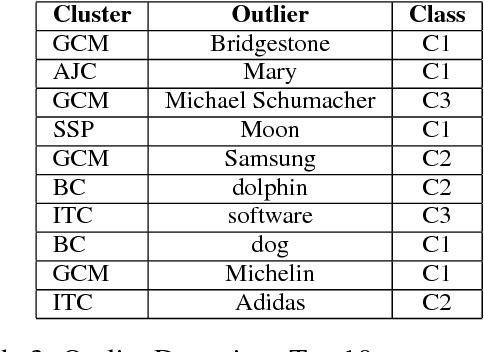
Abstract:Word Embeddings have recently imposed themselves as a standard for representing word meaning in NLP. Semantic similarity between word pairs has become the most common evaluation benchmark for these representations, with vector cosine being typically used as the only similarity metric. In this paper, we report experiments with a rank-based metric for WE, which performs comparably to vector cosine in similarity estimation and outperforms it in the recently-introduced and challenging task of outlier detection, thus suggesting that rank-based measures can improve clustering quality.
Universal Dependencies Parsing for Colloquial Singaporean English
May 18, 2017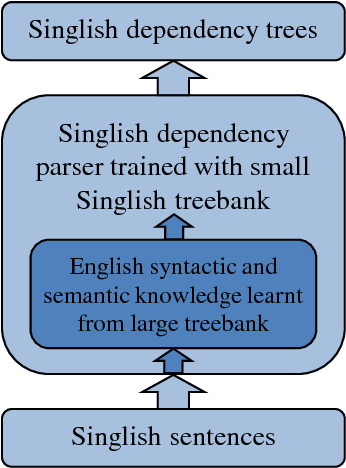
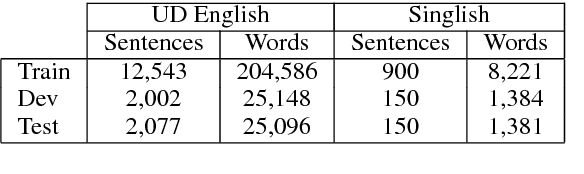
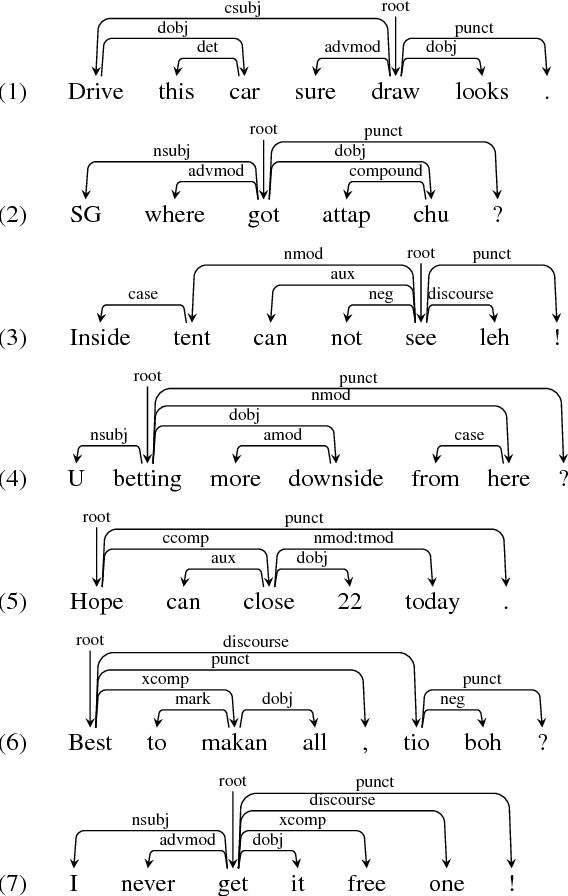

Abstract:Singlish can be interesting to the ACL community both linguistically as a major creole based on English, and computationally for information extraction and sentiment analysis of regional social media. We investigate dependency parsing of Singlish by constructing a dependency treebank under the Universal Dependencies scheme, and then training a neural network model by integrating English syntactic knowledge into a state-of-the-art parser trained on the Singlish treebank. Results show that English knowledge can lead to 25% relative error reduction, resulting in a parser of 84.47% accuracies. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to use neural stacking to improve cross-lingual dependency parsing on low-resource languages. We make both our annotation and parser available for further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge