Gopal Sharma
Qonvolution: Towards Learning High-Frequency Signals with Queried Convolution
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Accurately learning high-frequency signals is a challenge in computer vision and graphics, as neural networks often struggle with these signals due to spectral bias or optimization difficulties. While current techniques like Fourier encodings have made great strides in improving performance, there remains scope for improvement when presented with high-frequency information. This paper introduces Queried-Convolutions (Qonvolutions), a simple yet powerful modification using the neighborhood properties of convolution. Qonvolution convolves a low-frequency signal with queries (such as coordinates) to enhance the learning of intricate high-frequency signals. We empirically demonstrate that Qonvolutions enhance performance across a variety of high-frequency learning tasks crucial to both the computer vision and graphics communities, including 1D regression, 2D super-resolution, 2D image regression, and novel view synthesis (NVS). In particular, by combining Gaussian splatting with Qonvolutions for NVS, we showcase state-of-the-art performance on real-world complex scenes, even outperforming powerful radiance field models on image quality.
3D Gaussian Splatting as Markov Chain Monte Carlo
Apr 15, 2024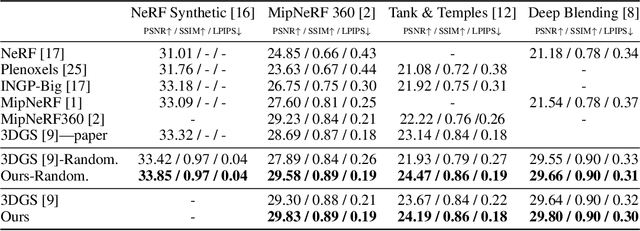


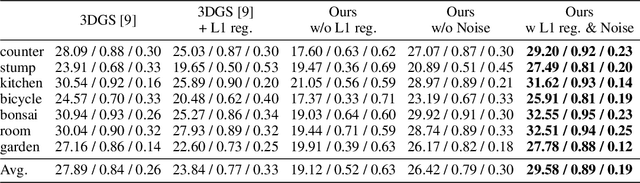
Abstract:While 3D Gaussian Splatting has recently become popular for neural rendering, current methods rely on carefully engineered cloning and splitting strategies for placing Gaussians, which does not always generalize and may lead to poor-quality renderings. In addition, for real-world scenes, they rely on a good initial point cloud to perform well. In this work, we rethink 3D Gaussians as random samples drawn from an underlying probability distribution describing the physical representation of the scene -- in other words, Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) samples. Under this view, we show that the 3D Gaussian updates are strikingly similar to a Stochastic Langevin Gradient Descent (SGLD) update. As with MCMC, samples are nothing but past visit locations, adding new Gaussians under our framework can simply be realized without heuristics as placing Gaussians at existing Gaussian locations. To encourage using fewer Gaussians for efficiency, we introduce an L1-regularizer on the Gaussians. On various standard evaluation scenes, we show that our method provides improved rendering quality, easy control over the number of Gaussians, and robustness to initialization.
Unsupervised Keypoints from Pretrained Diffusion Models
Dec 05, 2023



Abstract:Unsupervised learning of keypoints and landmarks has seen significant progress with the help of modern neural network architectures, but performance is yet to match the supervised counterpart, making their practicability questionable. We leverage the emergent knowledge within text-to-image diffusion models, towards more robust unsupervised keypoints. Our core idea is to find text embeddings that would cause the generative model to consistently attend to compact regions in images (i.e. keypoints). To do so, we simply optimize the text embedding such that the cross-attention maps within the denoising network are localized as Gaussians with small standard deviations. We validate our performance on multiple datasets: the CelebA, CUB-200-2011, Tai-Chi-HD, DeepFashion, and Human3.6m datasets. We achieve significantly improved accuracy, sometimes even outperforming supervised ones, particularly for data that is non-aligned and less curated. Our code is publicly available and can be found through our project page: https://ubc-vision.github.io/StableKeypoints/
PointNeRF++: A multi-scale, point-based Neural Radiance Field
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:Point clouds offer an attractive source of information to complement images in neural scene representations, especially when few images are available. Neural rendering methods based on point clouds do exist, but they do not perform well when the point cloud quality is low -- e.g., sparse or incomplete, which is often the case with real-world data. We overcome these problems with a simple representation that aggregates point clouds at multiple scale levels with sparse voxel grids at different resolutions. To deal with point cloud sparsity, we average across multiple scale levels -- but only among those that are valid, i.e., that have enough neighboring points in proximity to the ray of a pixel. To help model areas without points, we add a global voxel at the coarsest scale, thus unifying "classical" and point-based NeRF formulations. We validate our method on the NeRF Synthetic, ScanNet, and KITTI-360 datasets, outperforming the state of the art by a significant margin.
Volumetric Rendering with Baked Quadrature Fields
Dec 02, 2023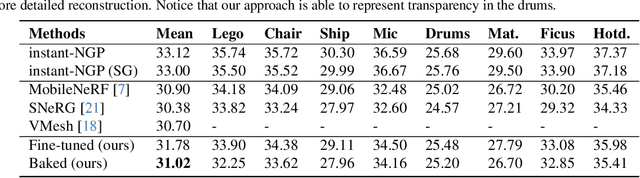
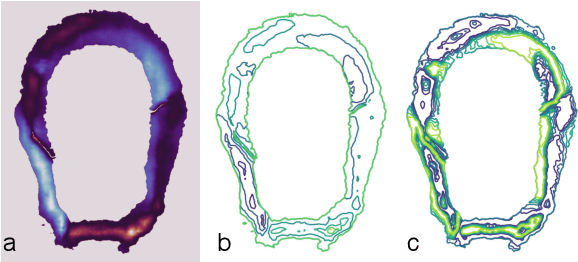
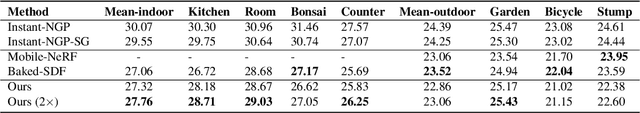
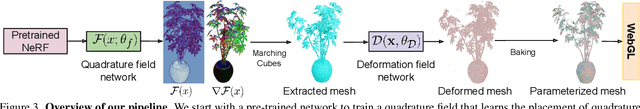
Abstract:We propose a novel Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) representation for non-opaque scenes that allows fast inference by utilizing textured polygons. Despite the high-quality novel view rendering that NeRF provides, a critical limitation is that it relies on volume rendering that can be computationally expensive and does not utilize the advancements in modern graphics hardware. Existing methods for this problem fall short when it comes to modelling volumetric effects as they rely purely on surface rendering. We thus propose to model the scene with polygons, which can then be used to obtain the quadrature points required to model volumetric effects, and also their opacity and colour from the texture. To obtain such polygonal mesh, we train a specialized field whose zero-crossings would correspond to the quadrature points when volume rendering, and perform marching cubes on this field. We then rasterize the polygons and utilize the fragment shaders to obtain the final colour image. Our method allows rendering on various devices and easy integration with existing graphics frameworks while keeping the benefits of volume rendering alive.
Accelerating Neural Field Training via Soft Mining
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:We present an approach to accelerate Neural Field training by efficiently selecting sampling locations. While Neural Fields have recently become popular, it is often trained by uniformly sampling the training domain, or through handcrafted heuristics. We show that improved convergence and final training quality can be achieved by a soft mining technique based on importance sampling: rather than either considering or ignoring a pixel completely, we weigh the corresponding loss by a scalar. To implement our idea we use Langevin Monte-Carlo sampling. We show that by doing so, regions with higher error are being selected more frequently, leading to more than 2x improvement in convergence speed. The code and related resources for this study are publicly available at https://ubc-vision.github.io/nf-soft-mining/.
Unsupervised Semantic Correspondence Using Stable Diffusion
May 24, 2023Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models are now capable of generating images that are often indistinguishable from real images. To generate such images, these models must understand the semantics of the objects they are asked to generate. In this work we show that, without any training, one can leverage this semantic knowledge within diffusion models to find semantic correspondences -- locations in multiple images that have the same semantic meaning. Specifically, given an image, we optimize the prompt embeddings of these models for maximum attention on the regions of interest. These optimized embeddings capture semantic information about the location, which can then be transferred to another image. By doing so we obtain results on par with the strongly supervised state of the art on the PF-Willow dataset and significantly outperform (20.9% relative for the SPair-71k dataset) any existing weakly or unsupervised method on PF-Willow, CUB-200 and SPair-71k datasets.
Attention Beats Concatenation for Conditioning Neural Fields
Sep 21, 2022



Abstract:Neural fields model signals by mapping coordinate inputs to sampled values. They are becoming an increasingly important backbone architecture across many fields from vision and graphics to biology and astronomy. In this paper, we explore the differences between common conditioning mechanisms within these networks, an essential ingredient in shifting neural fields from memorization of signals to generalization, where the set of signals lying on a manifold is modelled jointly. In particular, we are interested in the scaling behaviour of these mechanisms to increasingly high-dimensional conditioning variables. As we show in our experiments, high-dimensional conditioning is key to modelling complex data distributions, thus it is important to determine what architecture choices best enable this when working on such problems. To this end, we run experiments modelling 2D, 3D, and 4D signals with neural fields, employing concatenation, hyper-network, and attention-based conditioning strategies -- a necessary but laborious effort that has not been performed in the literature. We find that attention-based conditioning outperforms other approaches in a variety of settings.
MvDeCor: Multi-view Dense Correspondence Learning for Fine-grained 3D Segmentation
Aug 18, 2022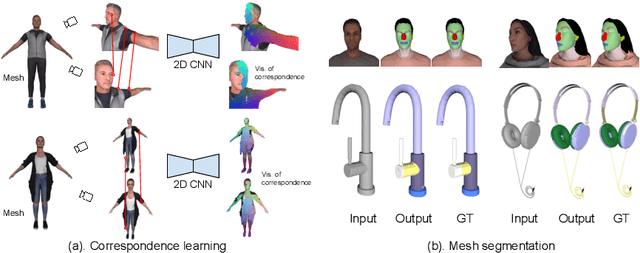
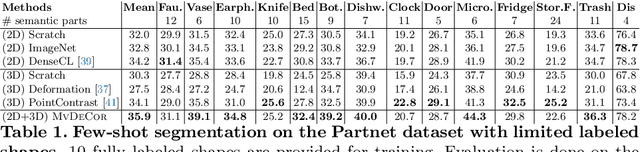
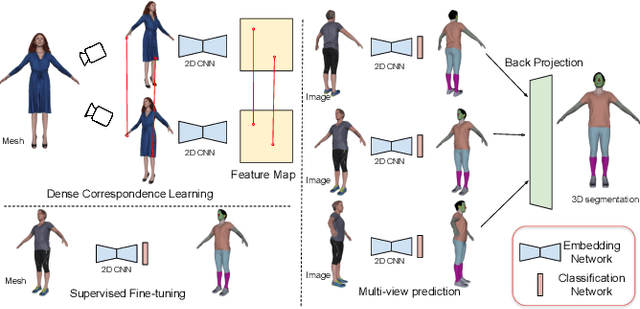
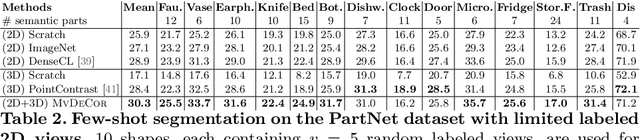
Abstract:We propose to utilize self-supervised techniques in the 2D domain for fine-grained 3D shape segmentation tasks. This is inspired by the observation that view-based surface representations are more effective at modeling high-resolution surface details and texture than their 3D counterparts based on point clouds or voxel occupancy. Specifically, given a 3D shape, we render it from multiple views, and set up a dense correspondence learning task within the contrastive learning framework. As a result, the learned 2D representations are view-invariant and geometrically consistent, leading to better generalization when trained on a limited number of labeled shapes compared to alternatives that utilize self-supervision in 2D or 3D alone. Experiments on textured (RenderPeople) and untextured (PartNet) 3D datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives in fine-grained part segmentation. The improvements over baselines are greater when only a sparse set of views is available for training or when shapes are textured, indicating that MvDeCor benefits from both 2D processing and 3D geometric reasoning.
SurFit: Learning to Fit Surfaces Improves Few Shot Learning on Point Clouds
Dec 27, 2021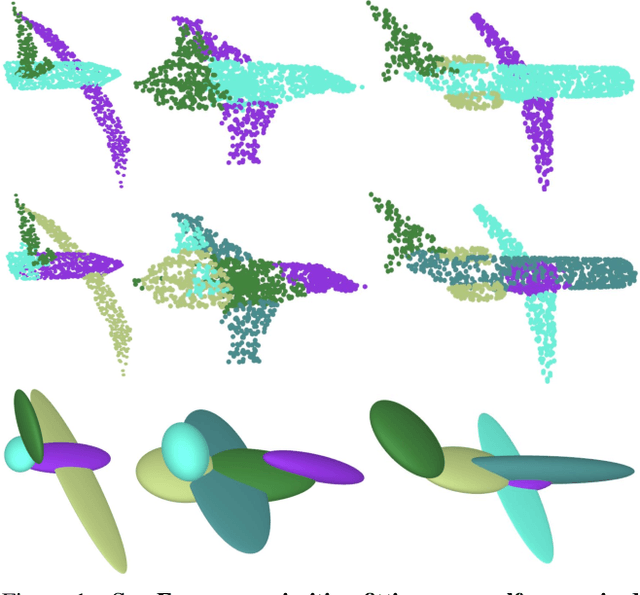
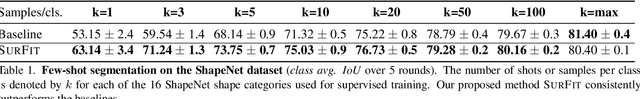
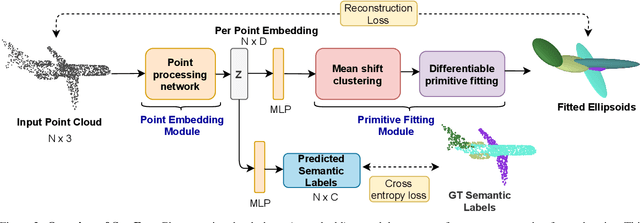
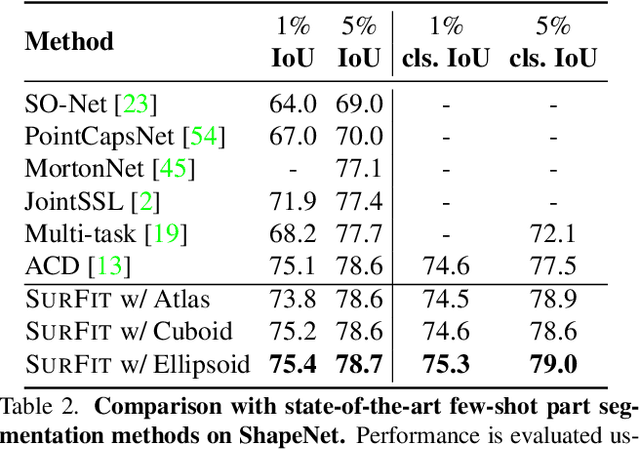
Abstract:We present SurFit, a simple approach for label efficient learning of 3D shape segmentation networks. SurFit is based on a self-supervised task of decomposing the surface of a 3D shape into geometric primitives. It can be readily applied to existing network architectures for 3D shape segmentation and improves their performance in the few-shot setting, as we demonstrate in the widely used ShapeNet and PartNet benchmarks. SurFit outperforms the prior state-of-the-art in this setting, suggesting that decomposability into primitives is a useful prior for learning representations predictive of semantic parts. We present a number of experiments varying the choice of geometric primitives and downstream tasks to demonstrate the effectiveness of the method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge