Tao Chang
EFTViT: Efficient Federated Training of Vision Transformers with Masked Images on Resource-Constrained Edge Devices
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning research has recently shifted from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to Vision Transformers (ViTs) due to their superior capacity. ViTs training demands higher computational resources due to the lack of 2D inductive biases inherent in CNNs. However, efficient federated training of ViTs on resource-constrained edge devices remains unexplored in the community. In this paper, we propose EFTViT, a hierarchical federated framework that leverages masked images to enable efficient, full-parameter training on resource-constrained edge devices, offering substantial benefits for learning on heterogeneous data. In general, we patchify images and randomly mask a portion of the patches, observing that excluding them from training has minimal impact on performance while substantially reducing computation costs and enhancing data content privacy protection. Specifically, EFTViT comprises a series of lightweight local modules and a larger global module, updated independently on clients and the central server, respectively. The local modules are trained on masked image patches, while the global module is trained on intermediate patch features uploaded from the local client, balanced through a proposed median sampling strategy to erase client data distribution privacy. We analyze the computational complexity and privacy protection of EFTViT. Extensive experiments on popular benchmarks show that EFTViT achieves up to 28.17% accuracy improvement, reduces local training computational cost by up to 2.8$\times$, and cuts local training time by up to 4.4$\times$ compared to existing methods.
Visual-and-Language Navigation: A Survey and Taxonomy
Sep 01, 2021
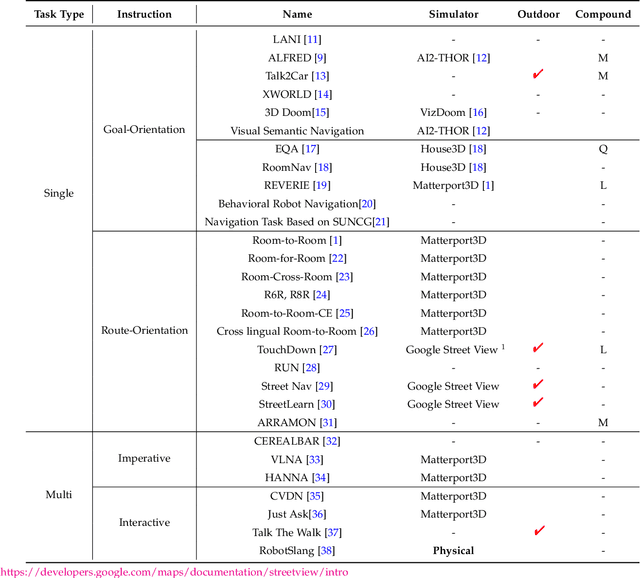


Abstract:An agent that can understand natural-language instruction and carry out corresponding actions in the visual world is one of the long-term challenges of Artificial Intelligent (AI). Due to multifarious instructions from humans, it requires the agent can link natural language to vision and action in unstructured, previously unseen environments. If the instruction given by human is a navigation task, this challenge is called Visual-and-Language Navigation (VLN). It is a booming multi-disciplinary field of increasing importance and with extraordinary practicality. Instead of focusing on the details of specific methods, this paper provides a comprehensive survey on VLN tasks and makes a classification carefully according the different characteristics of language instructions in these tasks. According to when the instructions are given, the tasks can be divided into single-turn and multi-turn. For single-turn tasks, we further divided them into goal-orientation and route-orientation based on whether the instructions contain a route. For multi-turn tasks, we divided them into imperative task and interactive task based on whether the agent responses to the instructions. This taxonomy enable researchers to better grasp the key point of a specific task and identify directions for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge