Longrong Yang
UItron: Foundational GUI Agent with Advanced Perception and Planning
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:GUI agent aims to enable automated operations on Mobile/PC devices, which is an important task toward achieving artificial general intelligence. The rapid advancement of VLMs accelerates the development of GUI agents, owing to their powerful capabilities in visual understanding and task planning. However, building a GUI agent remains a challenging task due to the scarcity of operation trajectories, the availability of interactive infrastructure, and the limitation of initial capabilities in foundation models. In this work, we introduce UItron, an open-source foundational model for automatic GUI agents, featuring advanced GUI perception, grounding, and planning capabilities. UItron highlights the necessity of systemic data engineering and interactive infrastructure as foundational components for advancing GUI agent development. It not only systematically studies a series of data engineering strategies to enhance training effects, but also establishes an interactive environment connecting both Mobile and PC devices. In training, UItron adopts supervised finetuning over perception and planning tasks in various GUI scenarios, and then develop a curriculum reinforcement learning framework to enable complex reasoning and exploration for online environments. As a result, UItron achieves superior performance in benchmarks of GUI perception, grounding, and planning. In particular, UItron highlights the interaction proficiency with top-tier Chinese mobile APPs, as we identified a general lack of Chinese capabilities even in state-of-the-art solutions. To this end, we manually collect over one million steps of operation trajectories across the top 100 most popular apps, and build the offline and online agent evaluation environments. Experimental results demonstrate that UItron achieves significant progress in Chinese app scenarios, propelling GUI agents one step closer to real-world application.
DocTron-Formula: Generalized Formula Recognition in Complex and Structured Scenarios
Aug 01, 2025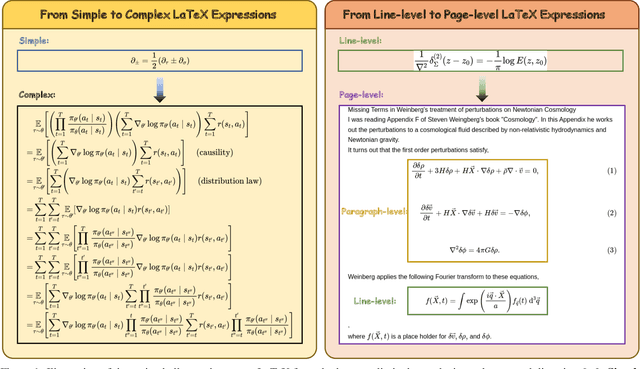

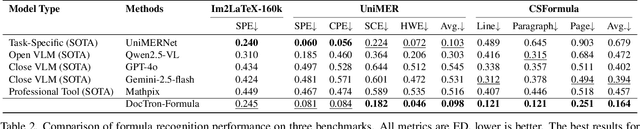
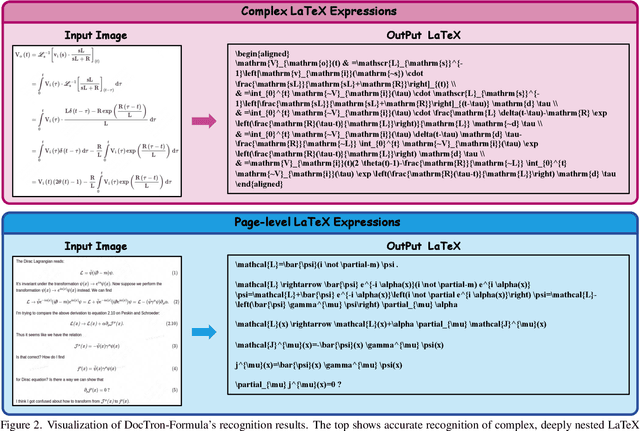
Abstract:Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for mathematical formula is essential for the intelligent analysis of scientific literature. However, both task-specific and general vision-language models often struggle to handle the structural diversity, complexity, and real-world variability inherent in mathematical content. In this work, we present DocTron-Formula, a unified framework built upon general vision-language models, thereby eliminating the need for specialized architectures. Furthermore, we introduce CSFormula, a large-scale and challenging dataset that encompasses multidisciplinary and structurally complex formulas at the line, paragraph, and page levels. Through straightforward supervised fine-tuning, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across a variety of styles, scientific domains, and complex layouts. Experimental results demonstrate that our method not only surpasses specialized models in terms of accuracy and robustness, but also establishes a new paradigm for the automated understanding of complex scientific documents.
Long-Tailed Distribution-Aware Router For Mixture-of-Experts in Large Vision-Language Model
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The mixture-of-experts (MoE), which replaces dense models with sparse architectures, has gained attention in large vision-language models (LVLMs) for achieving comparable performance with fewer activated parameters. Existing MoE frameworks for LVLMs focus on token-to-expert routing (TER), encouraging different experts to specialize in processing distinct tokens. However, these frameworks often rely on the load balancing mechanism, overlooking the inherent distributional differences between vision and language. To this end, we propose a Long-Tailed Distribution-aware Router (LTDR) for vision-language TER, tackling two challenges: (1) Distribution-aware router for modality-specific routing. We observe that language TER follows a uniform distribution, whereas vision TER exhibits a long-tailed distribution. This discrepancy necessitates distinct routing strategies tailored to each modality. (2) Enhancing expert activation for vision tail tokens. Recognizing the importance of vision tail tokens, we introduce an oversampling-like strategy by increasing the number of activated experts for these tokens. Experiments on extensive benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our approach.
Solving Token Gradient Conflict in Mixture-of-Experts for Large Vision-Language Model
Jun 28, 2024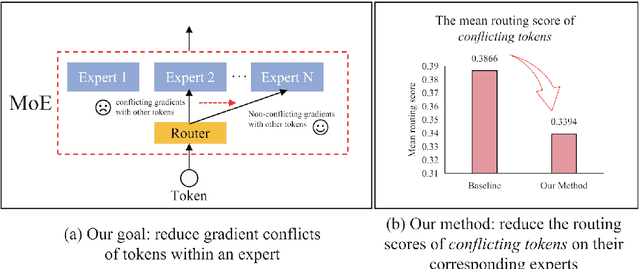
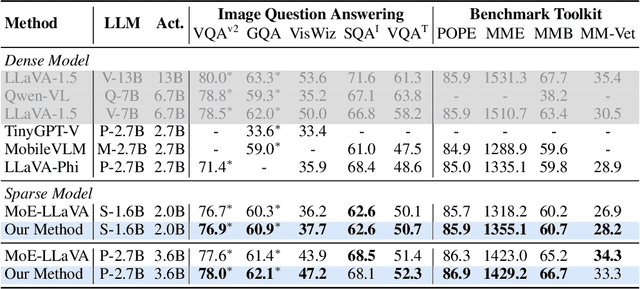
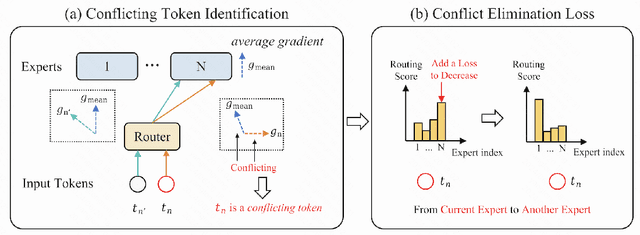
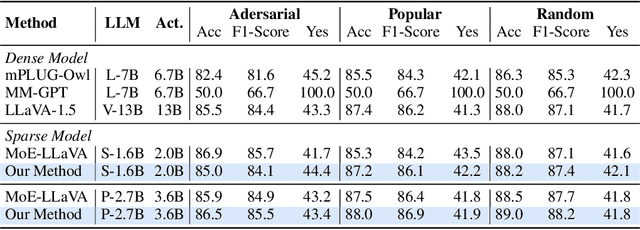
Abstract:The Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) has gained increasing attention in the study of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). It uses a sparse model to replace the dense model, achieving comparable performance while activating fewer parameters during inference, thus significantly reducing the inference cost. Existing MoE methods in LVLMs encourage different experts to handle different tokens, and thus they employ a router to predict the routing for each token. However, the predictions are based solely on sample features and do not truly reveal the optimization direction of tokens. This can lead to severe optimization conflicts between different tokens within an expert. To address this problem, this paper proposes a novel method based on token-level gradient analysis. Specifically, we first use token-level gradients to identify conflicting tokens in experts. Then, we add a specialized loss tailored to eliminate conflicts among tokens within each expert. Our method can serve as a plug-in for diverse Large Vision-Language Models, and extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/longrongyang/STGC.
Bridging Cross-task Protocol Inconsistency for Distillation in Dense Object Detection
Aug 28, 2023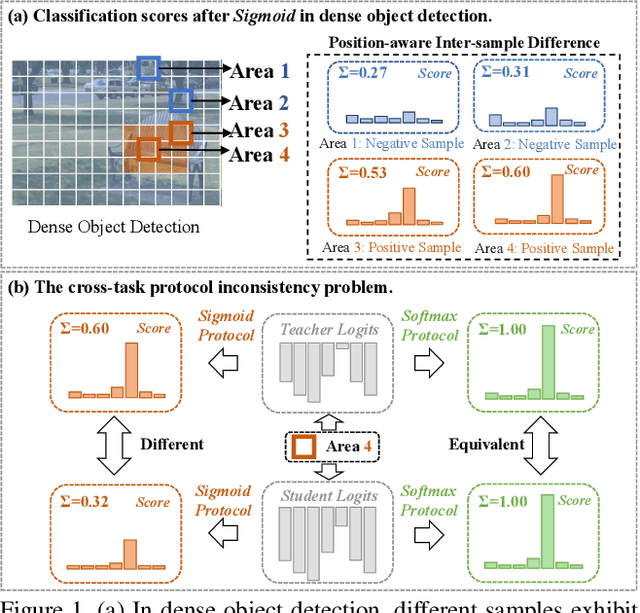
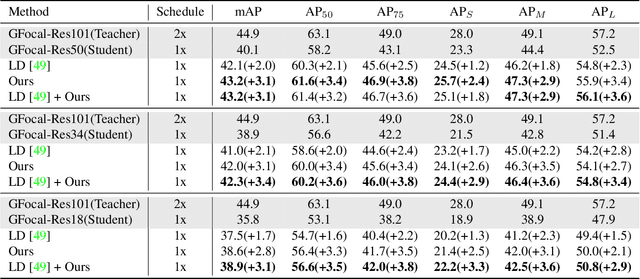
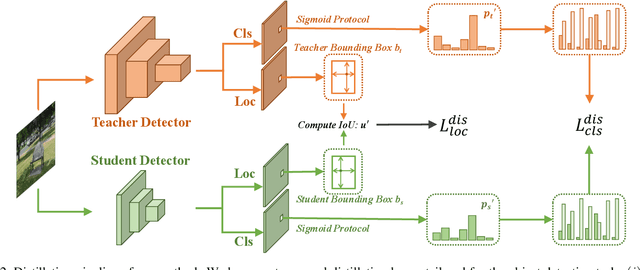
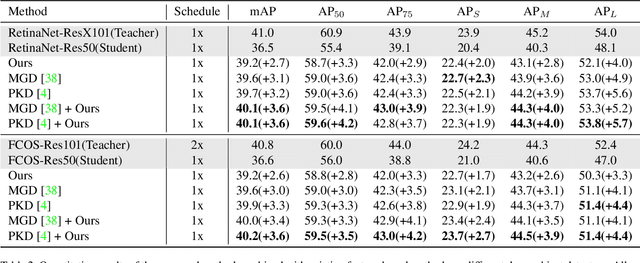
Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) has shown potential for learning compact models in dense object detection. However, the commonly used softmax-based distillation ignores the absolute classification scores for individual categories. Thus, the optimum of the distillation loss does not necessarily lead to the optimal student classification scores for dense object detectors. This cross-task protocol inconsistency is critical, especially for dense object detectors, since the foreground categories are extremely imbalanced. To address the issue of protocol differences between distillation and classification, we propose a novel distillation method with cross-task consistent protocols, tailored for the dense object detection. For classification distillation, we address the cross-task protocol inconsistency problem by formulating the classification logit maps in both teacher and student models as multiple binary-classification maps and applying a binary-classification distillation loss to each map. For localization distillation, we design an IoU-based Localization Distillation Loss that is free from specific network structures and can be compared with existing localization distillation losses. Our proposed method is simple but effective, and experimental results demonstrate its superiority over existing methods. Code is available at https://github.com/TinyTigerPan/BCKD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge