Xianpan Zhou
Tiger200K: Manually Curated High Visual Quality Video Dataset from UGC Platform
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:The recent surge in open-source text-to-video generation models has significantly energized the research community, yet their dependence on proprietary training datasets remains a key constraint. While existing open datasets like Koala-36M employ algorithmic filtering of web-scraped videos from early platforms, they still lack the quality required for fine-tuning advanced video generation models. We present Tiger200K, a manually curated high visual quality video dataset sourced from User-Generated Content (UGC) platforms. By prioritizing visual fidelity and aesthetic quality, Tiger200K underscores the critical role of human expertise in data curation, and providing high-quality, temporally consistent video-text pairs for fine-tuning and optimizing video generation architectures through a simple but effective pipeline including shot boundary detection, OCR, border detecting, motion filter and fine bilingual caption. The dataset will undergo ongoing expansion and be released as an open-source initiative to advance research and applications in video generative models. Project page: https://tinytigerpan.github.io/tiger200k/
RealCam-Vid: High-resolution Video Dataset with Dynamic Scenes and Metric-scale Camera Movements
Apr 11, 2025
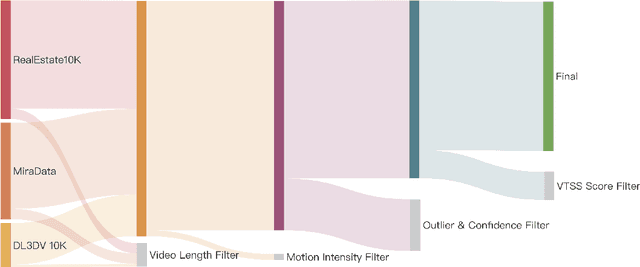
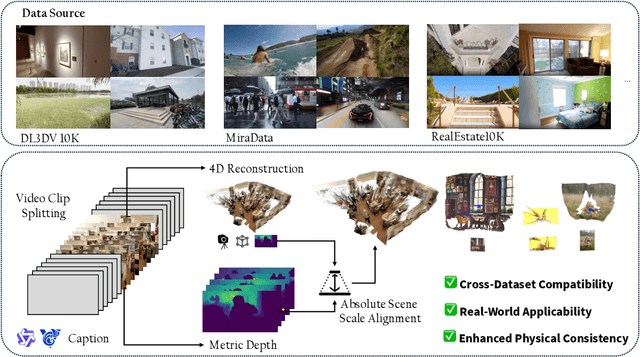
Abstract:Recent advances in camera-controllable video generation have been constrained by the reliance on static-scene datasets with relative-scale camera annotations, such as RealEstate10K. While these datasets enable basic viewpoint control, they fail to capture dynamic scene interactions and lack metric-scale geometric consistency-critical for synthesizing realistic object motions and precise camera trajectories in complex environments. To bridge this gap, we introduce the first fully open-source, high-resolution dynamic-scene dataset with metric-scale camera annotations in https://github.com/ZGCTroy/RealCam-Vid.
IFAdapter: Instance Feature Control for Grounded Text-to-Image Generation
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:While Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models excel at generating visually appealing images of individual instances, they struggle to accurately position and control the features generation of multiple instances. The Layout-to-Image (L2I) task was introduced to address the positioning challenges by incorporating bounding boxes as spatial control signals, but it still falls short in generating precise instance features. In response, we propose the Instance Feature Generation (IFG) task, which aims to ensure both positional accuracy and feature fidelity in generated instances. To address the IFG task, we introduce the Instance Feature Adapter (IFAdapter). The IFAdapter enhances feature depiction by incorporating additional appearance tokens and utilizing an Instance Semantic Map to align instance-level features with spatial locations. The IFAdapter guides the diffusion process as a plug-and-play module, making it adaptable to various community models. For evaluation, we contribute an IFG benchmark and develop a verification pipeline to objectively compare models' abilities to generate instances with accurate positioning and features. Experimental results demonstrate that IFAdapter outperforms other models in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
CustomCrafter: Customized Video Generation with Preserving Motion and Concept Composition Abilities
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:Customized video generation aims to generate high-quality videos guided by text prompts and subject's reference images. However, since it is only trained on static images, the fine-tuning process of subject learning disrupts abilities of video diffusion models (VDMs) to combine concepts and generate motions. To restore these abilities, some methods use additional video similar to the prompt to fine-tune or guide the model. This requires frequent changes of guiding videos and even re-tuning of the model when generating different motions, which is very inconvenient for users. In this paper, we propose CustomCrafter, a novel framework that preserves the model's motion generation and conceptual combination abilities without additional video and fine-tuning to recovery. For preserving conceptual combination ability, we design a plug-and-play module to update few parameters in VDMs, enhancing the model's ability to capture the appearance details and the ability of concept combinations for new subjects. For motion generation, we observed that VDMs tend to restore the motion of video in the early stage of denoising, while focusing on the recovery of subject details in the later stage. Therefore, we propose Dynamic Weighted Video Sampling Strategy. Using the pluggability of our subject learning modules, we reduce the impact of this module on motion generation in the early stage of denoising, preserving the ability to generate motion of VDMs. In the later stage of denoising, we restore this module to repair the appearance details of the specified subject, thereby ensuring the fidelity of the subject's appearance. Experimental results show that our method has a significant improvement compared to previous methods.
Bridging Cross-task Protocol Inconsistency for Distillation in Dense Object Detection
Aug 28, 2023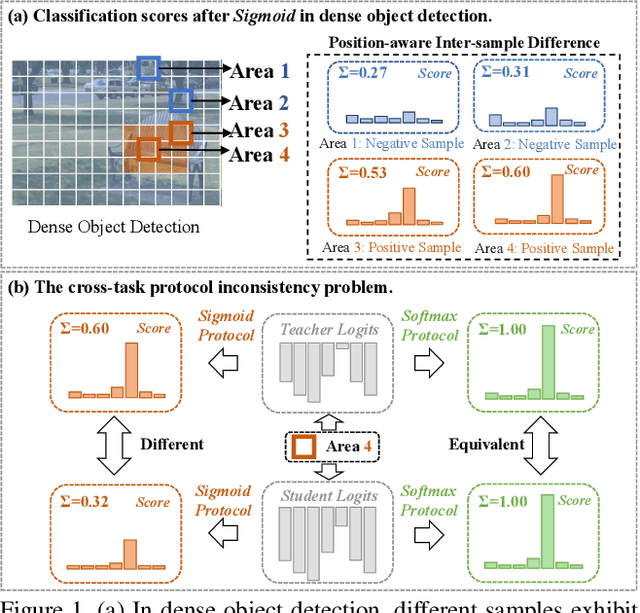
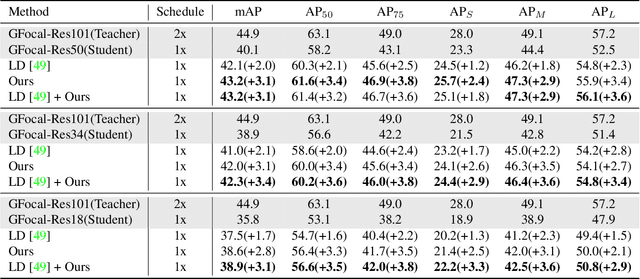
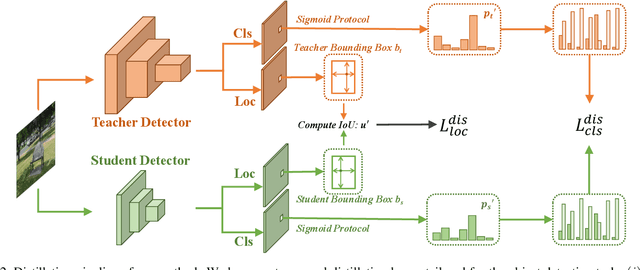
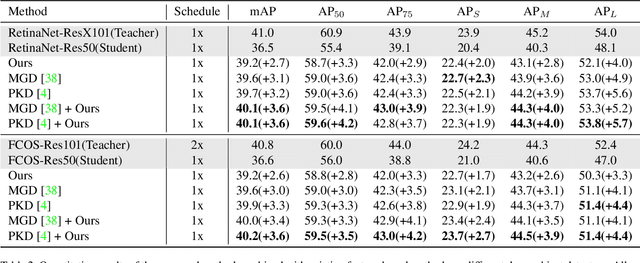
Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) has shown potential for learning compact models in dense object detection. However, the commonly used softmax-based distillation ignores the absolute classification scores for individual categories. Thus, the optimum of the distillation loss does not necessarily lead to the optimal student classification scores for dense object detectors. This cross-task protocol inconsistency is critical, especially for dense object detectors, since the foreground categories are extremely imbalanced. To address the issue of protocol differences between distillation and classification, we propose a novel distillation method with cross-task consistent protocols, tailored for the dense object detection. For classification distillation, we address the cross-task protocol inconsistency problem by formulating the classification logit maps in both teacher and student models as multiple binary-classification maps and applying a binary-classification distillation loss to each map. For localization distillation, we design an IoU-based Localization Distillation Loss that is free from specific network structures and can be compared with existing localization distillation losses. Our proposed method is simple but effective, and experimental results demonstrate its superiority over existing methods. Code is available at https://github.com/TinyTigerPan/BCKD.
LayoutDiffusion: Controllable Diffusion Model for Layout-to-image Generation
Mar 30, 2023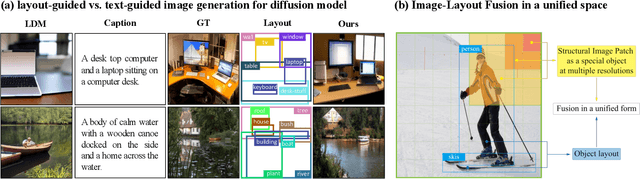
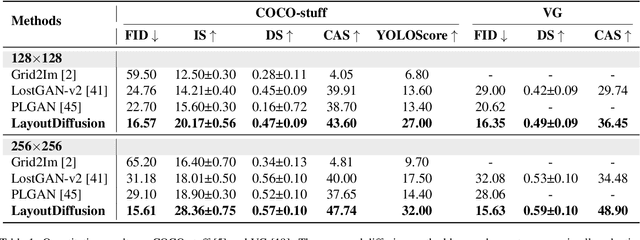
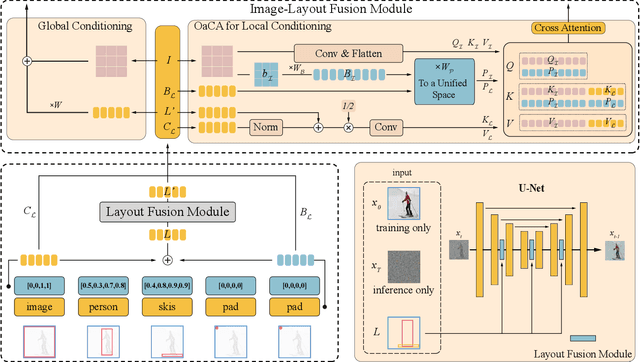

Abstract:Recently, diffusion models have achieved great success in image synthesis. However, when it comes to the layout-to-image generation where an image often has a complex scene of multiple objects, how to make strong control over both the global layout map and each detailed object remains a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a diffusion model named LayoutDiffusion that can obtain higher generation quality and greater controllability than the previous works. To overcome the difficult multimodal fusion of image and layout, we propose to construct a structural image patch with region information and transform the patched image into a special layout to fuse with the normal layout in a unified form. Moreover, Layout Fusion Module (LFM) and Object-aware Cross Attention (OaCA) are proposed to model the relationship among multiple objects and designed to be object-aware and position-sensitive, allowing for precisely controlling the spatial related information. Extensive experiments show that our LayoutDiffusion outperforms the previous SOTA methods on FID, CAS by relatively 46.35%, 26.70% on COCO-stuff and 44.29%, 41.82% on VG. Code is available at https://github.com/ZGCTroy/LayoutDiffusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge