Chun Li
ToolTok: Tool Tokenization for Efficient and Generalizable GUI Agents
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Existing GUI agent models relying on coordinate-based one-step visual grounding struggle with generalizing to varying input resolutions and aspect ratios. Alternatives introduce coordinate-free strategies yet suffer from learning under severe data scarcity. To address the limitations, we propose ToolTok, a novel paradigm of multi-step pathfinding for GUI agents, where operations are modeled as a sequence of progressive tool usage. Specifically, we devise tools aligned with human interaction habits and represent each tool using learnable token embeddings. To enable efficient embedding learning under limited supervision, ToolTok introduces a semantic anchoring mechanism that grounds each tool with semantically related concepts as natural inductive bias. To further enable a pre-trained large language model to progressively acquire tool semantics, we construct an easy-to-hard curriculum consisting of three tasks: token definition question-answering, pure text-guided tool selection, and simplified visual pathfinding. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks show that ToolTok achieves superior performance among models of comparable scale (4B) and remains competitive with a substantially larger model (235B). Notably, these results are obtained using less than 1% of the training data required by other post-training approaches. In addition, ToolTok demonstrates strong generalization across unseen scenarios. Our training & inference code is open-source at https://github.com/ZephinueCode/ToolTok.
Robust Brain Tumor Segmentation with Incomplete MRI Modalities Using Hölder Divergence and Mutual Information-Enhanced Knowledge Transfer
Jul 02, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal MRI provides critical complementary information for accurate brain tumor segmentation. However, conventional methods struggle when certain modalities are missing due to issues such as image quality, protocol inconsistencies, patient allergies, or financial constraints. To address this, we propose a robust single-modality parallel processing framework that achieves high segmentation accuracy even with incomplete modalities. Leveraging Holder divergence and mutual information, our model maintains modality-specific features while dynamically adjusting network parameters based on the available inputs. By using these divergence- and information-based loss functions, the framework effectively quantifies discrepancies between predictions and ground-truth labels, resulting in consistently accurate segmentation. Extensive evaluations on the BraTS 2018 and BraTS 2020 datasets demonstrate superior performance over existing methods in handling missing modalities.
Unified Few-shot Crack Segmentation and its Precise 3D Automatic Measurement in Concrete Structures
Jan 15, 2025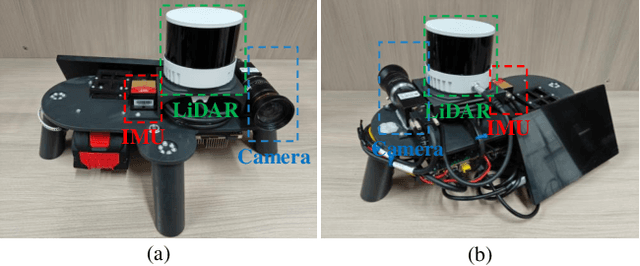
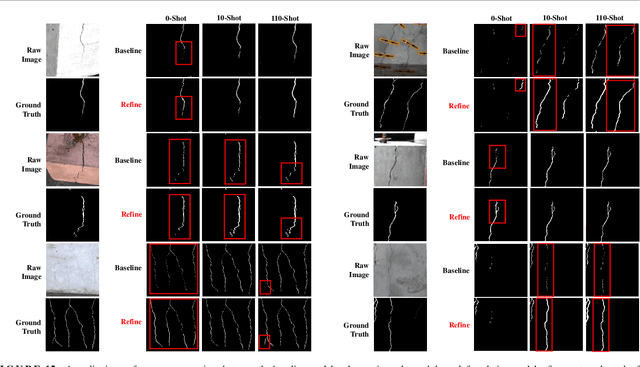
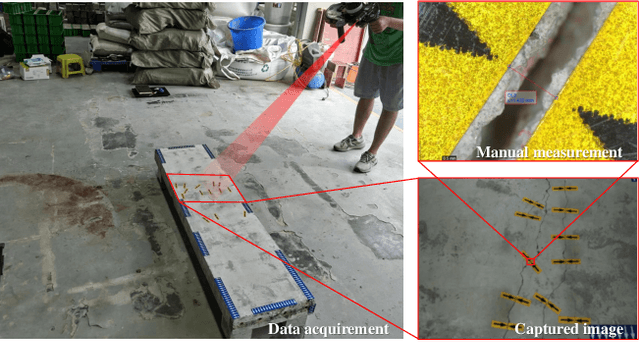
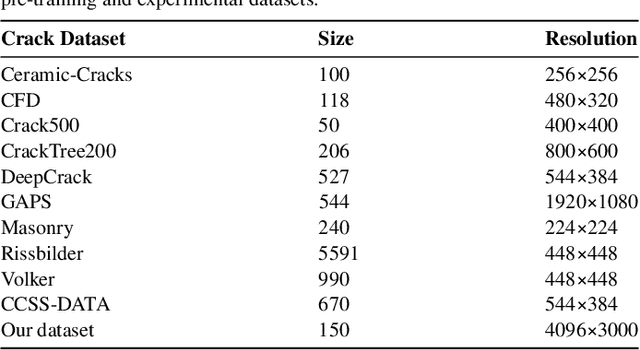
Abstract:Visual-Spatial Systems has become increasingly essential in concrete crack inspection. However, existing methods often lacks adaptability to diverse scenarios, exhibits limited robustness in image-based approaches, and struggles with curved or complex geometries. To address these limitations, an innovative framework for two-dimensional (2D) crack detection, three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction, and 3D automatic crack measurement was proposed by integrating computer vision technologies and multi-modal Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) in this study. Firstly, building on a base DeepLabv3+ segmentation model, and incorporating specific refinements utilizing foundation model Segment Anything Model (SAM), we developed a crack segmentation method with strong generalization across unfamiliar scenarios, enabling the generation of precise 2D crack masks. To enhance the accuracy and robustness of 3D reconstruction, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) point clouds were utilized together with image data and segmentation masks. By leveraging both image- and LiDAR-SLAM, we developed a multi-frame and multi-modal fusion framework that produces dense, colorized point clouds, effectively capturing crack semantics at a 3D real-world scale. Furthermore, the crack geometric attributions were measured automatically and directly within 3D dense point cloud space, surpassing the limitations of conventional 2D image-based measurements. This advancement makes the method suitable for structural components with curved and complex 3D geometries. Experimental results across various concrete structures highlight the significant improvements and unique advantages of the proposed method, demonstrating its effectiveness, accuracy, and robustness in real-world applications.
General Information Metrics for Improving AI Model Training Efficiency
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:To address the growing size of AI model training data and the lack of a universal data selection methodology-factors that significantly drive up training costs -- this paper presents the General Information Metrics Evaluation (GIME) method. GIME leverages general information metrics from Objective Information Theory (OIT), including volume, delay, scope, granularity, variety, duration, sampling rate, aggregation, coverage, distortion, and mismatch to optimize dataset selection for training purposes. Comprehensive experiments conducted across diverse domains, such as CTR Prediction, Civil Case Prediction, and Weather Forecasting, demonstrate that GIME effectively preserves model performance while substantially reducing both training time and costs. Additionally, applying GIME within the Judicial AI Program led to a remarkable 39.56% reduction in total model training expenses, underscoring its potential to support efficient and sustainable AI development.
EFTViT: Efficient Federated Training of Vision Transformers with Masked Images on Resource-Constrained Edge Devices
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning research has recently shifted from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to Vision Transformers (ViTs) due to their superior capacity. ViTs training demands higher computational resources due to the lack of 2D inductive biases inherent in CNNs. However, efficient federated training of ViTs on resource-constrained edge devices remains unexplored in the community. In this paper, we propose EFTViT, a hierarchical federated framework that leverages masked images to enable efficient, full-parameter training on resource-constrained edge devices, offering substantial benefits for learning on heterogeneous data. In general, we patchify images and randomly mask a portion of the patches, observing that excluding them from training has minimal impact on performance while substantially reducing computation costs and enhancing data content privacy protection. Specifically, EFTViT comprises a series of lightweight local modules and a larger global module, updated independently on clients and the central server, respectively. The local modules are trained on masked image patches, while the global module is trained on intermediate patch features uploaded from the local client, balanced through a proposed median sampling strategy to erase client data distribution privacy. We analyze the computational complexity and privacy protection of EFTViT. Extensive experiments on popular benchmarks show that EFTViT achieves up to 28.17% accuracy improvement, reduces local training computational cost by up to 2.8$\times$, and cuts local training time by up to 4.4$\times$ compared to existing methods.
Robust Divergence Learning for Missing-Modality Segmentation
Nov 13, 2024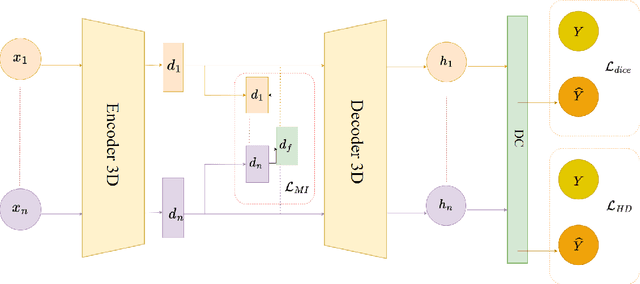
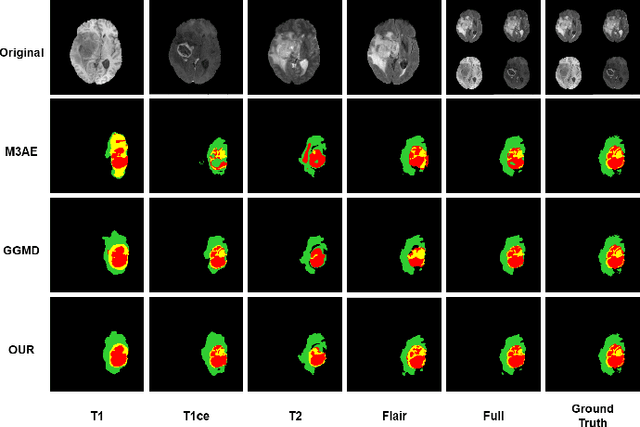
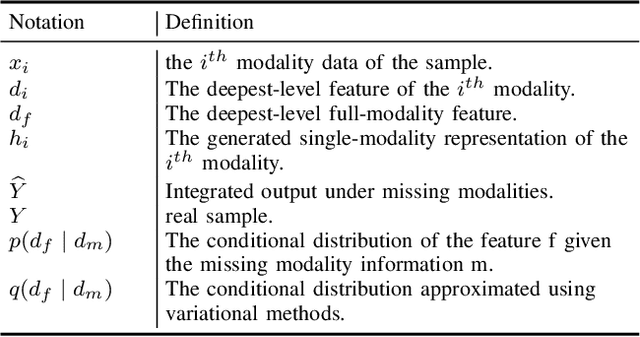
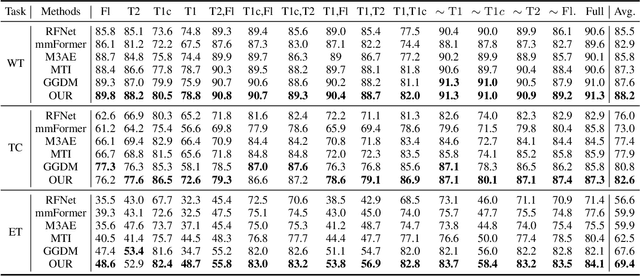
Abstract:Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides essential complementary information for analyzing brain tumor subregions. While methods using four common MRI modalities for automatic segmentation have shown success, they often face challenges with missing modalities due to image quality issues, inconsistent protocols, allergic reactions, or cost factors. Thus, developing a segmentation paradigm that handles missing modalities is clinically valuable. A novel single-modality parallel processing network framework based on H\"older divergence and mutual information is introduced. Each modality is independently input into a shared network backbone for parallel processing, preserving unique information. Additionally, a dynamic sharing framework is introduced that adjusts network parameters based on modality availability. A H\"older divergence and mutual information-based loss functions are used for evaluating discrepancies between predictions and labels. Extensive testing on the BraTS 2018 and BraTS 2020 datasets demonstrates that our method outperforms existing techniques in handling missing modalities and validates each component's effectiveness.
Uncertainty Quantification via Hölder Divergence for Multi-View Representation Learning
Oct 29, 2024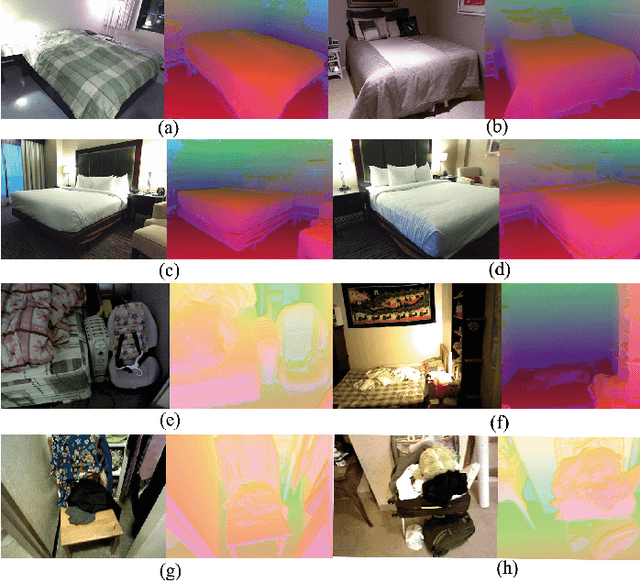
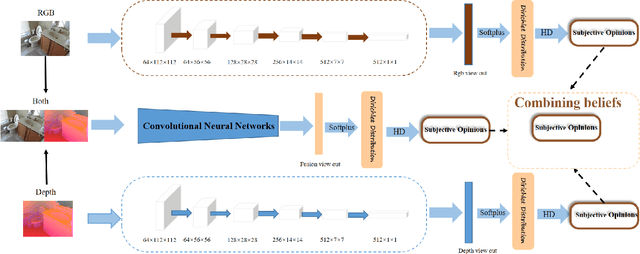
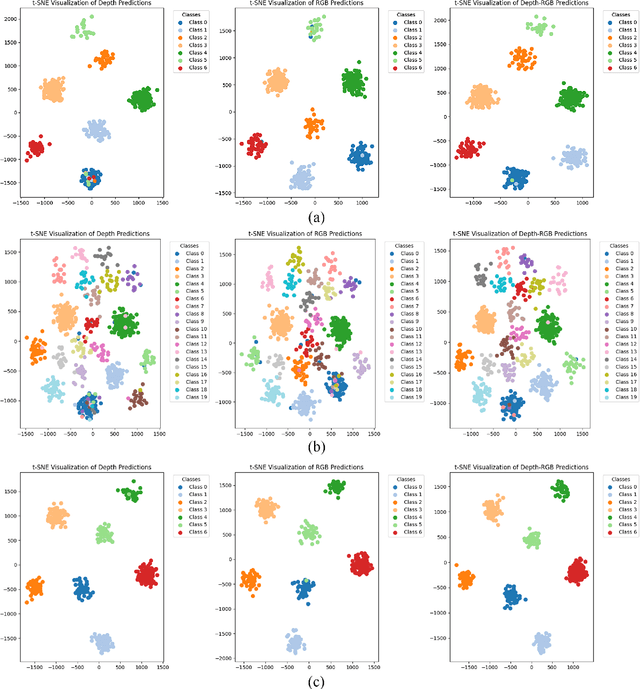
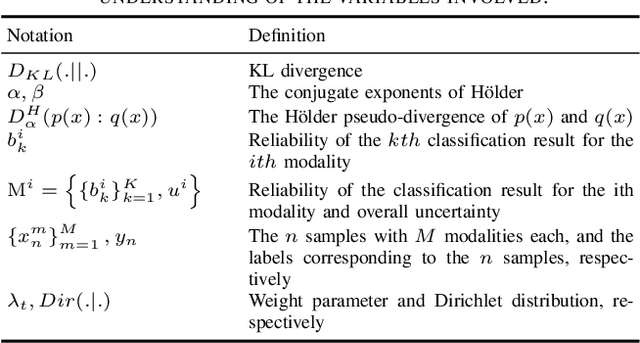
Abstract:Evidence-based deep learning represents a burgeoning paradigm for uncertainty estimation, offering reliable predictions with negligible extra computational overheads. Existing methods usually adopt Kullback-Leibler divergence to estimate the uncertainty of network predictions, ignoring domain gaps among various modalities. To tackle this issue, this paper introduces a novel algorithm based on H\"older Divergence (HD) to enhance the reliability of multi-view learning by addressing inherent uncertainty challenges from incomplete or noisy data. Generally, our method extracts the representations of multiple modalities through parallel network branches, and then employs HD to estimate the prediction uncertainties. Through the Dempster-Shafer theory, integration of uncertainty from different modalities, thereby generating a comprehensive result that considers all available representations. Mathematically, HD proves to better measure the ``distance'' between real data distribution and predictive distribution of the model and improve the performances of multi-class recognition tasks. Specifically, our method surpass the existing state-of-the-art counterparts on all evaluating benchmarks. We further conduct extensive experiments on different backbones to verify our superior robustness. It is demonstrated that our method successfully pushes the corresponding performance boundaries. Finally, we perform experiments on more challenging scenarios, \textit{i.e.}, learning with incomplete or noisy data, revealing that our method exhibits a high tolerance to such corrupted data.
Unveiling Incomplete Modality Brain Tumor Segmentation: Leveraging Masked Predicted Auto-Encoder and Divergence Learning
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Brain tumor segmentation remains a significant challenge, particularly in the context of multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) where missing modality images are common in clinical settings, leading to reduced segmentation accuracy. To address this issue, we propose a novel strategy, which is called masked predicted pre-training, enabling robust feature learning from incomplete modality data. Additionally, in the fine-tuning phase, we utilize a knowledge distillation technique to align features between complete and missing modality data, simultaneously enhancing model robustness. Notably, we leverage the Holder pseudo-divergence instead of the KLD for distillation loss, offering improve mathematical interpretability and properties. Extensive experiments on the BRATS2018 and BRATS2020 datasets demonstrate significant performance enhancements compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
Semi-Supervised Disease Classification based on Limited Medical Image Data
May 07, 2024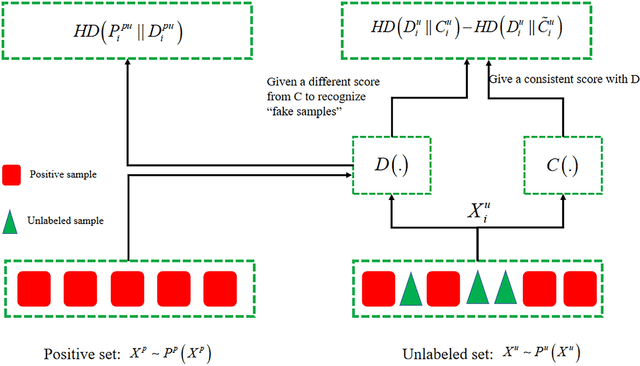
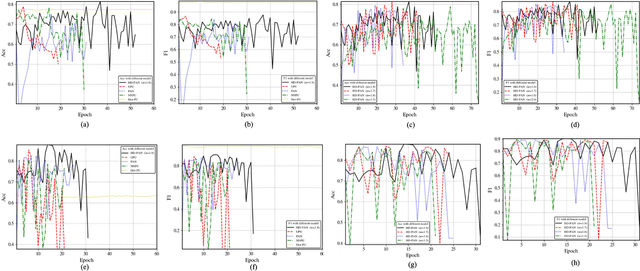
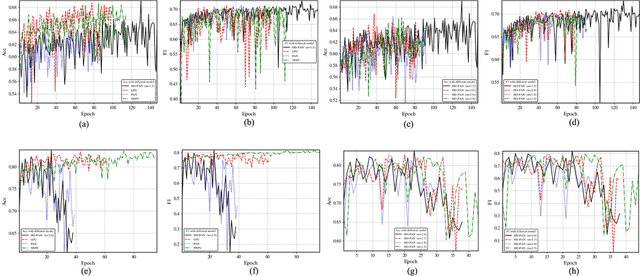
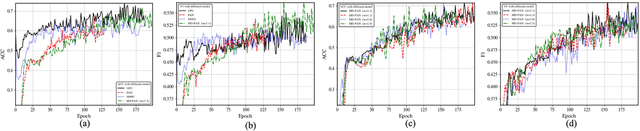
Abstract:In recent years, significant progress has been made in the field of learning from positive and unlabeled examples (PU learning), particularly in the context of advancing image and text classification tasks. However, applying PU learning to semi-supervised disease classification remains a formidable challenge, primarily due to the limited availability of labeled medical images. In the realm of medical image-aided diagnosis algorithms, numerous theoretical and practical obstacles persist. The research on PU learning for medical image-assisted diagnosis holds substantial importance, as it aims to reduce the time spent by professional experts in classifying images. Unlike natural images, medical images are typically accompanied by a scarcity of annotated data, while an abundance of unlabeled cases exists. Addressing these challenges, this paper introduces a novel generative model inspired by H\"older divergence, specifically designed for semi-supervised disease classification using positive and unlabeled medical image data. In this paper, we present a comprehensive formulation of the problem and establish its theoretical feasibility through rigorous mathematical analysis. To evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, we conduct extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets commonly used in PU medical learning: BreastMNIST, PneumoniaMNIST, BloodMNIST, OCTMNIST, and AMD. The experimental results clearly demonstrate the superiority of our method over existing approaches based on KL divergence. Notably, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on all five disease classification benchmarks. By addressing the limitations imposed by limited labeled data and harnessing the untapped potential of unlabeled medical images, our novel generative model presents a promising direction for enhancing semi-supervised disease classification in the field of medical image analysis.
Multinomial Random Forests: Fill the Gap between Theoretical Consistency and Empirical Soundness
Mar 10, 2019
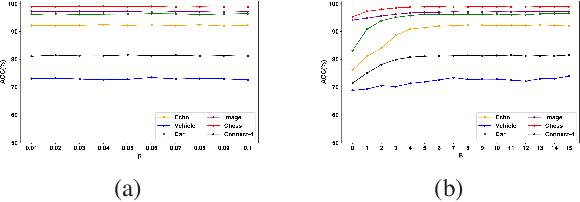

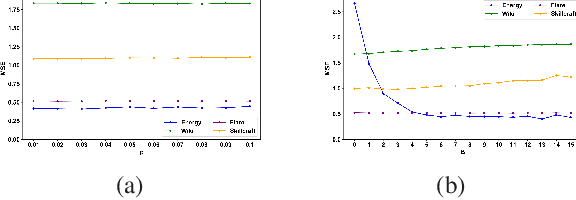
Abstract:Random forests (RF) are one of the most widely used ensemble learning methods in classification and regression tasks. Despite its impressive performance, its theoretical consistency, which would ensure that its result converges to the optimum as the sample size increases, has been left far behind. Several consistent random forest variants have been proposed, yet all with relatively poor performance compared to the original random forests. In this paper, a novel RF framework named multinomial random forests (MRF) is proposed. In the MRF, an impurity-based multinomial distribution is constructed as the basis for the selection of a splitting point. This ensures that a certain degree of randomness is achieved while the overall quality of the trees is not much different from the original random forests. We prove the consistency of the MRF and demonstrate with multiple datasets that it performs similarly as the original random forests and better than existent consistent random forest variants for both classification and regression tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge