Boliang Zhang
GOD model: Privacy Preserved AI School for Personal Assistant
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:Personal AI assistants (e.g., Apple Intelligence, Meta AI) offer proactive recommendations that simplify everyday tasks, but their reliance on sensitive user data raises concerns about privacy and trust. To address these challenges, we introduce the Guardian of Data (GOD), a secure, privacy-preserving framework for training and evaluating AI assistants directly on-device. Unlike traditional benchmarks, the GOD model measures how well assistants can anticipate user needs-such as suggesting gifts-while protecting user data and autonomy. Functioning like an AI school, it addresses the cold start problem by simulating user queries and employing a curriculum-based approach to refine the performance of each assistant. Running within a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), it safeguards user data while applying reinforcement and imitation learning to refine AI recommendations. A token-based incentive system encourages users to share data securely, creating a data flywheel that drives continuous improvement. By integrating privacy, personalization, and trust, the GOD model provides a scalable, responsible path for advancing personal AI assistants. For community collaboration, part of the framework is open-sourced at https://github.com/PIN-AI/God-Model.
MeetDot: Videoconferencing with Live Translation Captions
Sep 20, 2021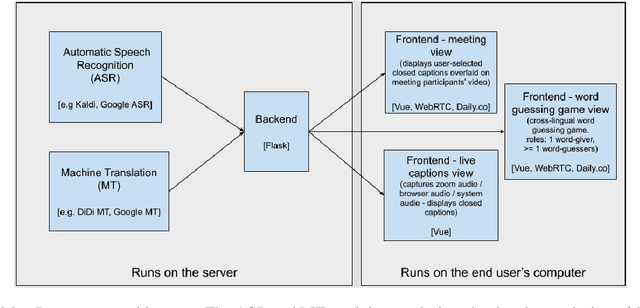
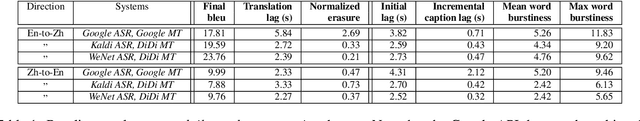
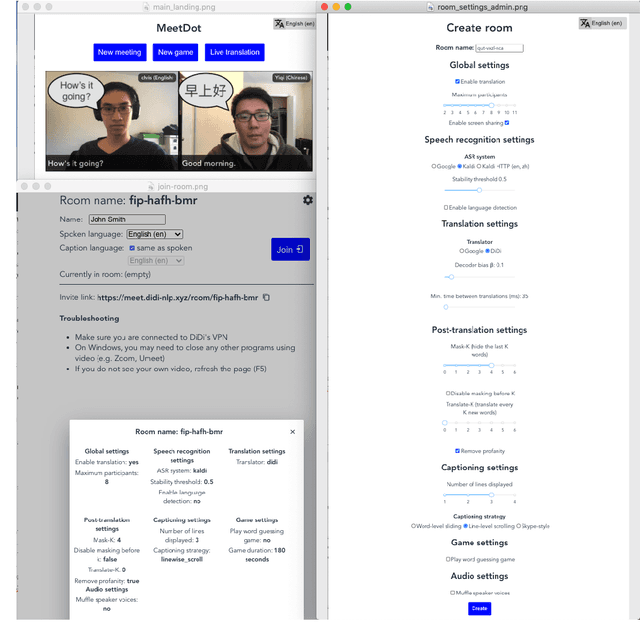
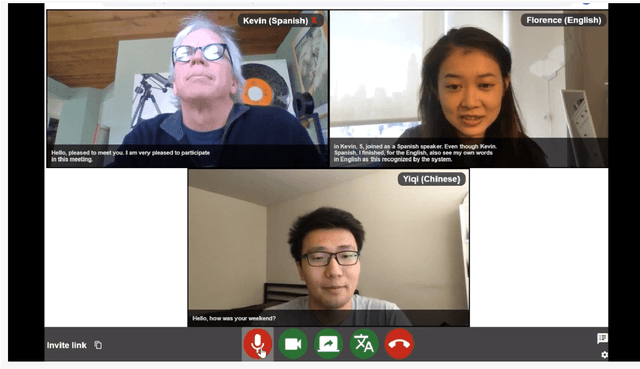
Abstract:We present MeetDot, a videoconferencing system with live translation captions overlaid on screen. The system aims to facilitate conversation between people who speak different languages, thereby reducing communication barriers between multilingual participants. Currently, our system supports speech and captions in 4 languages and combines automatic speech recognition (ASR) and machine translation (MT) in a cascade. We use the re-translation strategy to translate the streamed speech, resulting in caption flicker. Additionally, our system has very strict latency requirements to have acceptable call quality. We implement several features to enhance user experience and reduce their cognitive load, such as smooth scrolling captions and reducing caption flicker. The modular architecture allows us to integrate different ASR and MT services in our backend. Our system provides an integrated evaluation suite to optimize key intrinsic evaluation metrics such as accuracy, latency and erasure. Finally, we present an innovative cross-lingual word-guessing game as an extrinsic evaluation metric to measure end-to-end system performance. We plan to make our system open-source for research purposes.
A Hybrid Task-Oriented Dialog System with Domain and Task Adaptive Pretraining
Feb 08, 2021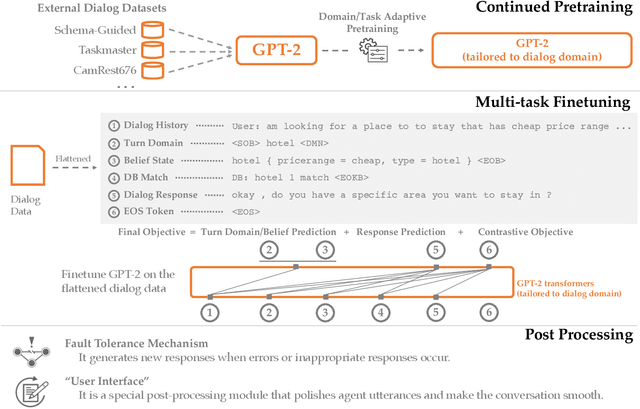
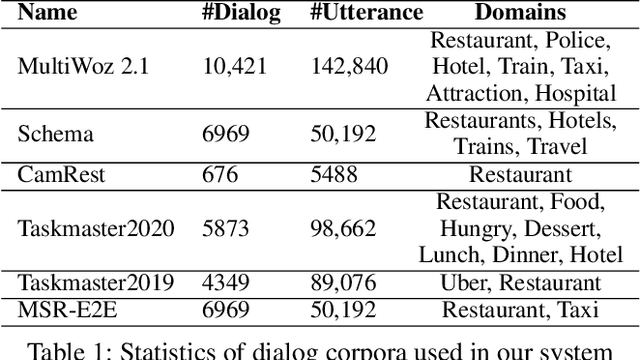
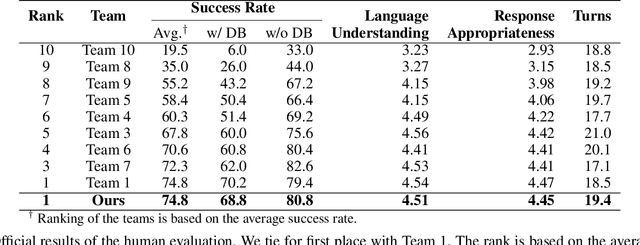
Abstract:This paper describes our submission for the End-to-end Multi-domain Task Completion Dialog shared task at the 9th Dialog System Technology Challenge (DSTC-9). Participants in the shared task build an end-to-end task completion dialog system which is evaluated by human evaluation and a user simulator based automatic evaluation. Different from traditional pipelined approaches where modules are optimized individually and suffer from cascading failure, we propose an end-to-end dialog system that 1) uses Generative Pretraining 2 (GPT-2) as the backbone to jointly solve Natural Language Understanding, Dialog State Tracking, and Natural Language Generation tasks, 2) adopts Domain and Task Adaptive Pretraining to tailor GPT-2 to the dialog domain before finetuning, 3) utilizes heuristic pre/post-processing rules that greatly simplify the prediction tasks and improve generalizability, and 4) equips a fault tolerance module to correct errors and inappropriate responses. Our proposed method significantly outperforms baselines and ties for first place in the official evaluation. We make our source code publicly available.
Global Attention for Name Tagging
Oct 19, 2020



Abstract:Many name tagging approaches use local contextual information with much success, but fail when the local context is ambiguous or limited. We present a new framework to improve name tagging by utilizing local, document-level, and corpus-level contextual information. We retrieve document-level context from other sentences within the same document and corpus-level context from sentences in other topically related documents. We propose a model that learns to incorporate document-level and corpus-level contextual information alongside local contextual information via global attentions, which dynamically weight their respective contextual information, and gating mechanisms, which determine the influence of this information. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show the effectiveness of our approach, which achieves state-of-the-art results for Dutch, German, and Spanish on the CoNLL-2002 and CoNLL-2003 datasets.
MEEP: An Open-Source Platform for Human-Human Dialog Collection and End-to-End Agent Training
Oct 09, 2020
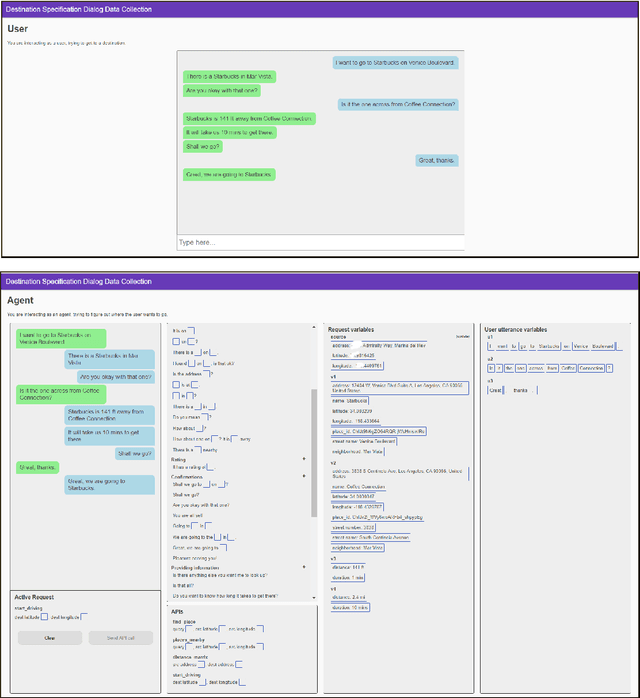


Abstract:We create a new task-oriented dialog platform (MEEP) where agents are given considerable freedom in terms of utterances and API calls, but are constrained to work within a push-button environment. We include facilities for collecting human-human dialog corpora, and for training automatic agents in an end-to-end fashion. We demonstrate MEEP with a dialog assistant that lets users specify trip destinations.
Parallel Corpus Filtering via Pre-trained Language Models
May 13, 2020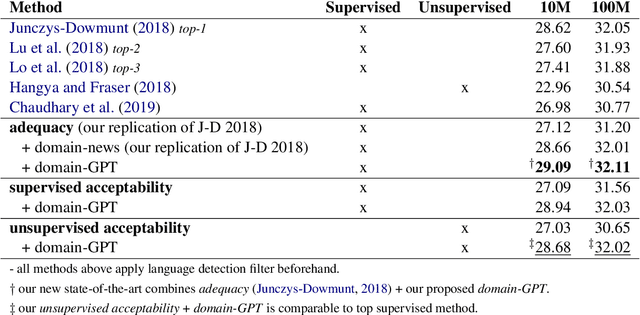
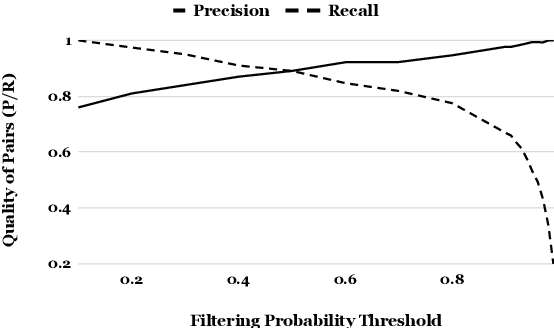
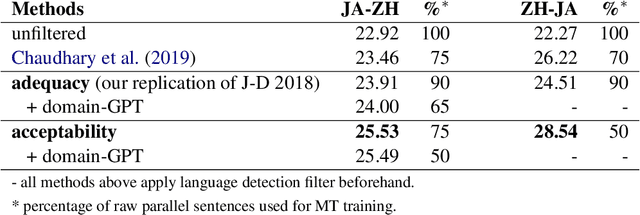
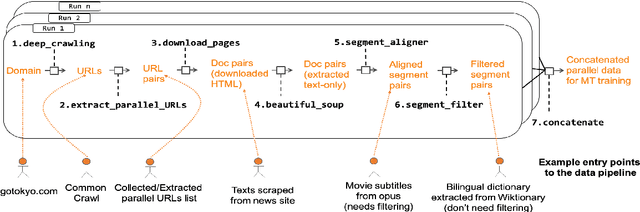
Abstract:Web-crawled data provides a good source of parallel corpora for training machine translation models. It is automatically obtained, but extremely noisy, and recent work shows that neural machine translation systems are more sensitive to noise than traditional statistical machine translation methods. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to filter out noisy sentence pairs from web-crawled corpora via pre-trained language models. We measure sentence parallelism by leveraging the multilingual capability of BERT and use the Generative Pre-training (GPT) language model as a domain filter to balance data domains. We evaluate the proposed method on the WMT 2018 Parallel Corpus Filtering shared task, and on our own web-crawled Japanese-Chinese parallel corpus. Our method significantly outperforms baselines and achieves a new state-of-the-art. In an unsupervised setting, our method achieves comparable performance to the top-1 supervised method. We also evaluate on a web-crawled Japanese-Chinese parallel corpus that we make publicly available.
Describing a Knowledge Base
Sep 30, 2018



Abstract:We aim to automatically generate natural language descriptions about an input structured knowledge base (KB). We build our generation framework based on a pointer network which can copy facts from the input KB, and add two attention mechanisms: (i) slot-aware attention to capture the association between a slot type and its corresponding slot value; and (ii) a new \emph{table position self-attention} to capture the inter-dependencies among related slots. For evaluation, besides standard metrics including BLEU, METEOR, and ROUGE, we propose a KB reconstruction based metric by extracting a KB from the generation output and comparing it with the input KB. We also create a new data set which includes 106,216 pairs of structured KBs and their corresponding natural language descriptions for two distinct entity types. Experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The reconstructed KB achieves 68.8% - 72.6% F-score.
Paper Abstract Writing through Editing Mechanism
May 15, 2018



Abstract:We present a paper abstract writing system based on an attentive neural sequence-to-sequence model that can take a title as input and automatically generate an abstract. We design a novel Writing-editing Network that can attend to both the title and the previously generated abstract drafts and then iteratively revise and polish the abstract. With two series of Turing tests, where the human judges are asked to distinguish the system-generated abstracts from human-written ones, our system passes Turing tests by junior domain experts at a rate up to 30% and by non-expert at a rate up to 80%.
Multi-lingual Common Semantic Space Construction via Cluster-consistent Word Embedding
Apr 21, 2018



Abstract:We construct a multilingual common semantic space based on distributional semantics, where words from multiple languages are projected into a shared space to enable knowledge and resource transfer across languages. Beyond word alignment, we introduce multiple cluster-level alignments and enforce the word clusters to be consistently distributed across multiple languages. We exploit three signals for clustering: (1) neighbor words in the monolingual word embedding space; (2) character-level information; and (3) linguistic properties (e.g., apposition, locative suffix) derived from linguistic structure knowledge bases available for thousands of languages. We introduce a new cluster-consistent correlational neural network to construct the common semantic space by aligning words as well as clusters. Intrinsic evaluation on monolingual and multilingual QVEC tasks shows our approach achieves significantly higher correlation with linguistic features than state-of-the-art multi-lingual embedding learning methods do. Using low-resource language name tagging as a case study for extrinsic evaluation, our approach achieves up to 24.5\% absolute F-score gain over the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge