Cong Liao
CoBa: Convergence Balancer for Multitask Finetuning of Large Language Models
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) benefits the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) by providing a single model with improved performance and generalization ability across tasks, presenting a resource-efficient alternative to developing separate models for each task. Yet, existing MTL strategies for LLMs often fall short by either being computationally intensive or failing to ensure simultaneous task convergence. This paper presents CoBa, a new MTL approach designed to effectively manage task convergence balance with minimal computational overhead. Utilizing Relative Convergence Scores (RCS), Absolute Convergence Scores (ACS), and a Divergence Factor (DF), CoBa dynamically adjusts task weights during the training process, ensuring that the validation loss of all tasks progress towards convergence at an even pace while mitigating the issue of individual task divergence. The results of our experiments involving three disparate datasets underscore that this approach not only fosters equilibrium in task improvement but enhances the LLMs' performance by up to 13% relative to the second-best baselines. Code is open-sourced at https://github.com/codefuse-ai/MFTCoder.
SQLfuse: Enhancing Text-to-SQL Performance through Comprehensive LLM Synergy
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-SQL conversion is a critical innovation, simplifying the transition from complex SQL to intuitive natural language queries, especially significant given SQL's prevalence in the job market across various roles. The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 has greatly advanced this field, offering improved natural language understanding and the ability to generate nuanced SQL statements. However, the potential of open-source LLMs in Text-to-SQL applications remains underexplored, with many frameworks failing to leverage their full capabilities, particularly in handling complex database queries and incorporating feedback for iterative refinement. Addressing these limitations, this paper introduces SQLfuse, a robust system integrating open-source LLMs with a suite of tools to enhance Text-to-SQL translation's accuracy and usability. SQLfuse features four modules: schema mining, schema linking, SQL generation, and a SQL critic module, to not only generate but also continuously enhance SQL query quality. Demonstrated by its leading performance on the Spider Leaderboard and deployment by Ant Group, SQLfuse showcases the practical merits of open-source LLMs in diverse business contexts.
A Survey on Language Models for Code
Nov 19, 2023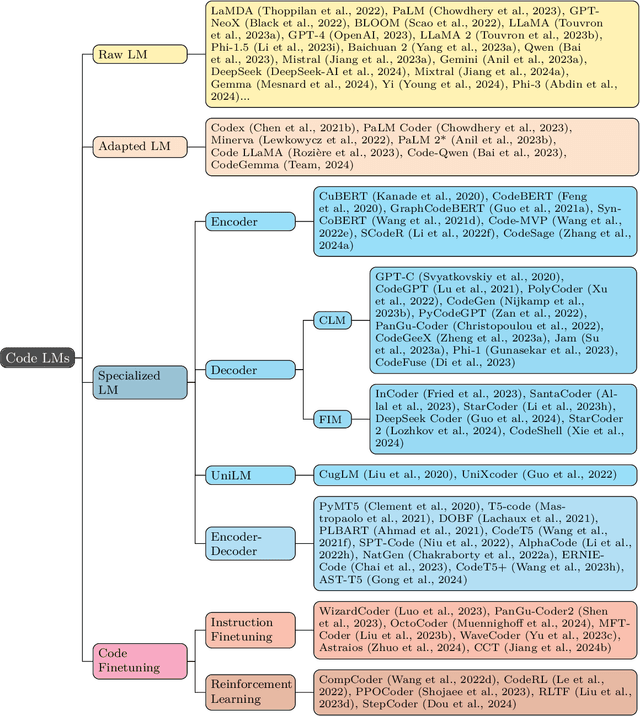
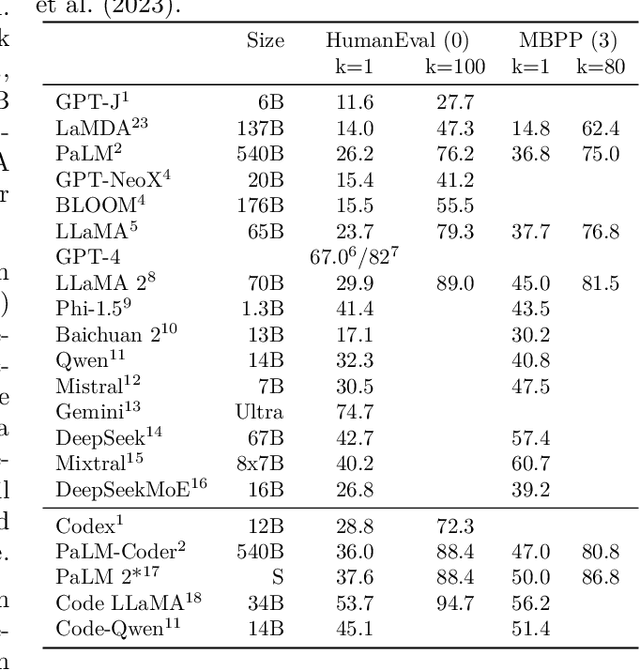
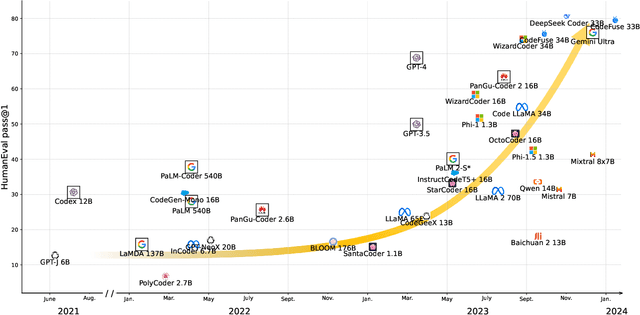
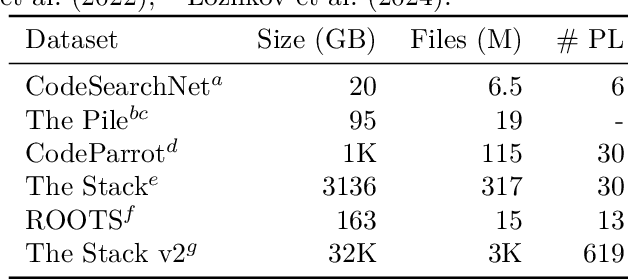
Abstract:In this work we systematically review the recent advancements in code processing with language models, covering 50+ models, 30+ evaluation tasks, 150+ datasets, and 550 related works. We break down code processing models into general language models represented by the GPT family and specialized models that are specifically pretrained on code, often with tailored objectives. We discuss the relations and differences between these models, and highlight the historical transition of code modeling from statistical models and RNNs to pretrained Transformers and LLMs, which is exactly the same course that had been taken by NLP. We also discuss code-specific features such as AST, CFG, and unit tests, along with their application in training code language models, and identify key challenges and potential future directions in this domain. We keep the survey open and updated on GitHub repository at https://github.com/codefuse-ai/Awesome-Code-LLM.
MFTCoder: Boosting Code LLMs with Multitask Fine-Tuning
Nov 04, 2023Abstract:Code LLMs have emerged as a specialized research field, with remarkable studies dedicated to enhancing model's coding capabilities through fine-tuning on pre-trained models. Previous fine-tuning approaches were typically tailored to specific downstream tasks or scenarios, which meant separate fine-tuning for each task, requiring extensive training resources and posing challenges in terms of deployment and maintenance. Furthermore, these approaches failed to leverage the inherent interconnectedness among different code-related tasks. To overcome these limitations, we present a multi-task fine-tuning framework, MFTcoder, that enables simultaneous and parallel fine-tuning on multiple tasks. By incorporating various loss functions, we effectively address common challenges in multi-task learning, such as data imbalance, varying difficulty levels, and inconsistent convergence speeds. Extensive experiments have conclusively demonstrated that our multi-task fine-tuning approach outperforms both individual fine-tuning on single tasks and fine-tuning on a mixed ensemble of tasks. Moreover, MFTcoder offers efficient training capabilities, including efficient data tokenization modes and PEFT fine-tuning, resulting in significantly improved speed compared to traditional fine-tuning methods. MFTcoder seamlessly integrates with several mainstream open-source LLMs, such as CodeLLama and Qwen. Leveraging the CodeLLama foundation, our MFTcoder fine-tuned model, \textsc{CodeFuse-CodeLLama-34B}, achieves an impressive pass@1 score of 74.4\% on the HumaneEval benchmark, surpassing GPT-4 performance (67\%, zero-shot). MFTCoder is open-sourced at \url{https://github.com/codefuse-ai/MFTCOder}
CodeFuse-13B: A Pretrained Multi-lingual Code Large Language Model
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Code Large Language Models (Code LLMs) have gained significant attention in the industry due to their wide applications in the full lifecycle of software engineering. However, the effectiveness of existing models in understanding non-English inputs for multi-lingual code-related tasks is still far from well studied. This paper introduces CodeFuse-13B, an open-sourced pre-trained code LLM. It is specifically designed for code-related tasks with both English and Chinese prompts and supports over 40 programming languages. CodeFuse achieves its effectiveness by utilizing a high quality pre-training dataset that is carefully filtered by program analyzers and optimized during the training process. Extensive experiments are conducted using real-world usage scenarios, the industry-standard benchmark HumanEval-x, and the specially designed CodeFuseEval for Chinese prompts. To assess the effectiveness of CodeFuse, we actively collected valuable human feedback from the AntGroup's software development process where CodeFuse has been successfully deployed. The results demonstrate that CodeFuse-13B achieves a HumanEval pass@1 score of 37.10%, positioning it as one of the top multi-lingual code LLMs with similar parameter sizes. In practical scenarios, such as code generation, code translation, code comments, and testcase generation, CodeFuse performs better than other models when confronted with Chinese prompts.
A Meta Reinforcement Learning Approach for Predictive Autoscaling in the Cloud
May 31, 2022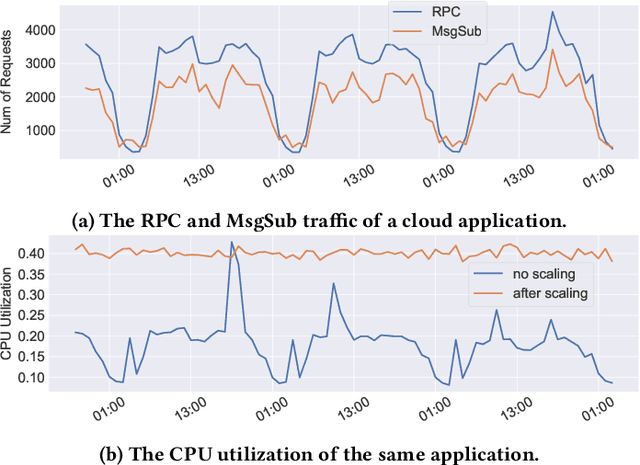
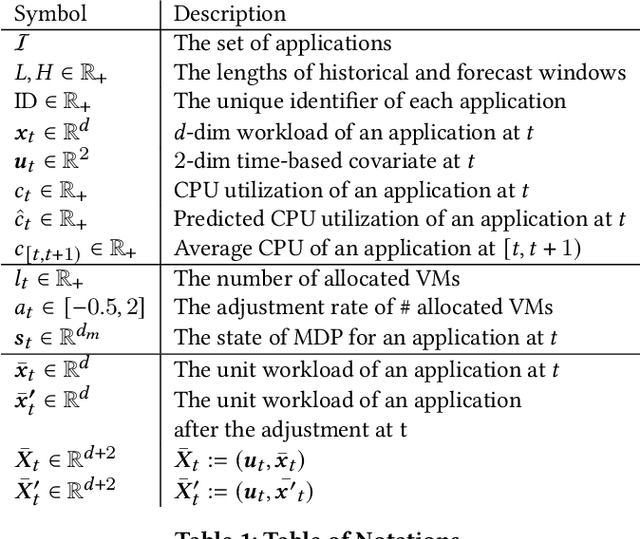
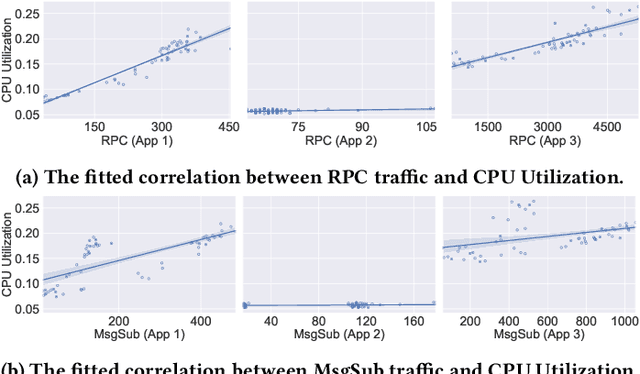
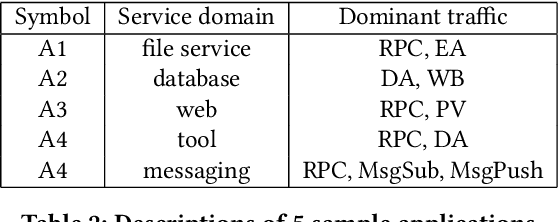
Abstract:Predictive autoscaling (autoscaling with workload forecasting) is an important mechanism that supports autonomous adjustment of computing resources in accordance with fluctuating workload demands in the Cloud. In recent works, Reinforcement Learning (RL) has been introduced as a promising approach to learn the resource management policies to guide the scaling actions under the dynamic and uncertain cloud environment. However, RL methods face the following challenges in steering predictive autoscaling, such as lack of accuracy in decision-making, inefficient sampling and significant variability in workload patterns that may cause policies to fail at test time. To this end, we propose an end-to-end predictive meta model-based RL algorithm, aiming to optimally allocate resource to maintain a stable CPU utilization level, which incorporates a specially-designed deep periodic workload prediction model as the input and embeds the Neural Process to guide the learning of the optimal scaling actions over numerous application services in the Cloud. Our algorithm not only ensures the predictability and accuracy of the scaling strategy, but also enables the scaling decisions to adapt to the changing workloads with high sample efficiency. Our method has achieved significant performance improvement compared to the existing algorithms and has been deployed online at Alipay, supporting the autoscaling of applications for the world-leading payment platform.
Backdoor Embedding in Convolutional Neural Network Models via Invisible Perturbation
Aug 30, 2018
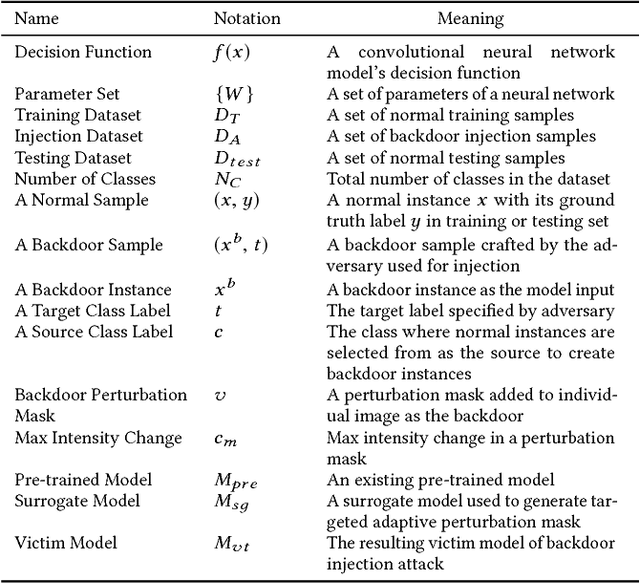
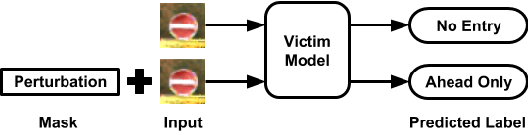
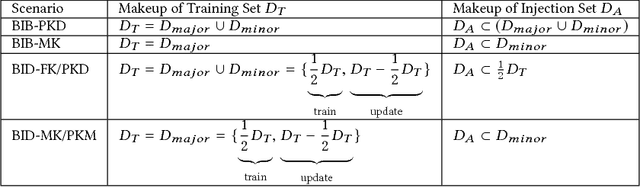
Abstract:Deep learning models have consistently outperformed traditional machine learning models in various classification tasks, including image classification. As such, they have become increasingly prevalent in many real world applications including those where security is of great concern. Such popularity, however, may attract attackers to exploit the vulnerabilities of the deployed deep learning models and launch attacks against security-sensitive applications. In this paper, we focus on a specific type of data poisoning attack, which we refer to as a {\em backdoor injection attack}. The main goal of the adversary performing such attack is to generate and inject a backdoor into a deep learning model that can be triggered to recognize certain embedded patterns with a target label of the attacker's choice. Additionally, a backdoor injection attack should occur in a stealthy manner, without undermining the efficacy of the victim model. Specifically, we propose two approaches for generating a backdoor that is hardly perceptible yet effective in poisoning the model. We consider two attack settings, with backdoor injection carried out either before model training or during model updating. We carry out extensive experimental evaluations under various assumptions on the adversary model, and demonstrate that such attacks can be effective and achieve a high attack success rate (above $90\%$) at a small cost of model accuracy loss (below $1\%$) with a small injection rate (around $1\%$), even under the weakest assumption wherein the adversary has no knowledge either of the original training data or the classifier model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge