Haoyu Huang
AutoSchemaKG: Autonomous Knowledge Graph Construction through Dynamic Schema Induction from Web-Scale Corpora
May 29, 2025
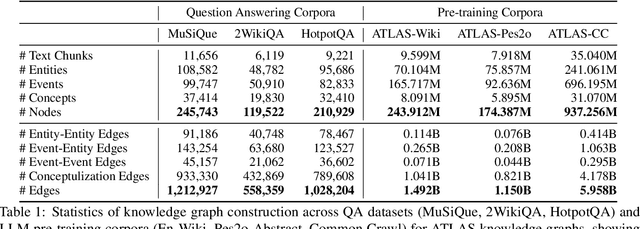

Abstract:We present AutoSchemaKG, a framework for fully autonomous knowledge graph construction that eliminates the need for predefined schemas. Our system leverages large language models to simultaneously extract knowledge triples and induce comprehensive schemas directly from text, modeling both entities and events while employing conceptualization to organize instances into semantic categories. Processing over 50 million documents, we construct ATLAS (Automated Triple Linking And Schema induction), a family of knowledge graphs with 900+ million nodes and 5.9 billion edges. This approach outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on multi-hop QA tasks and enhances LLM factuality. Notably, our schema induction achieves 95\% semantic alignment with human-crafted schemas with zero manual intervention, demonstrating that billion-scale knowledge graphs with dynamically induced schemas can effectively complement parametric knowledge in large language models.
Prompt as Knowledge Bank: Boost Vision-language model via Structural Representation for zero-shot medical detection
Feb 22, 2025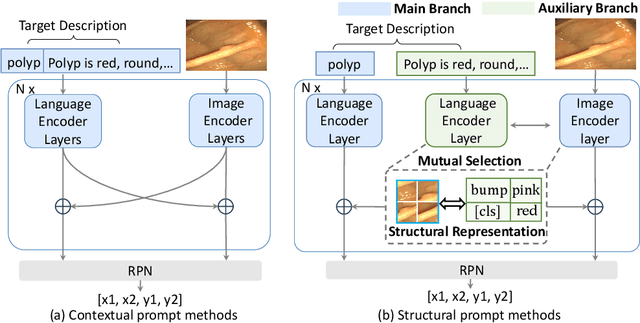

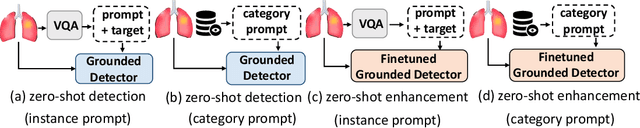

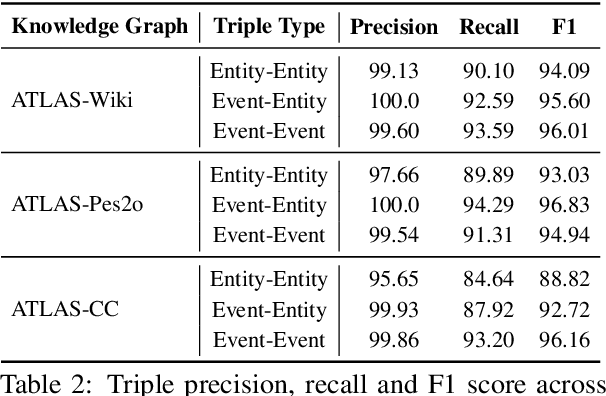
Abstract:Zero-shot medical detection can further improve detection performance without relying on annotated medical images even upon the fine-tuned model, showing great clinical value. Recent studies leverage grounded vision-language models (GLIP) to achieve this by using detailed disease descriptions as prompts for the target disease name during the inference phase. However, these methods typically treat prompts as equivalent context to the target name, making it difficult to assign specific disease knowledge based on visual information, leading to a coarse alignment between images and target descriptions. In this paper, we propose StructuralGLIP, which introduces an auxiliary branch to encode prompts into a latent knowledge bank layer-by-layer, enabling more context-aware and fine-grained alignment. Specifically, in each layer, we select highly similar features from both the image representation and the knowledge bank, forming structural representations that capture nuanced relationships between image patches and target descriptions. These features are then fused across modalities to further enhance detection performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that StructuralGLIP achieves a +4.1\% AP improvement over prior state-of-the-art methods across seven zero-shot medical detection benchmarks, and consistently improves fine-tuned models by +3.2\% AP on endoscopy image datasets.
Can LLMs be Good Graph Judger for Knowledge Graph Construction?
Nov 26, 2024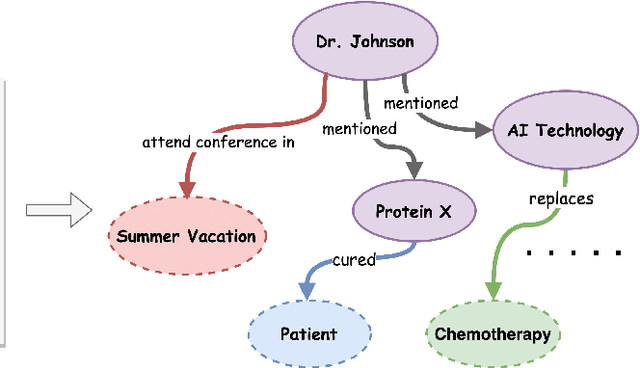
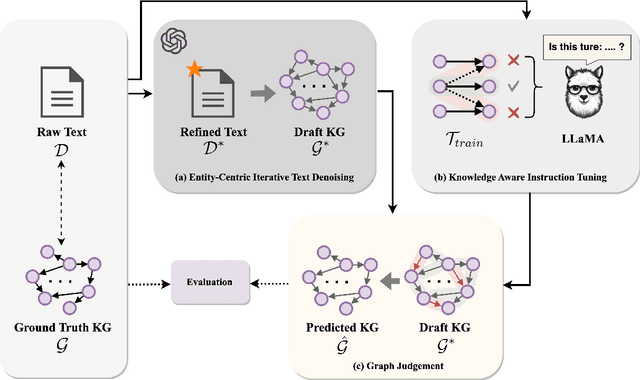
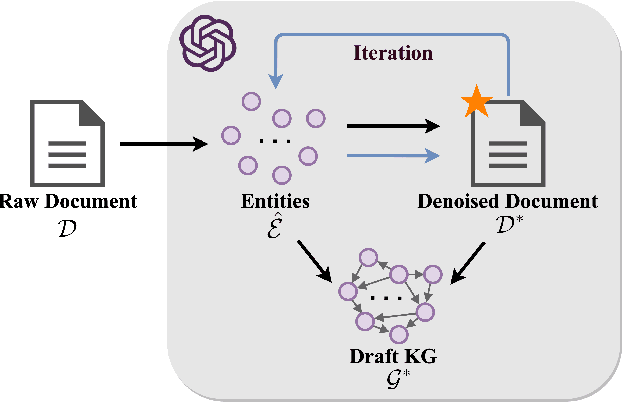
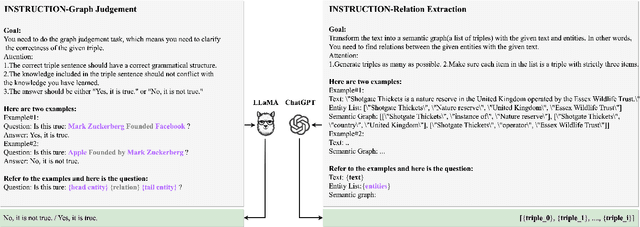
Abstract:In real-world scenarios, most of the data obtained from information retrieval (IR) system is unstructured. Converting natural language sentences into structured Knowledge Graphs (KGs) remains a critical challenge. The quality of constructed KGs may also impact the performance of some KG-dependent domains like GraphRAG systems and recommendation systems. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in addressing a wide range of natural language processing tasks. However, there are still challenges when utilizing LLMs to address the task of generating structured KGs. And we have identified three limitations with respect to existing KG construction methods. (1)There is a large amount of information and excessive noise in real-world documents, which could result in extracting messy information. (2)Native LLMs struggle to effectively extract accuracy knowledge from some domain-specific documents. (3)Hallucinations phenomenon cannot be overlooked when utilizing LLMs directly as an unsupervised method for constructing KGs. In this paper, we propose GraphJudger, a knowledge graph construction framework to address the aforementioned challenges. We introduce three innovative modules in our method, which are entity-centric iterative text denoising, knowledge aware instruction tuning and graph judgement, respectively. We seek to utilize the capacity of LLMs to function as a graph judger, a capability superior to their role only as a predictor for KG construction problems. Experiments conducted on two general text-graph pair datasets and one domain-specific text-graph pair dataset show superior performances compared to baseline methods. The code of our proposed method is available at https://github.com/hhy-huang/GraphJudger.
VersusDebias: Universal Zero-Shot Debiasing for Text-to-Image Models via SLM-Based Prompt Engineering and Generative Adversary
Jul 28, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid development of Text-to-Image models, biases in human image generation against demographic groups social attract more and more concerns. Existing methods are designed based on certain models with fixed prompts, unable to accommodate the trend of high-speed updating of Text-to-Image (T2I) models and variable prompts in practical scenes. Additionally, they fail to consider the possibility of hallucinations, leading to deviations between expected and actual results. To address this issue, we introduce VersusDebias, a novel and universal debiasing framework for biases in T2I models, consisting of one generative adversarial mechanism (GAM) and one debiasing generation mechanism using a small language model (SLM). The self-adaptive GAM generates specialized attribute arrays for each prompts for diminishing the influence of hallucinations from T2I models. The SLM uses prompt engineering to generate debiased prompts for the T2I model, providing zero-shot debiasing ability and custom optimization for different models. Extensive experiments demonstrate VersusDebias's capability to rectify biases on arbitrary models across multiple protected attributes simultaneously, including gender, race, and age. Furthermore, VersusDebias outperforms existing methods in both zero-shot and few-shot situations, illustrating its extraordinary utility. Our work is openly accessible to the research community to ensure the reproducibility.
BIGbench: A Unified Benchmark for Social Bias in Text-to-Image Generative Models Based on Multi-modal LLM
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-Image (T2I) generative models are becoming more crucial in terms of their ability to generate complex and high-quality images, which also raises concerns about the social biases in their outputs, especially in human generation. Sociological research has established systematic classifications of bias; however, existing research of T2I models often conflates different types of bias, hindering the progress of these methods. In this paper, we introduce BIGbench, a unified benchmark for Biases of Image Generation with a well-designed dataset. In contrast to existing benchmarks, BIGbench classifies and evaluates complex biases into four dimensions: manifestation of bias, visibility of bias, acquired attributes, and protected attributes. Additionally, BIGbench applies advanced multi-modal large language models (MLLM), achieving fully automated evaluation while maintaining high accuracy. We apply BIGbench to evaluate eight recent general T2I models and three debiased methods. We also conduct human evaluation, whose results demonstrated the effectiveness of BIGbench in aligning images and identifying various biases. Besides, our study also revealed new research directions about biases, including the side-effect of irrelevant protected attributes and distillation. Our dataset and benchmark is openly accessible to the research community to ensure the reproducibility.
General Automatic Solution Generation of Social Problems
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Given the escalating intricacy and multifaceted nature of contemporary social systems, manually generating solutions to address pertinent social issues has become a formidable task. In response to this challenge, the rapid development of artificial intelligence has spurred the exploration of computational methodologies aimed at automatically generating solutions. However, current methods for auto-generation of solutions mainly concentrate on local social regulations that pertain to specific scenarios. Here, we report an automatic social operating system (ASOS) designed for general social solution generation, which is built upon agent-based models, enabling both global and local analyses and regulations of social problems across spatial and temporal dimensions. ASOS adopts a hypergraph with extensible social semantics for a comprehensive and structured representation of social dynamics. It also incorporates a generalized protocol for standardized hypergraph operations and a symbolic hybrid framework that delivers interpretable solutions, yielding a balance between regulatory efficacy and function viability. To demonstrate the effectiveness of ASOS, we apply it to the domain of averting extreme events within international oil futures markets. By generating a new trading role supplemented by new mechanisms, ASOS can adeptly discern precarious market conditions and make front-running interventions for non-profit purposes. This study demonstrates that ASOS provides an efficient and systematic approach for generating solutions for enhancing our society.
Kepler: Robust Learning for Faster Parametric Query Optimization
Jun 11, 2023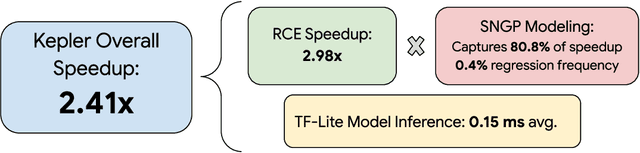

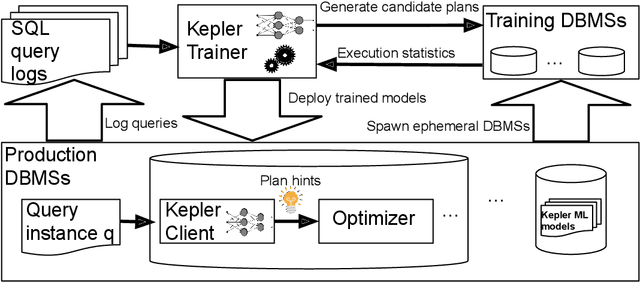
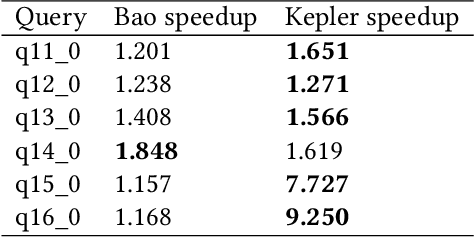
Abstract:Most existing parametric query optimization (PQO) techniques rely on traditional query optimizer cost models, which are often inaccurate and result in suboptimal query performance. We propose Kepler, an end-to-end learning-based approach to PQO that demonstrates significant speedups in query latency over a traditional query optimizer. Central to our method is Row Count Evolution (RCE), a novel plan generation algorithm based on perturbations in the sub-plan cardinality space. While previous approaches require accurate cost models, we bypass this requirement by evaluating candidate plans via actual execution data and training an ML model to predict the fastest plan given parameter binding values. Our models leverage recent advances in neural network uncertainty in order to robustly predict faster plans while avoiding regressions in query performance. Experimentally, we show that Kepler achieves significant improvements in query runtime on multiple datasets on PostgreSQL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge