Cilin Yan
CrossVid: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Cross-Video Reasoning in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Cross-Video Reasoning (CVR) presents a significant challenge in video understanding, which requires simultaneous understanding of multiple videos to aggregate and compare information across groups of videos. Most existing video understanding benchmarks focus on single-video analysis, failing to assess the ability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to simultaneously reason over various videos. Recent benchmarks evaluate MLLMs' capabilities on multi-view videos that capture different perspectives of the same scene. However, their limited tasks hinder a thorough assessment of MLLMs in diverse real-world CVR scenarios. To this end, we introduce CrossVid, the first benchmark designed to comprehensively evaluate MLLMs' spatial-temporal reasoning ability in cross-video contexts. Firstly, CrossVid encompasses a wide spectrum of hierarchical tasks, comprising four high-level dimensions and ten specific tasks, thereby closely reflecting the complex and varied nature of real-world video understanding. Secondly, CrossVid provides 5,331 videos, along with 9,015 challenging question-answering pairs, spanning single-choice, multiple-choice, and open-ended question formats. Through extensive experiments on various open-source and closed-source MLLMs, we observe that Gemini-2.5-Pro performs best on CrossVid, achieving an average accuracy of 50.4%. Notably, our in-depth case study demonstrates that most current MLLMs struggle with CVR tasks, primarily due to their inability to integrate or compare evidence distributed across multiple videos for reasoning. These insights highlight the potential of CrossVid to guide future advancements in enhancing MLLMs' CVR capabilities.
Efficient and Accurate Prompt Optimization: the Benefit of Memory in Exemplar-Guided Reflection
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Automatic prompt engineering aims to enhance the generation quality of large language models (LLMs). Recent works utilize feedbacks generated from erroneous cases to guide the prompt optimization. During inference, they may further retrieve several semantically-related exemplars and concatenate them to the optimized prompts to improve the performance. However, those works only utilize the feedback at the current step, ignoring historical and unseleccted feedbacks which are potentially beneficial. Moreover, the selection of exemplars only considers the general semantic relationship and may not be optimal in terms of task performance and matching with the optimized prompt. In this work, we propose an Exemplar-Guided Reflection with Memory mechanism (ERM) to realize more efficient and accurate prompt optimization. Specifically, we design an exemplar-guided reflection mechanism where the feedback generation is additionally guided by the generated exemplars. We further build two kinds of memory to fully utilize the historical feedback information and support more effective exemplar retrieval. Empirical evaluations show our method surpasses previous state-of-the-arts with less optimization steps, i.e., improving F1 score by 10.1 on LIAR dataset, and reducing half of the optimization steps on ProTeGi.
VISA: Reasoning Video Object Segmentation via Large Language Models
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:Existing Video Object Segmentation (VOS) relies on explicit user instructions, such as categories, masks, or short phrases, restricting their ability to perform complex video segmentation requiring reasoning with world knowledge. In this paper, we introduce a new task, Reasoning Video Object Segmentation (ReasonVOS). This task aims to generate a sequence of segmentation masks in response to implicit text queries that require complex reasoning abilities based on world knowledge and video contexts, which is crucial for structured environment understanding and object-centric interactions, pivotal in the development of embodied AI. To tackle ReasonVOS, we introduce VISA (Video-based large language Instructed Segmentation Assistant), to leverage the world knowledge reasoning capabilities of multi-modal LLMs while possessing the ability to segment and track objects in videos with a mask decoder. Moreover, we establish a comprehensive benchmark consisting of 35,074 instruction-mask sequence pairs from 1,042 diverse videos, which incorporates complex world knowledge reasoning into segmentation tasks for instruction-tuning and evaluation purposes of ReasonVOS models. Experiments conducted on 8 datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of VISA in tackling complex reasoning segmentation and vanilla referring segmentation in both video and image domains. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/cilinyan/VISA.
Mining Open Semantics from CLIP: A Relation Transition Perspective for Few-Shot Learning
Jun 17, 2024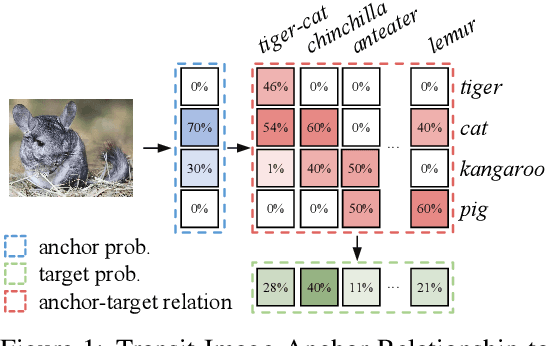
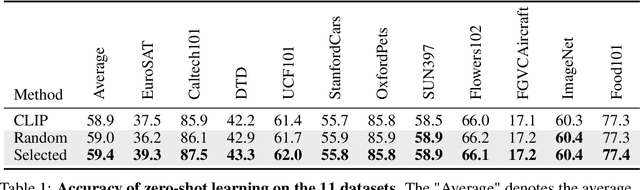
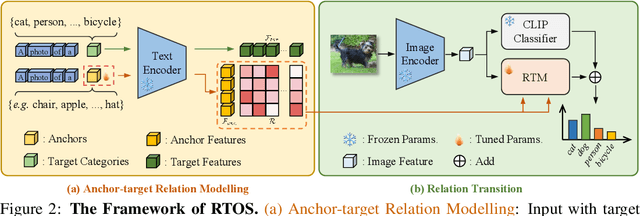
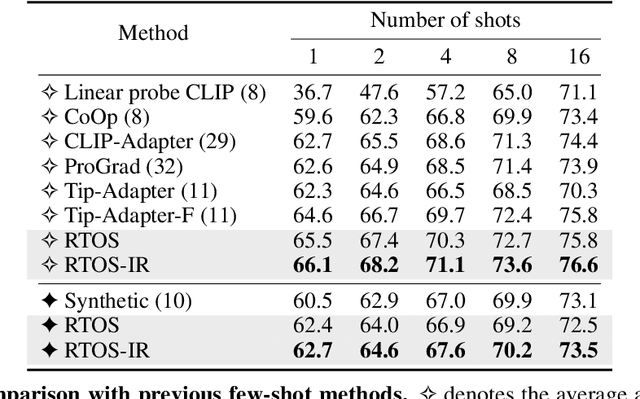
Abstract:Contrastive Vision-Language Pre-training(CLIP) demonstrates impressive zero-shot capability. The key to improve the adaptation of CLIP to downstream task with few exemplars lies in how to effectively model and transfer the useful knowledge embedded in CLIP. Previous work mines the knowledge typically based on the limited visual samples and close-set semantics (i.e., within target category set of downstream task). However, the aligned CLIP image/text encoders contain abundant relationships between visual features and almost infinite open semantics, which may benefit the few-shot learning but remains unexplored. In this paper, we propose to mine open semantics as anchors to perform a relation transition from image-anchor relationship to image-target relationship to make predictions. Specifically, we adopt a transformer module which takes the visual feature as "Query", the text features of the anchors as "Key" and the similarity matrix between the text features of anchor and target classes as "Value". In this way, the output of such a transformer module represents the relationship between the image and target categories, i.e., the classification predictions. To avoid manually selecting the open semantics, we make the [CLASS] token of input text embedding learnable. We conduct extensive experiments on eleven representative classification datasets. The results show that our method performs favorably against previous state-of-the-arts considering few-shot classification settings.
RSBuilding: Towards General Remote Sensing Image Building Extraction and Change Detection with Foundation Model
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:The intelligent interpretation of buildings plays a significant role in urban planning and management, macroeconomic analysis, population dynamics, etc. Remote sensing image building interpretation primarily encompasses building extraction and change detection. However, current methodologies often treat these two tasks as separate entities, thereby failing to leverage shared knowledge. Moreover, the complexity and diversity of remote sensing image scenes pose additional challenges, as most algorithms are designed to model individual small datasets, thus lacking cross-scene generalization. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive remote sensing image building understanding model, termed RSBuilding, developed from the perspective of the foundation model. RSBuilding is designed to enhance cross-scene generalization and task universality. Specifically, we extract image features based on the prior knowledge of the foundation model and devise a multi-level feature sampler to augment scale information. To unify task representation and integrate image spatiotemporal clues, we introduce a cross-attention decoder with task prompts. Addressing the current shortage of datasets that incorporate annotations for both tasks, we have developed a federated training strategy to facilitate smooth model convergence even when supervision for some tasks is missing, thereby bolstering the complementarity of different tasks. Our model was trained on a dataset comprising up to 245,000 images and validated on multiple building extraction and change detection datasets. The experimental results substantiate that RSBuilding can concurrently handle two structurally distinct tasks and exhibits robust zero-shot generalization capabilities.
1st Place Solution for the 5th LSVOS Challenge: Video Instance Segmentation
Aug 28, 2023



Abstract:Video instance segmentation is a challenging task that serves as the cornerstone of numerous downstream applications, including video editing and autonomous driving. In this report, we present further improvements to the SOTA VIS method, DVIS. First, we introduce a denoising training strategy for the trainable tracker, allowing it to achieve more stable and accurate object tracking in complex and long videos. Additionally, we explore the role of visual foundation models in video instance segmentation. By utilizing a frozen VIT-L model pre-trained by DINO v2, DVIS demonstrates remarkable performance improvements. With these enhancements, our method achieves 57.9 AP and 56.0 AP in the development and test phases, respectively, and ultimately ranked 1st in the VIS track of the 5th LSVOS Challenge. The code will be available at https://github.com/zhang-tao-whu/DVIS.
PiClick: Picking the desired mask in click-based interactive segmentation
Apr 23, 2023



Abstract:Click-based interactive segmentation enables productive pixel-level annotation and image editing with simple user clicks, whereas target ambiguity remains a problem hindering precise segmentation. That is, in scenes with rich context, one click may refer to multiple potential targets residing in corresponding masks, while most interactive segmentors can only generate one single mask and fail to capture the rich context. To resolve target ambiguity, we here propose PiClick to produce semantically diversified masks. PiClick leverages a transformer network design wherein mutually interactive mask queries are integrated to infuse target priors. Moreover, a Target Reasoning Module is designed in PiClick to automatically imply the best-matched mask from all proposals, significantly relieving target ambiguity as well as extra human intervention. Extensive experiments conducted on all 9 interactive segmentation datasets not only demonstrate the state-of-the-art segmentation performance of PiClick, but also reduces human interventions with multiple proposal generation and target reasoning. To promote direct usage and future endeavors, we release the source code of PiClick together with a plug-and-play annotation tool at https://github.com/cilinyan/PiClick.
Towards Open-Vocabulary Video Instance Segmentation
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:Video Instance Segmentation(VIS) aims at segmenting and categorizing objects in videos from a closed set of training categories, lacking the generalization ability to handle novel categories in real-world videos. To address this limitation, we make the following three contributions. First, we introduce the novel task of Open-Vocabulary Video Instance Segmentation, which aims to simultaneously segment, track, and classify objects in videos from open-set categories, including novel categories unseen during training. Second, to benchmark Open-Vocabulary VIS, we collect a Large-Vocabulary Video Instance Segmentation dataset(LV-VIS), that contains well-annotated objects from 1,212 diverse categories, significantly surpassing the category size of existing datasets by more than one order of magnitude. Third, we propose an efficient Memory-Induced Vision-Language Transformer, MindVLT, to first achieve Open-Vocabulary VIS in an end-to-end manner with near real-time inference speed. Extensive experiments on LV-VIS and four existing VIS datasets demonstrate the strong zero-shot generalization ability of MindVLT on novel categories. We will release the dataset and code to facilitate future endeavors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge