A Comprehensive Capability Analysis of GPT-3 and GPT-3.5 Series Models
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2023
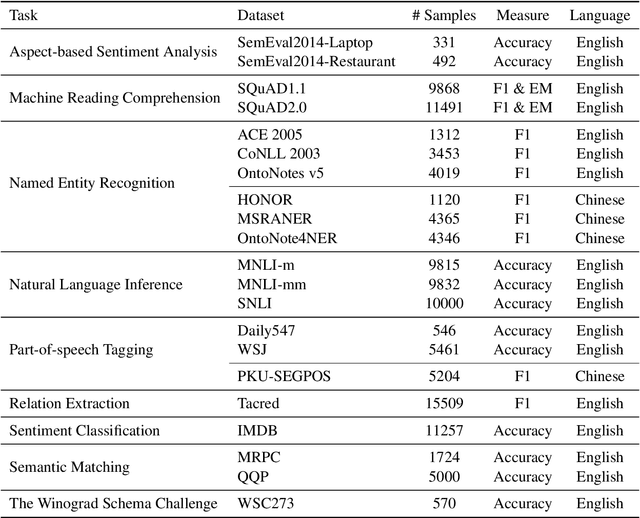
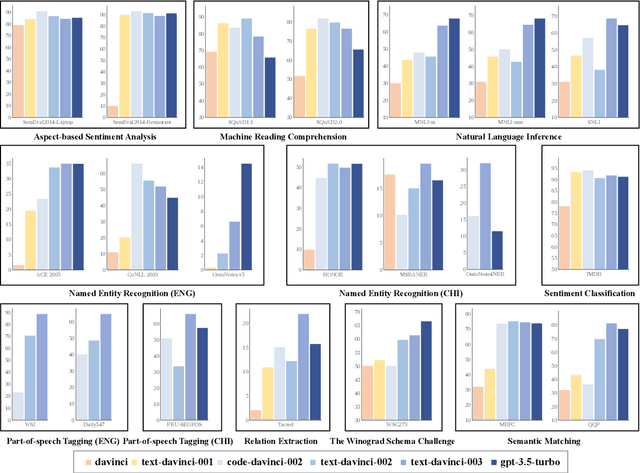
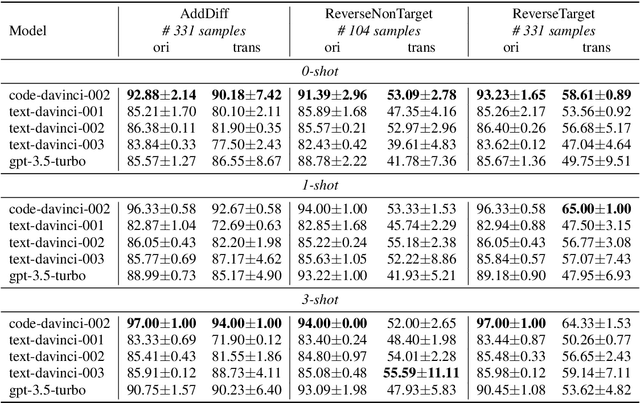
GPT series models, such as GPT-3, CodeX, InstructGPT, ChatGPT, and so on, have gained considerable attention due to their exceptional natural language processing capabilities. However, despite the abundance of research on the difference in capabilities between GPT series models and fine-tuned models, there has been limited attention given to the evolution of GPT series models' capabilities over time. To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the capabilities of GPT series models, we select six representative models, comprising two GPT-3 series models (i.e., davinci and text-davinci-001) and four GPT-3.5 series models (i.e., code-davinci-002, text-davinci-002, text-davinci-003, and gpt-3.5-turbo). We evaluate their performance on nine natural language understanding (NLU) tasks using 21 datasets. In particular, we compare the performance and robustness of different models for each task under zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Our extensive experiments reveal that the overall ability of GPT series models on NLU tasks does not increase gradually as the models evolve, especially with the introduction of the RLHF training strategy. While this strategy enhances the models' ability to generate human-like responses, it also compromises their ability to solve some tasks. Furthermore, our findings indicate that there is still room for improvement in areas such as model robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge