Guangcong Zheng
Dynamic-DINO: Fine-Grained Mixture of Experts Tuning for Real-time Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Jul 23, 2025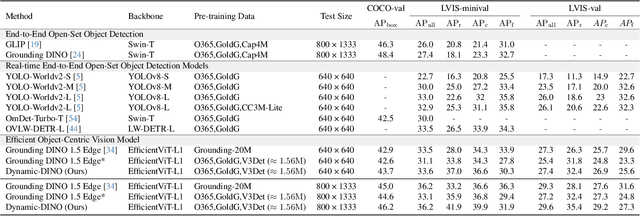
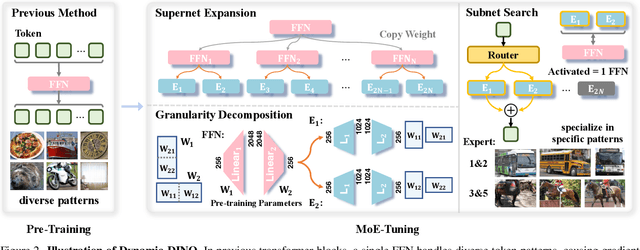

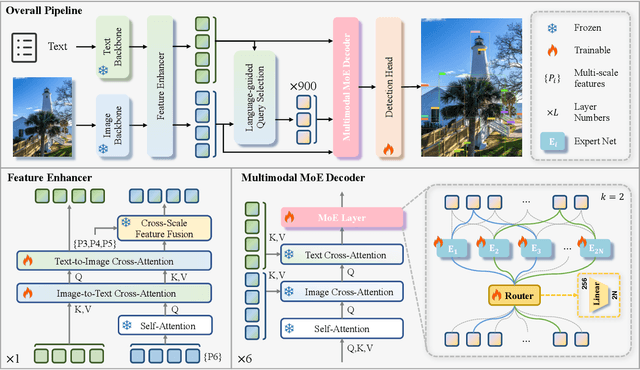
Abstract:The Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture has excelled in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), yet its potential in real-time open-vocabulary object detectors, which also leverage large-scale vision-language datasets but smaller models, remains unexplored. This work investigates this domain, revealing intriguing insights. In the shallow layers, experts tend to cooperate with diverse peers to expand the search space. While in the deeper layers, fixed collaborative structures emerge, where each expert maintains 2-3 fixed partners and distinct expert combinations are specialized in processing specific patterns. Concretely, we propose Dynamic-DINO, which extends Grounding DINO 1.5 Edge from a dense model to a dynamic inference framework via an efficient MoE-Tuning strategy. Additionally, we design a granularity decomposition mechanism to decompose the Feed-Forward Network (FFN) of base model into multiple smaller expert networks, expanding the subnet search space. To prevent performance degradation at the start of fine-tuning, we further propose a pre-trained weight allocation strategy for the experts, coupled with a specific router initialization. During inference, only the input-relevant experts are activated to form a compact subnet. Experiments show that, pretrained with merely 1.56M open-source data, Dynamic-DINO outperforms Grounding DINO 1.5 Edge, pretrained on the private Grounding20M dataset.
Frame-Level Captions for Long Video Generation with Complex Multi Scenes
May 27, 2025Abstract:Generating long videos that can show complex stories, like movie scenes from scripts, has great promise and offers much more than short clips. However, current methods that use autoregression with diffusion models often struggle because their step-by-step process naturally leads to a serious error accumulation (drift). Also, many existing ways to make long videos focus on single, continuous scenes, making them less useful for stories with many events and changes. This paper introduces a new approach to solve these problems. First, we propose a novel way to annotate datasets at the frame-level, providing detailed text guidance needed for making complex, multi-scene long videos. This detailed guidance works with a Frame-Level Attention Mechanism to make sure text and video match precisely. A key feature is that each part (frame) within these windows can be guided by its own distinct text prompt. Our training uses Diffusion Forcing to provide the model with the ability to handle time flexibly. We tested our approach on difficult VBench 2.0 benchmarks ("Complex Plots" and "Complex Landscapes") based on the WanX2.1-T2V-1.3B model. The results show our method is better at following instructions in complex, changing scenes and creates high-quality long videos. We plan to share our dataset annotation methods and trained models with the research community. Project page: https://zgctroy.github.io/frame-level-captions .
RealCam-Vid: High-resolution Video Dataset with Dynamic Scenes and Metric-scale Camera Movements
Apr 11, 2025
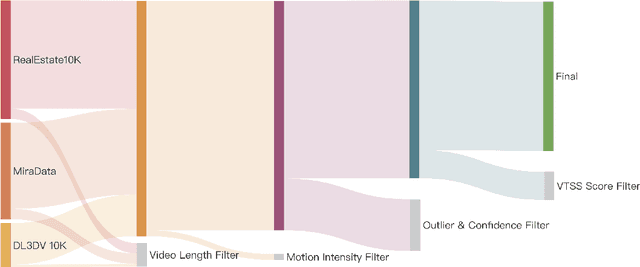
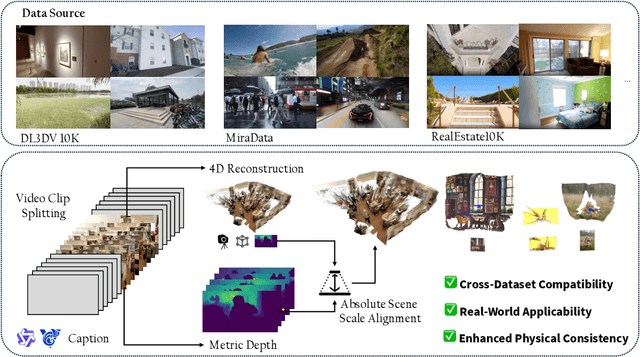
Abstract:Recent advances in camera-controllable video generation have been constrained by the reliance on static-scene datasets with relative-scale camera annotations, such as RealEstate10K. While these datasets enable basic viewpoint control, they fail to capture dynamic scene interactions and lack metric-scale geometric consistency-critical for synthesizing realistic object motions and precise camera trajectories in complex environments. To bridge this gap, we introduce the first fully open-source, high-resolution dynamic-scene dataset with metric-scale camera annotations in https://github.com/ZGCTroy/RealCam-Vid.
Energy-Guided Optimization for Personalized Image Editing with Pretrained Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of pretrained text-driven diffusion models has significantly enriched applications in image generation and editing. However, as the demand for personalized content editing increases, new challenges emerge especially when dealing with arbitrary objects and complex scenes. Existing methods usually mistakes mask as the object shape prior, which struggle to achieve a seamless integration result. The mostly used inversion noise initialization also hinders the identity consistency towards the target object. To address these challenges, we propose a novel training-free framework that formulates personalized content editing as the optimization of edited images in the latent space, using diffusion models as the energy function guidance conditioned by reference text-image pairs. A coarse-to-fine strategy is proposed that employs text energy guidance at the early stage to achieve a natural transition toward the target class and uses point-to-point feature-level image energy guidance to perform fine-grained appearance alignment with the target object. Additionally, we introduce the latent space content composition to enhance overall identity consistency with the target. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method excels in object replacement even with a large domain gap, highlighting its potential for high-quality, personalized image editing.
VideoMaker: Zero-shot Customized Video Generation with the Inherent Force of Video Diffusion Models
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot customized video generation has gained significant attention due to its substantial application potential. Existing methods rely on additional models to extract and inject reference subject features, assuming that the Video Diffusion Model (VDM) alone is insufficient for zero-shot customized video generation. However, these methods often struggle to maintain consistent subject appearance due to suboptimal feature extraction and injection techniques. In this paper, we reveal that VDM inherently possesses the force to extract and inject subject features. Departing from previous heuristic approaches, we introduce a novel framework that leverages VDM's inherent force to enable high-quality zero-shot customized video generation. Specifically, for feature extraction, we directly input reference images into VDM and use its intrinsic feature extraction process, which not only provides fine-grained features but also significantly aligns with VDM's pre-trained knowledge. For feature injection, we devise an innovative bidirectional interaction between subject features and generated content through spatial self-attention within VDM, ensuring that VDM has better subject fidelity while maintaining the diversity of the generated video.Experiments on both customized human and object video generation validate the effectiveness of our framework.
CamI2V: Camera-Controlled Image-to-Video Diffusion Model
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Recently, camera pose, as a user-friendly and physics-related condition, has been introduced into text-to-video diffusion model for camera control. However, existing methods simply inject camera conditions through a side input. These approaches neglect the inherent physical knowledge of camera pose, resulting in imprecise camera control, inconsistencies, and also poor interpretability. In this paper, we emphasize the necessity of integrating explicit physical constraints into model design. Epipolar attention is proposed for modeling all cross-frame relationships from a novel perspective of noised condition. This ensures that features are aggregated from corresponding epipolar lines in all noised frames, overcoming the limitations of current attention mechanisms in tracking displaced features across frames, especially when features move significantly with the camera and become obscured by noise. Additionally, we introduce register tokens to handle cases without intersections between frames, commonly caused by rapid camera movements, dynamic objects, or occlusions. To support image-to-video, we propose the multiple guidance scale to allow for precise control for image, text, and camera, respectively. Furthermore, we establish a more robust and reproducible evaluation pipeline to solve the inaccuracy and instability of existing camera control measurement. We achieve a 25.5\% improvement in camera controllability on RealEstate10K while maintaining strong generalization to out-of-domain images. Only 24GB and 12GB are required for training and inference, respectively. We plan to release checkpoints, along with training and evaluation codes. Dynamic videos are best viewed at \url{https://zgctroy.github.io/CamI2V}.
CustomCrafter: Customized Video Generation with Preserving Motion and Concept Composition Abilities
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:Customized video generation aims to generate high-quality videos guided by text prompts and subject's reference images. However, since it is only trained on static images, the fine-tuning process of subject learning disrupts abilities of video diffusion models (VDMs) to combine concepts and generate motions. To restore these abilities, some methods use additional video similar to the prompt to fine-tune or guide the model. This requires frequent changes of guiding videos and even re-tuning of the model when generating different motions, which is very inconvenient for users. In this paper, we propose CustomCrafter, a novel framework that preserves the model's motion generation and conceptual combination abilities without additional video and fine-tuning to recovery. For preserving conceptual combination ability, we design a plug-and-play module to update few parameters in VDMs, enhancing the model's ability to capture the appearance details and the ability of concept combinations for new subjects. For motion generation, we observed that VDMs tend to restore the motion of video in the early stage of denoising, while focusing on the recovery of subject details in the later stage. Therefore, we propose Dynamic Weighted Video Sampling Strategy. Using the pluggability of our subject learning modules, we reduce the impact of this module on motion generation in the early stage of denoising, preserving the ability to generate motion of VDMs. In the later stage of denoising, we restore this module to repair the appearance details of the specified subject, thereby ensuring the fidelity of the subject's appearance. Experimental results show that our method has a significant improvement compared to previous methods.
BEVSpread: Spread Voxel Pooling for Bird's-Eye-View Representation in Vision-based Roadside 3D Object Detection
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Vision-based roadside 3D object detection has attracted rising attention in autonomous driving domain, since it encompasses inherent advantages in reducing blind spots and expanding perception range. While previous work mainly focuses on accurately estimating depth or height for 2D-to-3D mapping, ignoring the position approximation error in the voxel pooling process. Inspired by this insight, we propose a novel voxel pooling strategy to reduce such error, dubbed BEVSpread. Specifically, instead of bringing the image features contained in a frustum point to a single BEV grid, BEVSpread considers each frustum point as a source and spreads the image features to the surrounding BEV grids with adaptive weights. To achieve superior propagation performance, a specific weight function is designed to dynamically control the decay speed of the weights according to distance and depth. Aided by customized CUDA parallel acceleration, BEVSpread achieves comparable inference time as the original voxel pooling. Extensive experiments on two large-scale roadside benchmarks demonstrate that, as a plug-in, BEVSpread can significantly improve the performance of existing frustum-based BEV methods by a large margin of (1.12, 5.26, 3.01) AP in vehicle, pedestrian and cyclist.
LayoutDiffusion: Controllable Diffusion Model for Layout-to-image Generation
Mar 30, 2023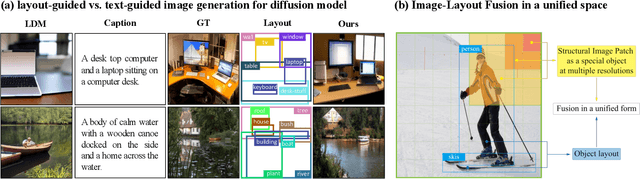
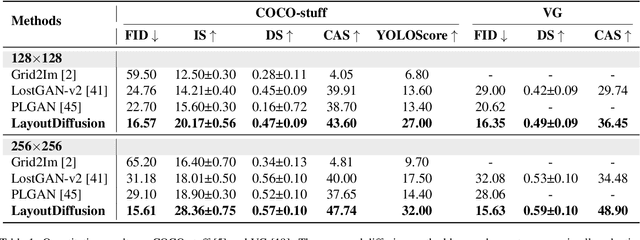
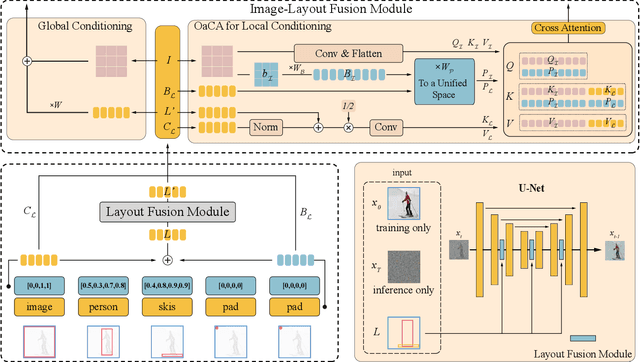

Abstract:Recently, diffusion models have achieved great success in image synthesis. However, when it comes to the layout-to-image generation where an image often has a complex scene of multiple objects, how to make strong control over both the global layout map and each detailed object remains a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a diffusion model named LayoutDiffusion that can obtain higher generation quality and greater controllability than the previous works. To overcome the difficult multimodal fusion of image and layout, we propose to construct a structural image patch with region information and transform the patched image into a special layout to fuse with the normal layout in a unified form. Moreover, Layout Fusion Module (LFM) and Object-aware Cross Attention (OaCA) are proposed to model the relationship among multiple objects and designed to be object-aware and position-sensitive, allowing for precisely controlling the spatial related information. Extensive experiments show that our LayoutDiffusion outperforms the previous SOTA methods on FID, CAS by relatively 46.35%, 26.70% on COCO-stuff and 44.29%, 41.82% on VG. Code is available at https://github.com/ZGCTroy/LayoutDiffusion.
Entropy-driven Sampling and Training Scheme for Conditional Diffusion Generation
Jun 27, 2022



Abstract:Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) is able to make flexible conditional image generation from prior noise to real data, by introducing an independent noise-aware classifier to provide conditional gradient guidance at each time step of denoising process. However, due to the ability of classifier to easily discriminate an incompletely generated image only with high-level structure, the gradient, which is a kind of class information guidance, tends to vanish early, leading to the collapse from conditional generation process into the unconditional process. To address this problem, we propose two simple but effective approaches from two perspectives. For sampling procedure, we introduce the entropy of predicted distribution as the measure of guidance vanishing level and propose an entropy-aware scaling method to adaptively recover the conditional semantic guidance. For training stage, we propose the entropy-aware optimization objectives to alleviate the overconfident prediction for noisy data.On ImageNet1000 256x256, with our proposed sampling scheme and trained classifier, the pretrained conditional and unconditional DDPM model can achieve 10.89% (4.59 to 4.09) and 43.5% (12 to 6.78) FID improvement respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge