Jianfeng Xu
DiffFace-Edit: A Diffusion-Based Facial Dataset for Forgery-Semantic Driven Deepfake Detection Analysis
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Generative models now produce imperceptible, fine-grained manipulated faces, posing significant privacy risks. However, existing AI-generated face datasets generally lack focus on samples with fine-grained regional manipulations. Furthermore, no researchers have yet studied the real impact of splice attacks, which occur between real and manipulated samples, on detectors. We refer to these as detector-evasive samples. Based on this, we introduce the DiffFace-Edit dataset, which has the following advantages: 1) It contains over two million AI-generated fake images. 2) It features edits across eight facial regions (e.g., eyes, nose) and includes a richer variety of editing combinations, such as single-region and multi-region edits. Additionally, we specifically analyze the impact of detector-evasive samples on detection models. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of the dataset and propose a cross-domain evaluation that combines IMDL methods. Dataset will be available at https://github.com/ywh1093/DiffFace-Edit.
Information Science Principles of Machine Learning: A Causal Chain Meta-Framework Based on Formalized Information Mapping
May 19, 2025Abstract:[Objective] This study focuses on addressing the current lack of a unified formal theoretical framework in machine learning, as well as the deficiencies in interpretability and ethical safety assurance. [Methods] A formal information model is first constructed, utilizing sets of well-formed formulas to explicitly define the ontological states and carrier mappings of typical components in machine learning. Learnable and processable predicates, along with learning and processing functions, are introduced to analyze the logical deduction and constraint rules of the causal chains within models. [Results] A meta-framework for machine learning theory (MLT-MF) is established. Based on this framework, universal definitions for model interpretability and ethical safety are proposed. Furthermore, three key theorems are proved: the equivalence of model interpretability and information recoverability, the assurance of ethical safety, and the estimation of generalization error. [Limitations] The current framework assumes ideal conditions with noiseless information-enabling mappings and primarily targets model learning and processing logic in static scenarios. It does not yet address information fusion and conflict resolution across ontological spaces in multimodal or multi-agent systems. [Conclusions] This work overcomes the limitations of fragmented research and provides a unified theoretical foundation for systematically addressing the critical challenges currently faced in machine learning.
General Information Metrics for Improving AI Model Training Efficiency
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:To address the growing size of AI model training data and the lack of a universal data selection methodology-factors that significantly drive up training costs -- this paper presents the General Information Metrics Evaluation (GIME) method. GIME leverages general information metrics from Objective Information Theory (OIT), including volume, delay, scope, granularity, variety, duration, sampling rate, aggregation, coverage, distortion, and mismatch to optimize dataset selection for training purposes. Comprehensive experiments conducted across diverse domains, such as CTR Prediction, Civil Case Prediction, and Weather Forecasting, demonstrate that GIME effectively preserves model performance while substantially reducing both training time and costs. Additionally, applying GIME within the Judicial AI Program led to a remarkable 39.56% reduction in total model training expenses, underscoring its potential to support efficient and sustainable AI development.
FairAdapter: Detecting AI-generated Images with Improved Fairness
Nov 22, 2024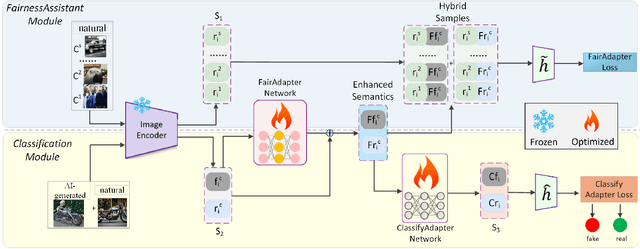
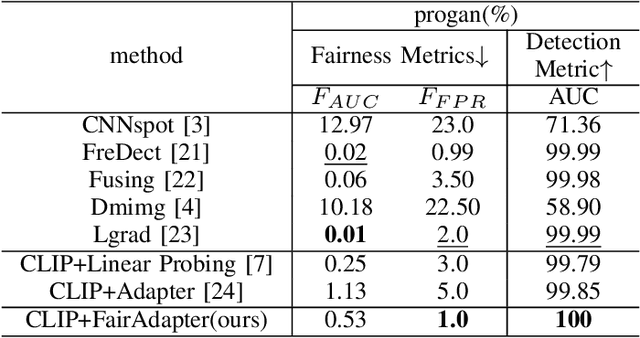
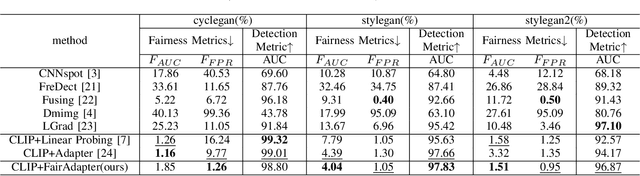
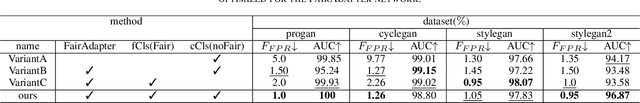
Abstract:The high-quality, realistic images generated by generative models pose significant challenges for exposing them.So far, data-driven deep neural networks have been justified as the most efficient forensics tools for the challenges. However, they may be over-fitted to certain semantics, resulting in considerable inconsistency in detection performance across different contents of generated samples. It could be regarded as an issue of detection fairness. In this paper, we propose a novel framework named Fairadapter to tackle the issue. In comparison with existing state-of-the-art methods, our model achieves improved fairness performance. Our project: https://github.com/AppleDogDog/FairnessDetection
GOPT: Generalizable Online 3D Bin Packing via Transformer-based Deep Reinforcement Learning
Sep 09, 2024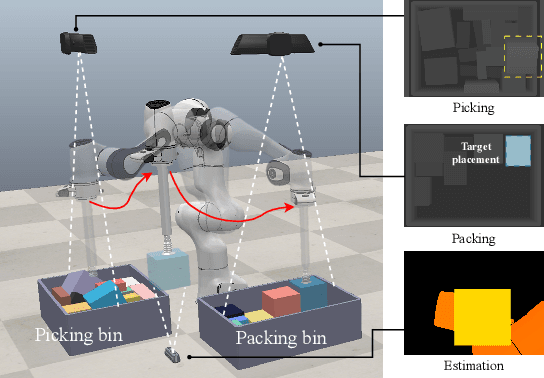
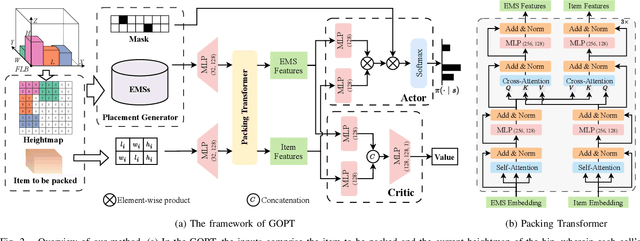
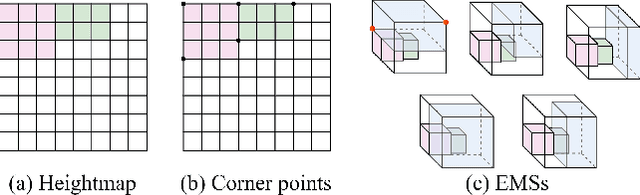
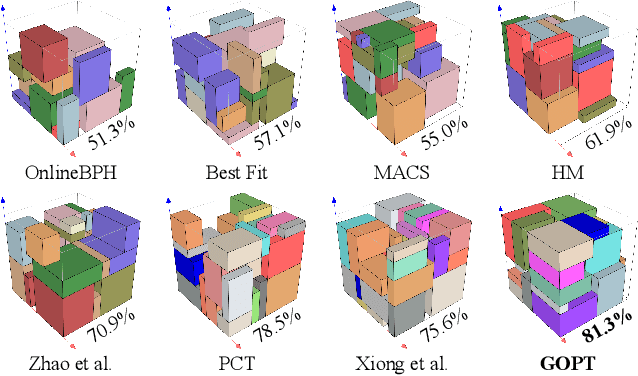
Abstract:Robotic object packing has broad practical applications in the logistics and automation industry, often formulated by researchers as the online 3D Bin Packing Problem (3D-BPP). However, existing DRL-based methods primarily focus on enhancing performance in limited packing environments while neglecting the ability to generalize across multiple environments characterized by different bin dimensions. To this end, we propose GOPT, a generalizable online 3D Bin Packing approach via Transformer-based deep reinforcement learning (DRL). First, we design a Placement Generator module to yield finite subspaces as placement candidates and the representation of the bin. Second, we propose a Packing Transformer, which fuses the features of the items and bin, to identify the spatial correlation between the item to be packed and available sub-spaces within the bin. Coupling these two components enables GOPT's ability to perform inference on bins of varying dimensions. We conduct extensive experiments and demonstrate that GOPT not only achieves superior performance against the baselines, but also exhibits excellent generalization capabilities. Furthermore, the deployment with a robot showcases the practical applicability of our method in the real world. The source code will be publicly available at https://github.com/Xiong5Heng/GOPT.
Residual Squeeze-and-Excitation Network for Fast Image Deraining
Jun 01, 2020



Abstract:Image deraining is an important image processing task as rain streaks not only severely degrade the visual quality of images but also significantly affect the performance of high-level vision tasks. Traditional methods progressively remove rain streaks via different recurrent neural networks. However, these methods fail to yield plausible rain-free images in an efficient manner. In this paper, we propose a residual squeeze-and-excitation network called RSEN for fast image deraining as well as superior deraining performance compared with state-of-the-art approaches. Specifically, RSEN adopts a lightweight encoder-decoder architecture to conduct rain removal in one stage. Besides, both encoder and decoder adopt a novel residual squeeze-and-excitation block as the core of feature extraction, which contains a residual block for producing hierarchical features, followed by a squeeze-and-excitation block for channel-wisely enhancing the resulted hierarchical features. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can not only considerably reduce the computational complexity but also significantly improve the deraining performance compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Prior-enlightened and Motion-robust Video Deblurring
Mar 26, 2020



Abstract:Various blur distortions in video will cause negative impact on both human viewing and video-based applications, which makes motion-robust deblurring methods urgently needed. Most existing works have strong dataset dependency and limited generalization ability in handling challenging scenarios, like blur in low contrast or severe motion areas, and non-uniform blur. Therefore, we propose a PRiOr-enlightened and MOTION-robust video deblurring model (PROMOTION) suitable for challenging blurs. On the one hand, we use 3D group convolution to efficiently encode heterogeneous prior information, explicitly enhancing the scenes' perception while mitigating the output's artifacts. On the other hand, we design the priors representing blur distribution, to better handle non-uniform blur in spatio-temporal domain. Besides the classical camera shake caused global blurry, we also prove the generalization for the downstream task suffering from local blur. Extensive experiments demonstrate we can achieve the state-of-the-art performance on well-known REDS and GoPro datasets, and bring machine task gain.
SASL: Saliency-Adaptive Sparsity Learning for Neural Network Acceleration
Mar 12, 2020



Abstract:Accelerating the inference speed of CNNs is critical to their deployment in real-world applications. Among all the pruning approaches, those implementing a sparsity learning framework have shown to be effective as they learn and prune the models in an end-to-end data-driven manner. However, these works impose the same sparsity regularization on all filters indiscriminately, which can hardly result in an optimal structure-sparse network. In this paper, we propose a Saliency-Adaptive Sparsity Learning (SASL) approach for further optimization. A novel and effective estimation of each filter, i.e., saliency, is designed, which is measured from two aspects: the importance for the prediction performance and the consumed computational resources. During sparsity learning, the regularization strength is adjusted according to the saliency, so our optimized format can better preserve the prediction performance while zeroing out more computation-heavy filters. The calculation for saliency introduces minimum overhead to the training process, which means our SASL is very efficient. During the pruning phase, in order to optimize the proposed data-dependent criterion, a hard sample mining strategy is utilized, which shows higher effectiveness and efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our method. Notably, on ILSVRC-2012 dataset, our approach can reduce 49.7% FLOPs of ResNet-50 with very negligible 0.39% top-1 and 0.05% top-5 accuracy degradation.
CAIL2019-SCM: A Dataset of Similar Case Matching in Legal Domain
Nov 25, 2019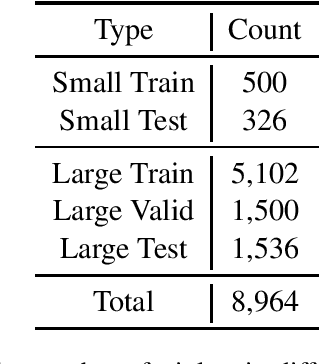
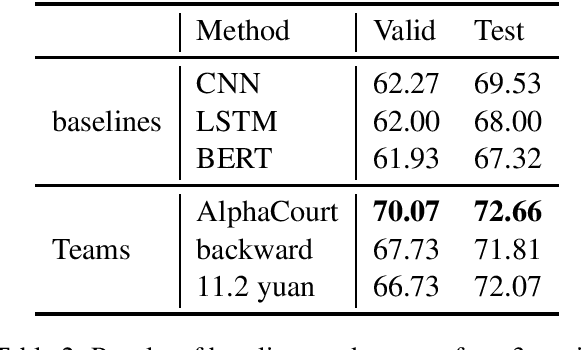
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce CAIL2019-SCM, Chinese AI and Law 2019 Similar Case Matching dataset. CAIL2019-SCM contains 8,964 triplets of cases published by the Supreme People's Court of China. CAIL2019-SCM focuses on detecting similar cases, and the participants are required to check which two cases are more similar in the triplets. There are 711 teams who participated in this year's competition, and the best team has reached a score of 71.88. We have also implemented several baselines to help researchers better understand this task. The dataset and more details can be found from https://github.com/china-ai-law-challenge/CAIL2019/tree/master/scm.
Overview of CAIL2018: Legal Judgment Prediction Competition
Oct 13, 2018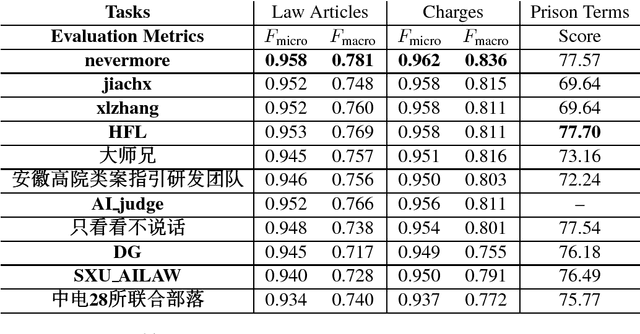
Abstract:In this paper, we give an overview of the Legal Judgment Prediction (LJP) competition at Chinese AI and Law challenge (CAIL2018). This competition focuses on LJP which aims to predict the judgment results according to the given facts. Specifically, in CAIL2018 , we proposed three subtasks of LJP for the contestants, i.e., predicting relevant law articles, charges and prison terms given the fact descriptions. CAIL2018 has attracted several hundreds participants (601 teams, 1, 144 contestants from 269 organizations). In this paper, we provide a detailed overview of the task definition, related works, outstanding methods and competition results in CAIL2018.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge