Debojeet Chatterjee
EgoQR: Efficient QR Code Reading in Egocentric Settings
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:QR codes have become ubiquitous in daily life, enabling rapid information exchange. With the increasing adoption of smart wearable devices, there is a need for efficient, and friction-less QR code reading capabilities from Egocentric point-of-views. However, adapting existing phone-based QR code readers to egocentric images poses significant challenges. Code reading from egocentric images bring unique challenges such as wide field-of-view, code distortion and lack of visual feedback as compared to phones where users can adjust the position and framing. Furthermore, wearable devices impose constraints on resources like compute, power and memory. To address these challenges, we present EgoQR, a novel system for reading QR codes from egocentric images, and is well suited for deployment on wearable devices. Our approach consists of two primary components: detection and decoding, designed to operate on high-resolution images on the device with minimal power consumption and added latency. The detection component efficiently locates potential QR codes within the image, while our enhanced decoding component extracts and interprets the encoded information. We incorporate innovative techniques to handle the specific challenges of egocentric imagery, such as varying perspectives, wider field of view, and motion blur. We evaluate our approach on a dataset of egocentric images, demonstrating 34% improvement in reading the code compared to an existing state of the art QR code readers.
Lumos : Empowering Multimodal LLMs with Scene Text Recognition
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Lumos, the first end-to-end multimodal question-answering system with text understanding capabilities. At the core of Lumos is a Scene Text Recognition (STR) component that extracts text from first person point-of-view images, the output of which is used to augment input to a Multimodal Large Language Model (MM-LLM). While building Lumos, we encountered numerous challenges related to STR quality, overall latency, and model inference. In this paper, we delve into those challenges, and discuss the system architecture, design choices, and modeling techniques employed to overcome these obstacles. We also provide a comprehensive evaluation for each component, showcasing high quality and efficiency.
Improving Opinion-based Question Answering Systems Through Label Error Detection and Overwrite
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Label error is a ubiquitous problem in annotated data. Large amounts of label error substantially degrades the quality of deep learning models. Existing methods to tackle the label error problem largely focus on the classification task, and either rely on task specific architecture or require non-trivial additional computations, which is undesirable or even unattainable for industry usage. In this paper, we propose LEDO: a model-agnostic and computationally efficient framework for Label Error Detection and Overwrite. LEDO is based on Monte Carlo Dropout combined with uncertainty metrics, and can be easily generalized to multiple tasks and data sets. Applying LEDO to an industry opinion-based question answering system demonstrates it is effective at improving accuracy in all the core models. Specifically, LEDO brings 1.1% MRR gain for the retrieval model, 1.5% PR AUC improvement for the machine reading comprehension model, and 0.9% rise in the Average Precision for the ranker, on top of the strong baselines with a large-scale social media dataset. Importantly, LEDO is computationally efficient compared to methods that require loss function change, and cost-effective as the resulting data can be used in the same continuous training pipeline for production. Further analysis shows that these gains come from an improved decision boundary after cleaning the label errors existed in the training data.
A Study on the Efficiency and Generalization of Light Hybrid Retrievers
Oct 04, 2022
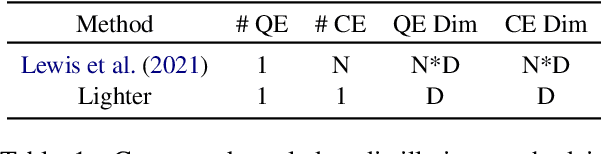
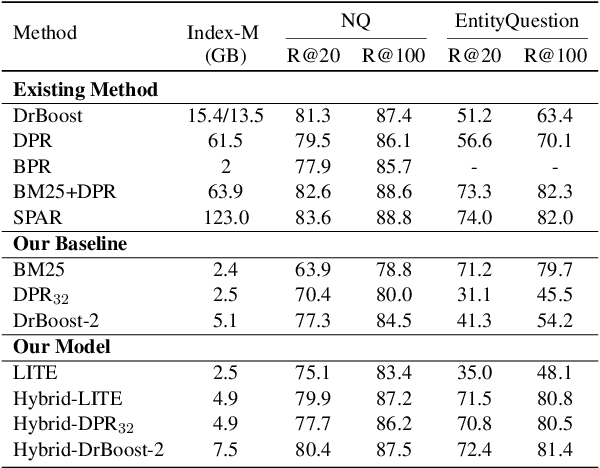
Abstract:Existing hybrid retrievers which integrate sparse and dense retrievers, are indexing-heavy, limiting their applicability in real-world on-devices settings. We ask the question "Is it possible to reduce the indexing memory of hybrid retrievers without sacrificing performance?" Driven by this question, we leverage an indexing-efficient dense retriever (i.e. DrBoost) to obtain a light hybrid retriever. Moreover, to further reduce the memory, we introduce a lighter dense retriever (LITE) which is jointly trained on contrastive learning and knowledge distillation from DrBoost. Compared to previous heavy hybrid retrievers, our Hybrid-LITE retriever saves 13 memory while maintaining 98.0 performance. In addition, we study the generalization of light hybrid retrievers along two dimensions, out-of-domain (OOD) generalization and robustness against adversarial attacks. We evaluate models on two existing OOD benchmarks and create six adversarial attack sets for robustness evaluation. Experiments show that our light hybrid retrievers achieve better robustness performance than both sparse and dense retrievers. Nevertheless there is a large room to improve the robustness of retrievers, and our datasets can aid future research.
Conversational Answer Generation and Factuality for Reading Comprehension Question-Answering
Mar 11, 2021
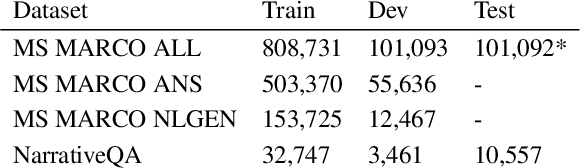
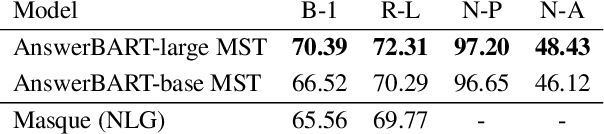
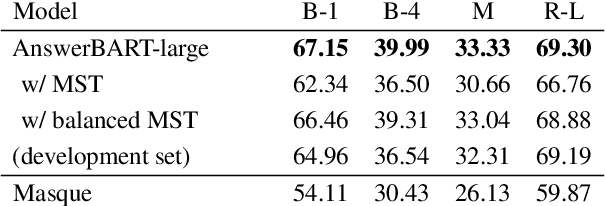
Abstract:Question answering (QA) is an important use case on voice assistants. A popular approach to QA is extractive reading comprehension (RC) which finds an answer span in a text passage. However, extractive answers are often unnatural in a conversational context which results in suboptimal user experience. In this work, we investigate conversational answer generation for QA. We propose AnswerBART, an end-to-end generative RC model which combines answer generation from multiple passages with passage ranking and answerability. Moreover, a hurdle in applying generative RC are hallucinations where the answer is factually inconsistent with the passage text. We leverage recent work from summarization to evaluate factuality. Experiments show that AnswerBART significantly improves over previous best published results on MS MARCO 2.1 NLGEN by 2.5 ROUGE-L and NarrativeQA by 9.4 ROUGE-L.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge