Can Zu
Advancing Translation Preference Modeling with RLHF: A Step Towards Cost-Effective Solution
Feb 27, 2024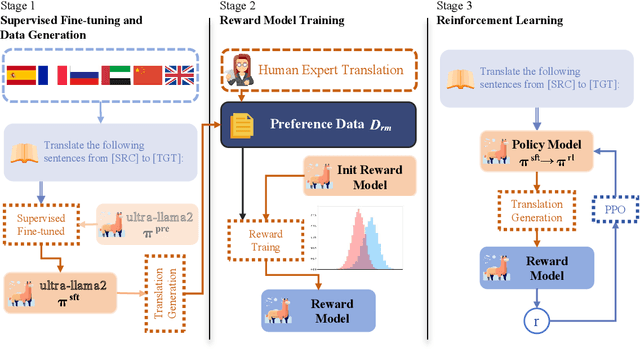

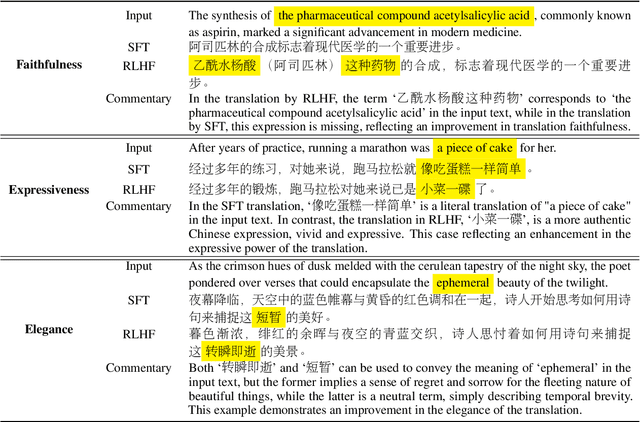
Abstract:Faithfulness, expressiveness, and elegance is the constant pursuit in machine translation. However, traditional metrics like \textit{BLEU} do not strictly align with human preference of translation quality. In this paper, we explore leveraging reinforcement learning with human feedback (\textit{RLHF}) to improve translation quality. It is non-trivial to collect a large high-quality dataset of human comparisons between translations, especially for low-resource languages. To address this issue, we propose a cost-effective preference learning strategy, optimizing reward models by distinguishing between human and machine translations. In this manner, the reward model learns the deficiencies of machine translation compared to human and guides subsequent improvements in machine translation. Experimental results demonstrate that \textit{RLHF} can effectively enhance translation quality and this improvement benefits other translation directions not trained with \textit{RLHF}. Further analysis indicates that the model's language capabilities play a crucial role in preference learning. A reward model with strong language capabilities can more sensitively learn the subtle differences in translation quality and align better with real human translation preferences.
LongAgent: Scaling Language Models to 128k Context through Multi-Agent Collaboration
Feb 18, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in understanding language and executing complex reasoning tasks. However, LLMs with long context windows have been notorious for their expensive training costs and high inference latency. Even the most advanced models such as GPT-4 and Claude2 often make mistakes when processing inputs of over $100k$ tokens, a phenomenon also known as \textit{lost in the middle}. In this paper, we propose \textsc{LongAgent}, a method based on multi-agent collaboration, which scales LLMs (e.g., LLaMA) to a context of 128K and demonstrates potential superiority in long-text processing compared to GPT-4. In \textsc{LongAgent}, a leader is responsible for understanding user intent and directing team members to acquire information from documents. Due to members' hallucinations, it is non-trivial for a leader to obtain accurate information from the responses of dozens to hundreds of members. To address this, we develop an \textit{inter-member communication} mechanism to resolve response conflicts caused by hallucinations through information sharing. Our experimental results indicate that \textsc{LongAgent} offers a promising alternative for long-text processing. The agent team instantiated with LLaMA-7B achieves significant improvements in tasks such as 128k-long text retrieval, multi-hop question answering, compared to GPT-4.
InstructUIE: Multi-task Instruction Tuning for Unified Information Extraction
Apr 17, 2023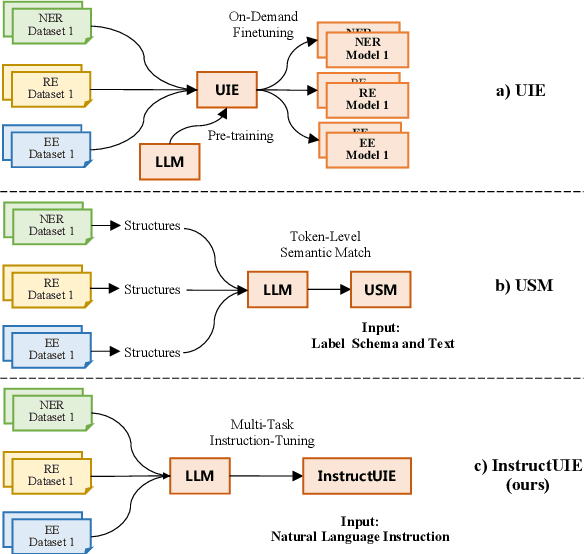
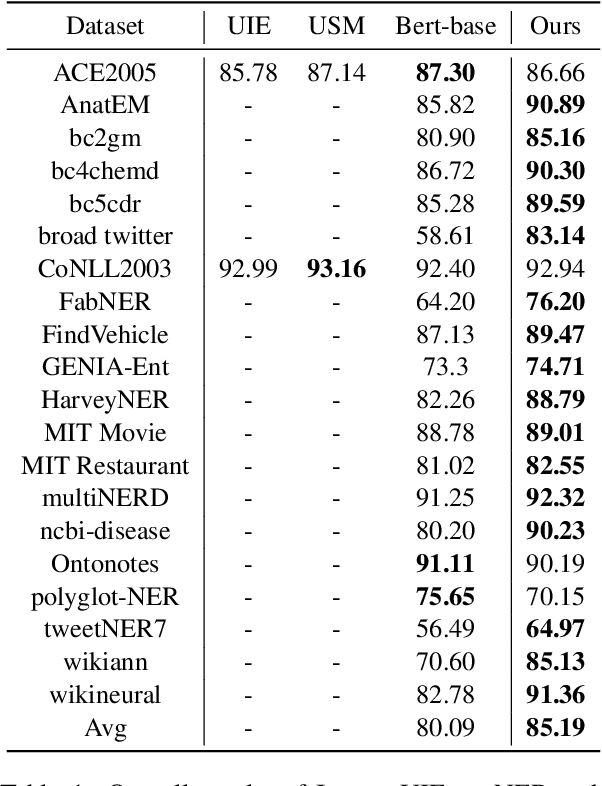
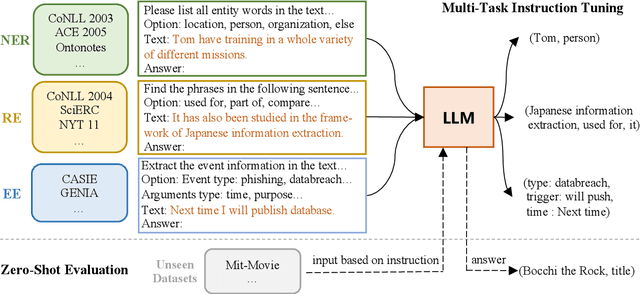
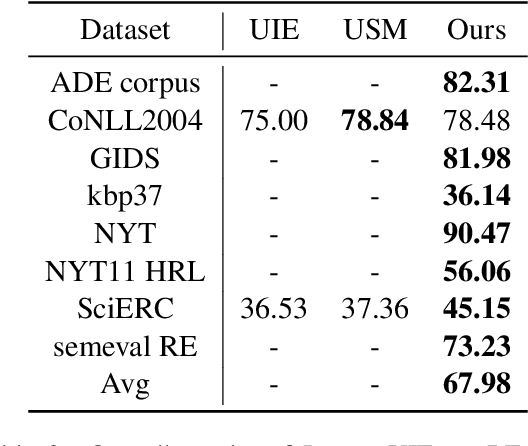
Abstract:Large language models have unlocked strong multi-task capabilities from reading instructive prompts. However, recent studies have shown that existing large models still have difficulty with information extraction tasks. For example, gpt-3.5-turbo achieved an F1 score of 18.22 on the Ontonotes dataset, which is significantly lower than the state-of-the-art performance. In this paper, we propose InstructUIE, a unified information extraction framework based on instruction tuning, which can uniformly model various information extraction tasks and capture the inter-task dependency. To validate the proposed method, we introduce IE INSTRUCTIONS, a benchmark of 32 diverse information extraction datasets in a unified text-to-text format with expert-written instructions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves comparable performance to Bert in supervised settings and significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art and gpt3.5 in zero-shot settings.
A Comprehensive Capability Analysis of GPT-3 and GPT-3.5 Series Models
Mar 18, 2023
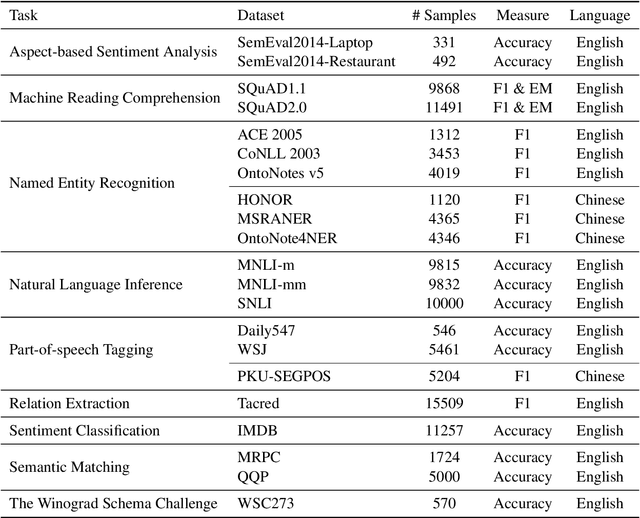
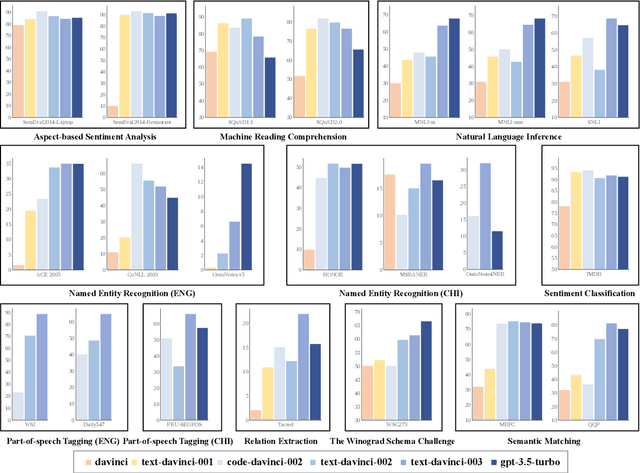
Abstract:GPT series models, such as GPT-3, CodeX, InstructGPT, ChatGPT, and so on, have gained considerable attention due to their exceptional natural language processing capabilities. However, despite the abundance of research on the difference in capabilities between GPT series models and fine-tuned models, there has been limited attention given to the evolution of GPT series models' capabilities over time. To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the capabilities of GPT series models, we select six representative models, comprising two GPT-3 series models (i.e., davinci and text-davinci-001) and four GPT-3.5 series models (i.e., code-davinci-002, text-davinci-002, text-davinci-003, and gpt-3.5-turbo). We evaluate their performance on nine natural language understanding (NLU) tasks using 21 datasets. In particular, we compare the performance and robustness of different models for each task under zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Our extensive experiments reveal that the overall ability of GPT series models on NLU tasks does not increase gradually as the models evolve, especially with the introduction of the RLHF training strategy. While this strategy enhances the models' ability to generate human-like responses, it also compromises their ability to solve some tasks. Furthermore, our findings indicate that there is still room for improvement in areas such as model robustness.
How Robust is GPT-3.5 to Predecessors? A Comprehensive Study on Language Understanding Tasks
Mar 01, 2023

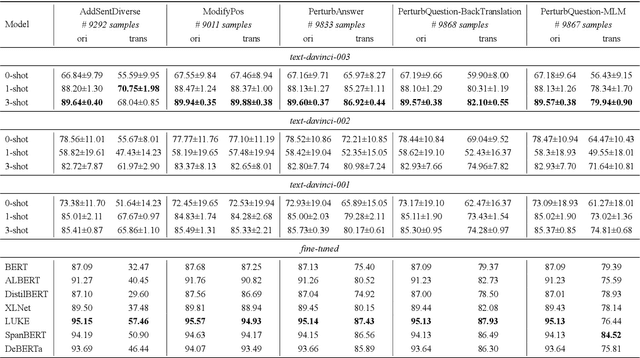

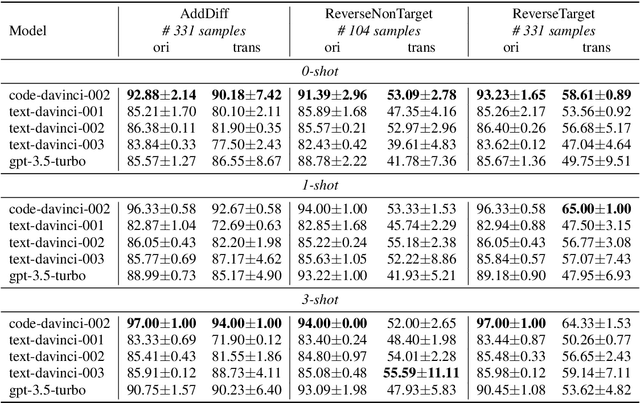
Abstract:The GPT-3.5 models have demonstrated impressive performance in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, showcasing their strong understanding and reasoning capabilities. However, their robustness and abilities to handle various complexities of the open world have yet to be explored, which is especially crucial in assessing the stability of models and is a key aspect of trustworthy AI. In this study, we perform a comprehensive experimental analysis of GPT-3.5, exploring its robustness using 21 datasets (about 116K test samples) with 66 text transformations from TextFlint that cover 9 popular Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks. Our findings indicate that while GPT-3.5 outperforms existing fine-tuned models on some tasks, it still encounters significant robustness degradation, such as its average performance dropping by up to 35.74\% and 43.59\% in natural language inference and sentiment analysis tasks, respectively. We also show that GPT-3.5 faces some specific robustness challenges, including robustness instability, prompt sensitivity, and number sensitivity. These insights are valuable for understanding its limitations and guiding future research in addressing these challenges to enhance GPT-3.5's overall performance and generalization abilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge