Xinan He
Simplicity Prevails: The Emergence of Generalizable AIGI Detection in Visual Foundation Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:While specialized detectors for AI-Generated Images (AIGI) achieve near-perfect accuracy on curated benchmarks, they suffer from a dramatic performance collapse in realistic, in-the-wild scenarios. In this work, we demonstrate that simplicity prevails over complex architectural designs. A simple linear classifier trained on the frozen features of modern Vision Foundation Models , including Perception Encoder, MetaCLIP 2, and DINOv3, establishes a new state-of-the-art. Through a comprehensive evaluation spanning traditional benchmarks, unseen generators, and challenging in-the-wild distributions, we show that this baseline not only matches specialized detectors on standard benchmarks but also decisively outperforms them on in-the-wild datasets, boosting accuracy by striking margins of over 30\%. We posit that this superior capability is an emergent property driven by the massive scale of pre-training data containing synthetic content. We trace the source of this capability to two distinct manifestations of data exposure: Vision-Language Models internalize an explicit semantic concept of forgery, while Self-Supervised Learning models implicitly acquire discriminative forensic features from the pretraining data. However, we also reveal persistent limitations: these models suffer from performance degradation under recapture and transmission, remain blind to VAE reconstruction and localized editing. We conclude by advocating for a paradigm shift in AI forensics, moving from overfitting on static benchmarks to harnessing the evolving world knowledge of foundation models for real-world reliability.
MPF-Net: Exposing High-Fidelity AI-Generated Video Forgeries via Hierarchical Manifold Deviation and Micro-Temporal Fluctuations
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement of video generation models such as Veo and Wan, the visual quality of synthetic content has reached a level where macro-level semantic errors and temporal inconsistencies are no longer prominent. However, this does not imply that the distinction between real and cutting-edge high-fidelity fake is untraceable. We argue that AI-generated videos are essentially products of a manifold-fitting process rather than a physical recording. Consequently, the pixel composition logic of consecutive adjacent frames residual in AI videos exhibits a structured and homogenous characteristic. We term this phenomenon `Manifold Projection Fluctuations' (MPF). Driven by this insight, we propose a hierarchical dual-path framework that operates as a sequential filtering process. The first, the Static Manifold Deviation Branch, leverages the refined perceptual boundaries of Large-Scale Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) to capture residual spatial anomalies or physical violations that deviate from the natural real-world manifold (off-manifold). For the remaining high-fidelity videos that successfully reside on-manifold and evade spatial detection, we introduce the Micro-Temporal Fluctuation Branch as a secondary, fine-grained filter. By analyzing the structured MPF that persists even in visually perfect sequences, our framework ensures that forgeries are exposed regardless of whether they manifest as global real-world manifold deviations or subtle computational fingerprints.
DiffFace-Edit: A Diffusion-Based Facial Dataset for Forgery-Semantic Driven Deepfake Detection Analysis
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Generative models now produce imperceptible, fine-grained manipulated faces, posing significant privacy risks. However, existing AI-generated face datasets generally lack focus on samples with fine-grained regional manipulations. Furthermore, no researchers have yet studied the real impact of splice attacks, which occur between real and manipulated samples, on detectors. We refer to these as detector-evasive samples. Based on this, we introduce the DiffFace-Edit dataset, which has the following advantages: 1) It contains over two million AI-generated fake images. 2) It features edits across eight facial regions (e.g., eyes, nose) and includes a richer variety of editing combinations, such as single-region and multi-region edits. Additionally, we specifically analyze the impact of detector-evasive samples on detection models. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of the dataset and propose a cross-domain evaluation that combines IMDL methods. Dataset will be available at https://github.com/ywh1093/DiffFace-Edit.
Fairness-Aware Deepfake Detection: Leveraging Dual-Mechanism Optimization
Nov 19, 2025



Abstract:Fairness is a core element in the trustworthy deployment of deepfake detection models, especially in the field of digital identity security. Biases in detection models toward different demographic groups, such as gender and race, may lead to systemic misjudgments, exacerbating the digital divide and social inequities. However, current fairness-enhanced detectors often improve fairness at the cost of detection accuracy. To address this challenge, we propose a dual-mechanism collaborative optimization framework. Our proposed method innovatively integrates structural fairness decoupling and global distribution alignment: decoupling channels sensitive to demographic groups at the model architectural level, and subsequently reducing the distance between the overall sample distribution and the distributions corresponding to each demographic group at the feature level. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared with other methods, our framework improves both inter-group and intra-group fairness while maintaining overall detection accuracy across domains.
Brought a Gun to a Knife Fight: Modern VFM Baselines Outgun Specialized Detectors on In-the-Wild AI Image Detection
Sep 16, 2025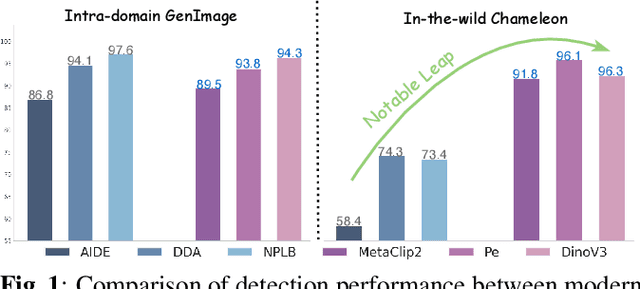
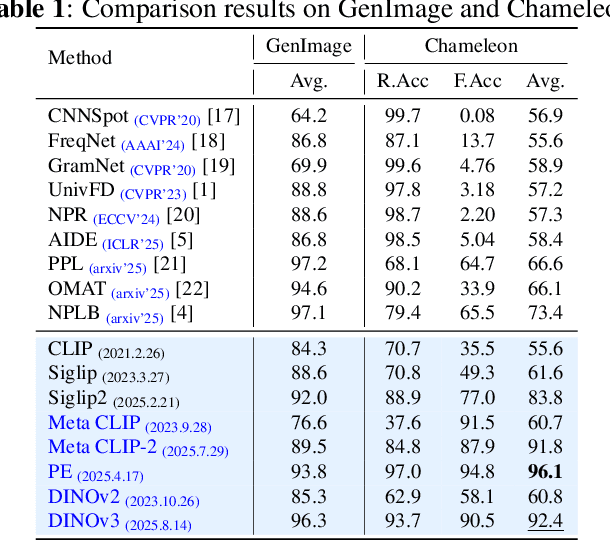
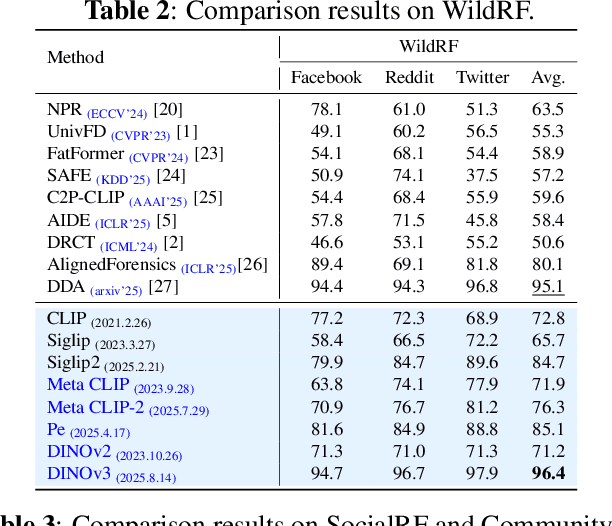
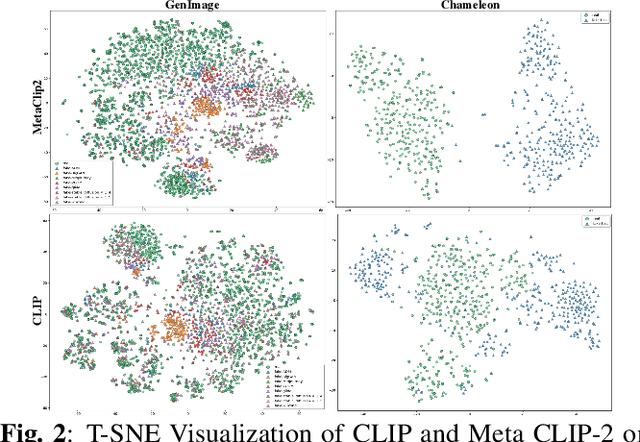
Abstract:While specialized detectors for AI-generated images excel on curated benchmarks, they fail catastrophically in real-world scenarios, as evidenced by their critically high false-negative rates on `in-the-wild' benchmarks. Instead of crafting another specialized `knife' for this problem, we bring a `gun' to the fight: a simple linear classifier on a modern Vision Foundation Model (VFM). Trained on identical data, this baseline decisively `outguns' bespoke detectors, boosting in-the-wild accuracy by a striking margin of over 20\%. Our analysis pinpoints the source of the VFM's `firepower': First, by probing text-image similarities, we find that recent VLMs (e.g., Perception Encoder, Meta CLIP2) have learned to align synthetic images with forgery-related concepts (e.g., `AI-generated'), unlike previous versions. Second, we speculate that this is due to data exposure, as both this alignment and overall accuracy plummet on a novel dataset scraped after the VFM's pre-training cut-off date, ensuring it was unseen during pre-training. Our findings yield two critical conclusions: 1) For the real-world `gunfight' of AI-generated image detection, the raw `firepower' of an updated VFM is far more effective than the `craftsmanship' of a static detector. 2) True generalization evaluation requires test data to be independent of the model's entire training history, including pre-training.
VLForgery Face Triad: Detection, Localization and Attribution via Multimodal Large Language Models
Mar 08, 2025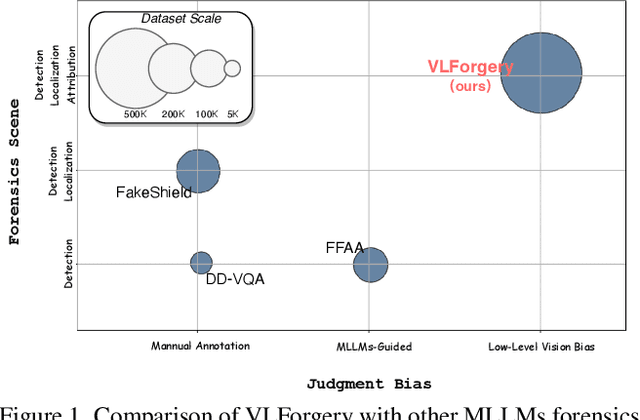

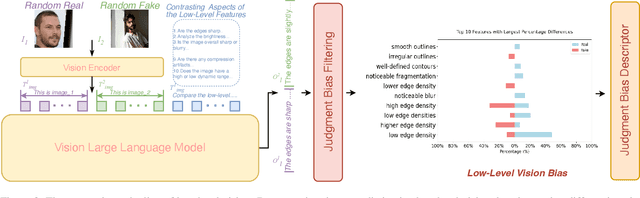

Abstract:Faces synthesized by diffusion models (DMs) with high-quality and controllable attributes pose a significant challenge for Deepfake detection. Most state-of-the-art detectors only yield a binary decision, incapable of forgery localization, attribution of forgery methods, and providing analysis on the cause of forgeries. In this work, we integrate Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) within DM-based face forensics, and propose a fine-grained analysis triad framework called VLForgery, that can 1) predict falsified facial images; 2) locate the falsified face regions subjected to partial synthesis; and 3) attribute the synthesis with specific generators. To achieve the above goals, we introduce VLF (Visual Language Forensics), a novel and diverse synthesis face dataset designed to facilitate rich interactions between Visual and Language modalities in MLLMs. Additionally, we propose an extrinsic knowledge-guided description method, termed EkCot, which leverages knowledge from the image generation pipeline to enable MLLMs to quickly capture image content. Furthermore, we introduce a low-level vision comparison pipeline designed to identify differential features between real and fake that MLLMs can inherently understand. These features are then incorporated into EkCot, enhancing its ability to analyze forgeries in a structured manner, following the sequence of detection, localization, and attribution. Extensive experiments demonstrate that VLForgery outperforms other state-of-the-art forensic approaches in detection accuracy, with additional potential for falsified region localization and attribution analysis.
FairAdapter: Detecting AI-generated Images with Improved Fairness
Nov 22, 2024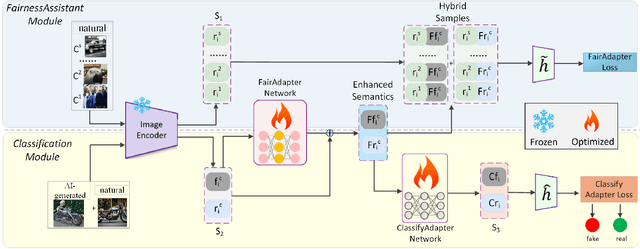
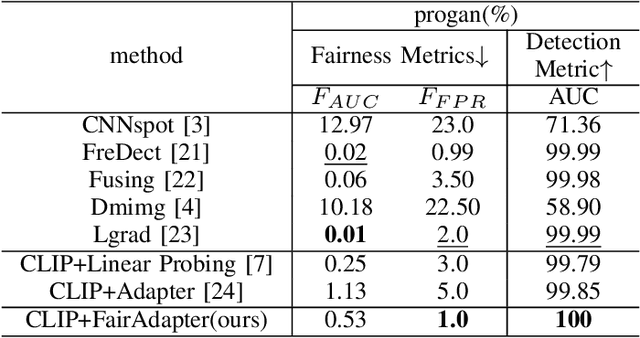
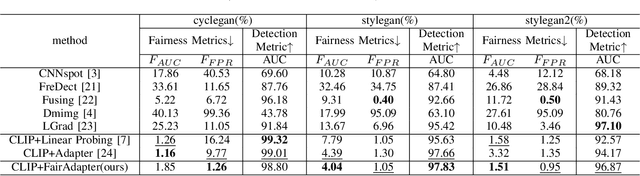
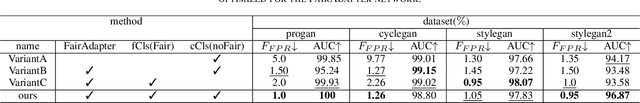
Abstract:The high-quality, realistic images generated by generative models pose significant challenges for exposing them.So far, data-driven deep neural networks have been justified as the most efficient forensics tools for the challenges. However, they may be over-fitted to certain semantics, resulting in considerable inconsistency in detection performance across different contents of generated samples. It could be regarded as an issue of detection fairness. In this paper, we propose a novel framework named Fairadapter to tackle the issue. In comparison with existing state-of-the-art methods, our model achieves improved fairness performance. Our project: https://github.com/AppleDogDog/FairnessDetection
Decoupling Forgery Semantics for Generalizable Deepfake Detection
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method for detecting DeepFakes, enhancing the generalization of detection through semantic decoupling. There are now multiple DeepFake forgery technologies that not only possess unique forgery semantics but may also share common forgery semantics. The unique forgery semantics and irrelevant content semantics may promote over-fitting and hamper generalization for DeepFake detectors. For our proposed method, after decoupling, the common forgery semantics could be extracted from DeepFakes, and subsequently be employed for developing the generalizability of DeepFake detectors. Also, to pursue additional generalizability, we designed an adaptive high-pass module and a two-stage training strategy to improve the independence of decoupled semantics. Evaluation on FF++, Celeb-DF, DFD, and DFDC datasets showcases our method's excellent detection and generalization performance. Code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DFS-GDD-0F42.
A3:Ambiguous Aberrations Captured via Astray-Learning for Facial Forgery Semantic Sublimation
May 24, 2024Abstract:Prior DeepFake detection methods have faced a core challenge in preserving generalizability and fairness effectively. In this paper, we proposed an approach akin to decoupling and sublimating forgery semantics, named astray-learning. The primary objective of the proposed method is to blend hybrid forgery semantics derived from high-frequency components into authentic imagery, named aberrations. The ambiguity of aberrations is beneficial to reducing the model's bias towards specific semantics. Consequently, it can enhance the model's generalization ability and maintain the detection fairness. All codes for astray-learning are publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/astray-learning-C49B .
Preserving Fairness Generalization in Deepfake Detection
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Although effective deepfake detection models have been developed in recent years, recent studies have revealed that these models can result in unfair performance disparities among demographic groups, such as race and gender. This can lead to particular groups facing unfair targeting or exclusion from detection, potentially allowing misclassified deepfakes to manipulate public opinion and undermine trust in the model. The existing method for addressing this problem is providing a fair loss function. It shows good fairness performance for intra-domain evaluation but does not maintain fairness for cross-domain testing. This highlights the significance of fairness generalization in the fight against deepfakes. In this work, we propose the first method to address the fairness generalization problem in deepfake detection by simultaneously considering features, loss, and optimization aspects. Our method employs disentanglement learning to extract demographic and domain-agnostic forgery features, fusing them to encourage fair learning across a flattened loss landscape. Extensive experiments on prominent deepfake datasets demonstrate our method's effectiveness, surpassing state-of-the-art approaches in preserving fairness during cross-domain deepfake detection. The code is available at https://github.com/Purdue-M2/Fairness-Generalization
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge