Bruno Loureiro
Optimal scaling laws in learning hierarchical multi-index models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:In this work, we provide a sharp theory of scaling laws for two-layer neural networks trained on a class of hierarchical multi-index targets, in a genuinely representation-limited regime. We derive exact information-theoretic scaling laws for subspace recovery and prediction error, revealing how the hierarchical features of the target are sequentially learned through a cascade of phase transitions. We further show that these optimal rates are achieved by a simple, target-agnostic spectral estimator, which can be interpreted as the small learning-rate limit of gradient descent on the first-layer weights. Once an adapted representation is identified, the readout can be learned statistically optimally, using an efficient procedure. As a consequence, we provide a unified and rigorous explanation of scaling laws, plateau phenomena, and spectral structure in shallow neural networks trained on such hierarchical targets.
When pre-training hurts LoRA fine-tuning: a dynamical analysis via single-index models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Pre-training on a source task is usually expected to facilitate fine-tuning on similar downstream problems. In this work, we mathematically show that this naive intuition is not always true: excessive pre-training can computationally slow down fine-tuning optimization. We study this phenomenon for low-rank adaptation (LoRA) fine-tuning on single-index models trained under one-pass SGD. Leveraging a summary statistics description of the fine-tuning dynamics, we precisely characterize how the convergence rate depends on the initial fine-tuning alignment and the degree of non-linearity of the target task. The key take away is that even when the pre-training and down- stream tasks are well aligned, strong pre-training can induce a prolonged search phase and hinder convergence. Our theory thus provides a unified picture of how pre-training strength and task difficulty jointly shape the dynamics and limitations of LoRA fine-tuning in a nontrivial tractable model.
A Random Matrix Theory of Masked Self-Supervised Regression
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:In the era of transformer models, masked self-supervised learning (SSL) has become a foundational training paradigm. A defining feature of masked SSL is that training aggregates predictions across many masking patterns, giving rise to a joint, matrix-valued predictor rather than a single vector-valued estimator. This object encodes how coordinates condition on one another and poses new analytical challenges. We develop a precise high-dimensional analysis of masked modeling objectives in the proportional regime where the number of samples scales with the ambient dimension. Our results provide explicit expressions for the generalization error and characterize the spectral structure of the learned predictor, revealing how masked modeling extracts structure from data. For spiked covariance models, we show that the joint predictor undergoes a Baik--Ben Arous--Péché (BBP)-type phase transition, identifying when masked SSL begins to recover latent signals. Finally, we identify structured regimes in which masked self-supervised learning provably outperforms PCA, highlighting potential advantages of SSL objectives over classical unsupervised methods
Kernel ridge regression under power-law data: spectrum and generalization
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:In this work, we investigate high-dimensional kernel ridge regression (KRR) on i.i.d. Gaussian data with anisotropic power-law covariance. This setting differs fundamentally from the classical source & capacity conditions for KRR, where power-law assumptions are typically imposed on the kernel eigen-spectrum itself. Our contributions are twofold. First, we derive an explicit characterization of the kernel spectrum for polynomial inner-product kernels, giving a precise description of how the kernel eigen-spectrum inherits the data decay. Second, we provide an asymptotic analysis of the excess risk in the high-dimensional regime for a particular kernel with this spectral behavior, showing that the sample complexity is governed by the effective dimension of the data rather than the ambient dimension. These results establish a fundamental advantage of learning with power-law anisotropic data over isotropic data. To our knowledge, this is the first rigorous treatment of non-linear KRR under power-law data.
On the existence of consistent adversarial attacks in high-dimensional linear classification
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:What fundamentally distinguishes an adversarial attack from a misclassification due to limited model expressivity or finite data? In this work, we investigate this question in the setting of high-dimensional binary classification, where statistical effects due to limited data availability play a central role. We introduce a new error metric that precisely capture this distinction, quantifying model vulnerability to consistent adversarial attacks -- perturbations that preserve the ground-truth labels. Our main technical contribution is an exact and rigorous asymptotic characterization of these metrics in both well-specified models and latent space models, revealing different vulnerability patterns compared to standard robust error measures. The theoretical results demonstrate that as models become more overparameterized, their vulnerability to label-preserving perturbations grows, offering theoretical insight into the mechanisms underlying model sensitivity to adversarial attacks.
Optimal Spectral Transitions in High-Dimensional Multi-Index Models
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:We consider the problem of how many samples from a Gaussian multi-index model are required to weakly reconstruct the relevant index subspace. Despite its increasing popularity as a testbed for investigating the computational complexity of neural networks, results beyond the single-index setting remain elusive. In this work, we introduce spectral algorithms based on the linearization of a message passing scheme tailored to this problem. Our main contribution is to show that the proposed methods achieve the optimal reconstruction threshold. Leveraging a high-dimensional characterization of the algorithms, we show that above the critical threshold the leading eigenvector correlates with the relevant index subspace, a phenomenon reminiscent of the Baik-Ben Arous-Peche (BBP) transition in spiked models arising in random matrix theory. Supported by numerical experiments and a rigorous theoretical framework, our work bridges critical gaps in the computational limits of weak learnability in multi-index model.
A Random Matrix Theory Perspective on the Spectrum of Learned Features and Asymptotic Generalization Capabilities
Oct 24, 2024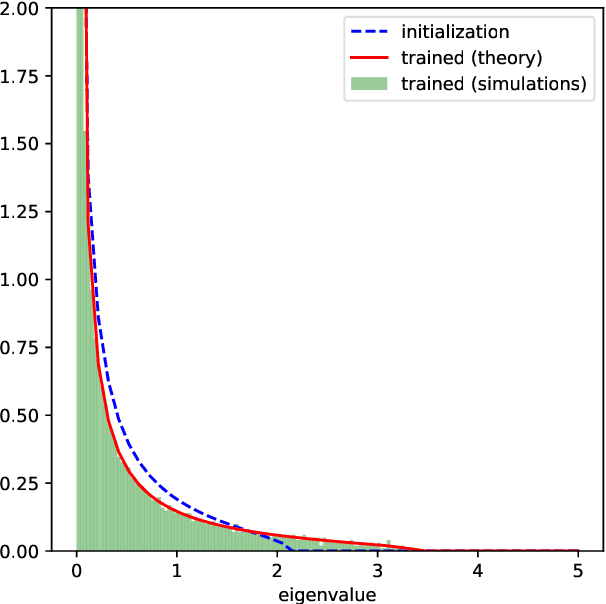
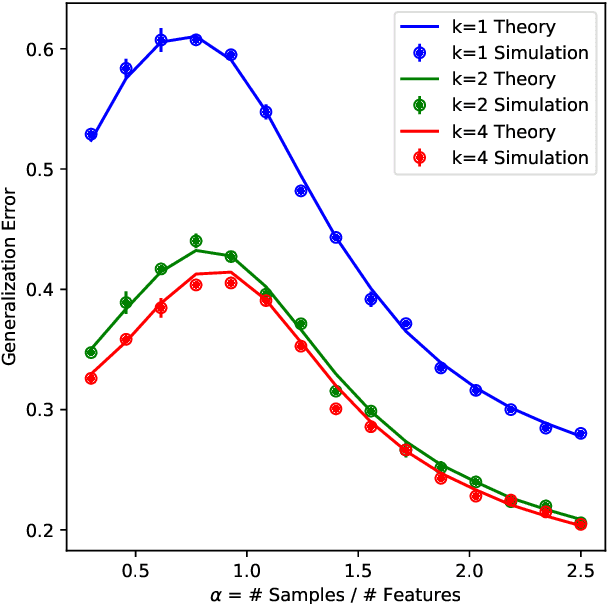
Abstract:A key property of neural networks is their capacity of adapting to data during training. Yet, our current mathematical understanding of feature learning and its relationship to generalization remain limited. In this work, we provide a random matrix analysis of how fully-connected two-layer neural networks adapt to the target function after a single, but aggressive, gradient descent step. We rigorously establish the equivalence between the updated features and an isotropic spiked random feature model, in the limit of large batch size. For the latter model, we derive a deterministic equivalent description of the feature empirical covariance matrix in terms of certain low-dimensional operators. This allows us to sharply characterize the impact of training in the asymptotic feature spectrum, and in particular, provides a theoretical grounding for how the tails of the feature spectrum modify with training. The deterministic equivalent further yields the exact asymptotic generalization error, shedding light on the mechanisms behind its improvement in the presence of feature learning. Our result goes beyond standard random matrix ensembles, and therefore we believe it is of independent technical interest. Different from previous work, our result holds in the challenging maximal learning rate regime, is fully rigorous and allows for finitely supported second layer initialization, which turns out to be crucial for studying the functional expressivity of the learned features. This provides a sharp description of the impact of feature learning in the generalization of two-layer neural networks, beyond the random features and lazy training regimes.
On the Geometry of Regularization in Adversarial Training: High-Dimensional Asymptotics and Generalization Bounds
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Regularization, whether explicit in terms of a penalty in the loss or implicit in the choice of algorithm, is a cornerstone of modern machine learning. Indeed, controlling the complexity of the model class is particularly important when data is scarce, noisy or contaminated, as it translates a statistical belief on the underlying structure of the data. This work investigates the question of how to choose the regularization norm $\lVert \cdot \rVert$ in the context of high-dimensional adversarial training for binary classification. To this end, we first derive an exact asymptotic description of the robust, regularized empirical risk minimizer for various types of adversarial attacks and regularization norms (including non-$\ell_p$ norms). We complement this analysis with a uniform convergence analysis, deriving bounds on the Rademacher Complexity for this class of problems. Leveraging our theoretical results, we quantitatively characterize the relationship between perturbation size and the optimal choice of $\lVert \cdot \rVert$, confirming the intuition that, in the data scarce regime, the type of regularization becomes increasingly important for adversarial training as perturbations grow in size.
A theoretical perspective on mode collapse in variational inference
Oct 17, 2024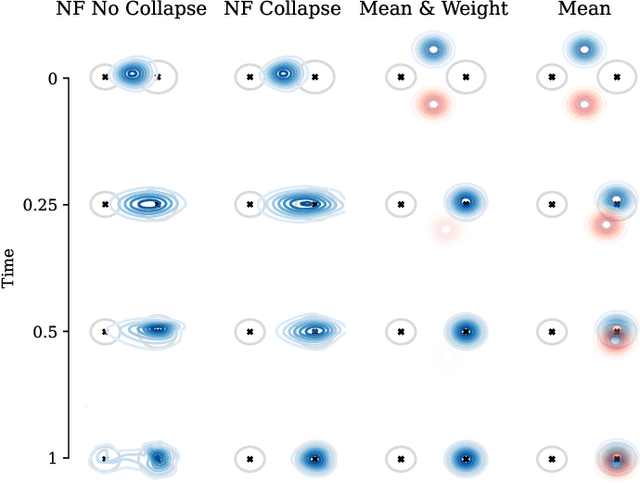

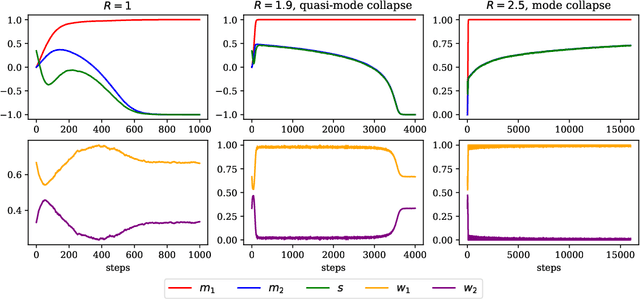

Abstract:While deep learning has expanded the possibilities for highly expressive variational families, the practical benefits of these tools for variational inference (VI) are often limited by the minimization of the traditional Kullback-Leibler objective, which can yield suboptimal solutions. A major challenge in this context is \emph{mode collapse}: the phenomenon where a model concentrates on a few modes of the target distribution during training, despite being statistically capable of expressing them all. In this work, we carry a theoretical investigation of mode collapse for the gradient flow on Gaussian mixture models. We identify the key low-dimensional statistics characterizing the flow, and derive a closed set of low-dimensional equations governing their evolution. Leveraging this compact description, we show that mode collapse is present even in statistically favorable scenarios, and identify two key mechanisms driving it: mean alignment and vanishing weight. Our theoretical findings are consistent with the implementation of VI using normalizing flows, a class of popular generative models, thereby offering practical insights.
Online Learning and Information Exponents: On The Importance of Batch size, and Time/Complexity Tradeoffs
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:We study the impact of the batch size $n_b$ on the iteration time $T$ of training two-layer neural networks with one-pass stochastic gradient descent (SGD) on multi-index target functions of isotropic covariates. We characterize the optimal batch size minimizing the iteration time as a function of the hardness of the target, as characterized by the information exponents. We show that performing gradient updates with large batches $n_b \lesssim d^{\frac{\ell}{2}}$ minimizes the training time without changing the total sample complexity, where $\ell$ is the information exponent of the target to be learned \citep{arous2021online} and $d$ is the input dimension. However, larger batch sizes than $n_b \gg d^{\frac{\ell}{2}}$ are detrimental for improving the time complexity of SGD. We provably overcome this fundamental limitation via a different training protocol, \textit{Correlation loss SGD}, which suppresses the auto-correlation terms in the loss function. We show that one can track the training progress by a system of low-dimensional ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Finally, we validate our theoretical results with numerical experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge