Ashish Sirasao
SDFP: Speculative Decoding with FIT-Pruned Models for Training-Free and Plug-and-Play LLM Acceleration
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) underpin interactive multimedia applications such as captioning, retrieval, recommendation, and creative content generation, yet their autoregressive decoding incurs substantial latency. Speculative decoding reduces latency using a lightweight draft model, but deployment is often limited by the cost and complexity of acquiring, tuning, and maintaining an effective draft model. Recent approaches usually require auxiliary training or specialization, and even training-free methods incur costly search or optimization. We propose SDFP, a fully training-free and plug-and-play framework that builds the draft model via Fisher Information Trace (FIT)-based layer pruning of a given LLM. Using layer sensitivity as a proxy for output perturbation, SDFP removes low-impact layers to obtain a compact draft while preserving compatibility with the original model for standard speculative verification. SDFP needs no additional training, hyperparameter tuning, or separately maintained drafts, enabling rapid, deployment-friendly draft construction. Across benchmarks, SDFP delivers 1.32x-1.5x decoding speedup without altering the target model's output distribution, supporting low-latency multimedia applications.
DiP-GO: A Diffusion Pruner via Few-step Gradient Optimization
Oct 22, 2024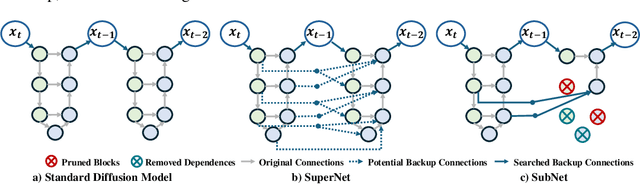
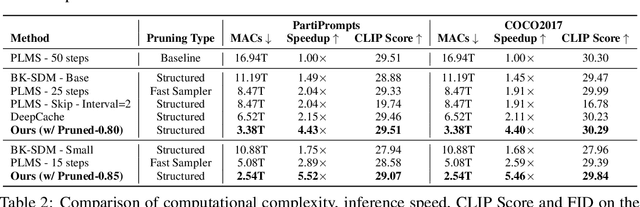
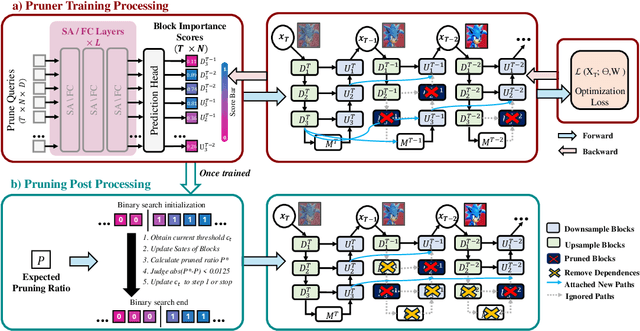
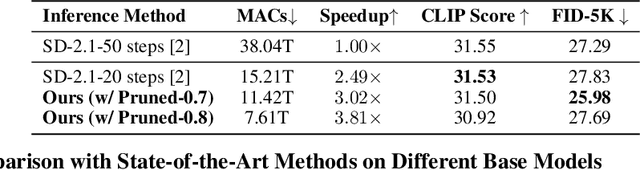
Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in the field of image generation due to their outstanding capabilities. However, these models require substantial computing resources because of the multi-step denoising process during inference. While traditional pruning methods have been employed to optimize these models, the retraining process necessitates large-scale training datasets and extensive computational costs to maintain generalization ability, making it neither convenient nor efficient. Recent studies attempt to utilize the similarity of features across adjacent denoising stages to reduce computational costs through simple and static strategies. However, these strategies cannot fully harness the potential of the similar feature patterns across adjacent timesteps. In this work, we propose a novel pruning method that derives an efficient diffusion model via a more intelligent and differentiable pruner. At the core of our approach is casting the model pruning process into a SubNet search process. Specifically, we first introduce a SuperNet based on standard diffusion via adding some backup connections built upon the similar features. We then construct a plugin pruner network and design optimization losses to identify redundant computation. Finally, our method can identify an optimal SubNet through few-step gradient optimization and a simple post-processing procedure. We conduct extensive experiments on various diffusion models including Stable Diffusion series and DiTs. Our DiP-GO approach achieves 4.4 x speedup for SD-1.5 without any loss of accuracy, significantly outperforming the previous state-of-the-art methods.
Enhancing One-shot Pruned Pre-trained Language Models through Sparse-Dense-Sparse Mechanism
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) are engineered to be robust in contextual understanding and exhibit outstanding performance in various natural language processing tasks. However, their considerable size incurs significant computational and storage costs. Modern pruning strategies employ one-shot techniques to compress PLMs without the need for retraining on task-specific or otherwise general data; however, these approaches often lead to an indispensable reduction in performance. In this paper, we propose SDS, a Sparse-Dense-Sparse pruning framework to enhance the performance of the pruned PLMs from a weight distribution optimization perspective. We outline the pruning process in three steps. Initially, we prune less critical connections in the model using conventional one-shot pruning methods. Next, we reconstruct a dense model featuring a pruning-friendly weight distribution by reactivating pruned connections with sparse regularization. Finally, we perform a second pruning round, yielding a superior pruned model compared to the initial pruning. Experimental results demonstrate that SDS outperforms the state-of-the-art pruning techniques SparseGPT and Wanda under an identical sparsity configuration. For instance, SDS reduces perplexity by 9.13 on Raw-Wikitext2 and improves accuracy by an average of 2.05% across multiple zero-shot benchmarks for OPT-125M with 2:4 sparsity.
Towards Scale-Aware Full Surround Monodepth with Transformers
Jul 15, 2024

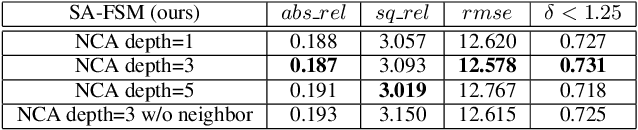
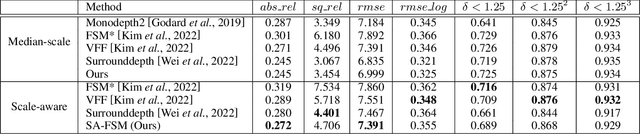
Abstract:Full surround monodepth (FSM) methods can learn from multiple camera views simultaneously in a self-supervised manner to predict the scale-aware depth, which is more practical for real-world applications in contrast to scale-ambiguous depth from a standalone monocular camera. In this work, we focus on enhancing the scale-awareness of FSM methods for depth estimation. To this end, we propose to improve FSM from two perspectives: depth network structure optimization and training pipeline optimization. First, we construct a transformer-based depth network with neighbor-enhanced cross-view attention (NCA). The cross-attention modules can better aggregate the cross-view context in both global and neighboring views. Second, we formulate a transformer-based feature matching scheme with progressive training to improve the structure-from-motion (SfM) pipeline. That allows us to learn scale-awareness with sufficient matches and further facilitate network convergence by removing mismatches based on SfM loss. Experiments demonstrate that the resulting Scale-aware full surround monodepth (SA-FSM) method largely improves the scale-aware depth predictions without median-scaling at the test time, and performs favorably against the state-of-the-art FSM methods, e.g., surpassing SurroundDepth by 3.8% in terms of accuracy at delta<1.25 on the DDAD benchmark.
Sparse Laneformer
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Lane detection is a fundamental task in autonomous driving, and has achieved great progress as deep learning emerges. Previous anchor-based methods often design dense anchors, which highly depend on the training dataset and remain fixed during inference. We analyze that dense anchors are not necessary for lane detection, and propose a transformer-based lane detection framework based on a sparse anchor mechanism. To this end, we generate sparse anchors with position-aware lane queries and angle queries instead of traditional explicit anchors. We adopt Horizontal Perceptual Attention (HPA) to aggregate the lane features along the horizontal direction, and adopt Lane-Angle Cross Attention (LACA) to perform interactions between lane queries and angle queries. We also propose Lane Perceptual Attention (LPA) based on deformable cross attention to further refine the lane predictions. Our method, named Sparse Laneformer, is easy-to-implement and end-to-end trainable. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Sparse Laneformer performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods, e.g., surpassing Laneformer by 3.0% F1 score and O2SFormer by 0.7% F1 score with fewer MACs on CULane with the same ResNet-34 backbone.
UPDP: A Unified Progressive Depth Pruner for CNN and Vision Transformer
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:Traditional channel-wise pruning methods by reducing network channels struggle to effectively prune efficient CNN models with depth-wise convolutional layers and certain efficient modules, such as popular inverted residual blocks. Prior depth pruning methods by reducing network depths are not suitable for pruning some efficient models due to the existence of some normalization layers. Moreover, finetuning subnet by directly removing activation layers would corrupt the original model weights, hindering the pruned model from achieving high performance. To address these issues, we propose a novel depth pruning method for efficient models. Our approach proposes a novel block pruning strategy and progressive training method for the subnet. Additionally, we extend our pruning method to vision transformer models. Experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing depth pruning methods across various pruning configurations. We obtained three pruned ConvNeXtV1 models with our method applying on ConvNeXtV1, which surpass most SOTA efficient models with comparable inference performance. Our method also achieves state-of-the-art pruning performance on the vision transformer model.
Separated RoadTopoFormer
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Understanding driving scenarios is crucial to realizing autonomous driving. Previous works such as map learning and BEV lane detection neglect the connection relationship between lane instances, and traffic elements detection tasks usually neglect the relationship with lane lines. To address these issues, the task is presented which includes 4 sub-tasks, the detection of traffic elements, the detection of lane centerlines, reasoning connection relationships among lanes, and reasoning assignment relationships between lanes and traffic elements. We present Separated RoadTopoFormer to tackle the issues, which is an end-to-end framework that detects lane centerline and traffic elements with reasoning relationships among them. We optimize each module separately to prevent interaction with each other and aggregate them together with few finetunes. For two detection heads, we adopted a DETR-like architecture to detect objects, and for the relationship head, we concat two instance features from front detectors and feed them to the classifier to obtain relationship probability. Our final submission achieves 0.445 OLS, which is competitive in both sub-task and combined scores.
XRBench: An Extended Reality (XR) Machine Learning Benchmark Suite for the Metaverse
Nov 16, 2022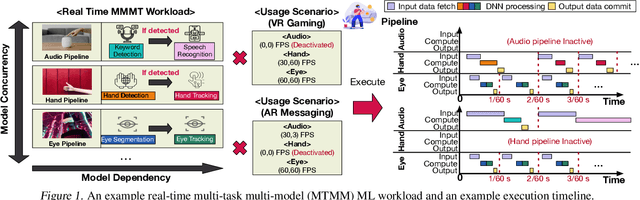
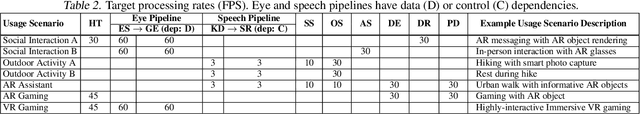
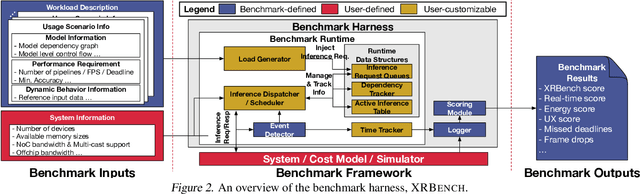
Abstract:Real-time multi-model multi-task (MMMT) workloads, a new form of deep learning inference workloads, are emerging for applications areas like extended reality (XR) to support metaverse use cases. These workloads combine user interactivity with computationally complex machine learning (ML) activities. Compared to standard ML applications, these ML workloads present unique difficulties and constraints. Real-time MMMT workloads impose heterogeneity and concurrency requirements on future ML systems and devices, necessitating the development of new capabilities. This paper begins with a discussion of the various characteristics of these real-time MMMT ML workloads and presents an ontology for evaluating the performance of future ML hardware for XR systems. Next, we present XRBench, a collection of MMMT ML tasks, models, and usage scenarios that execute these models in three representative ways: cascaded, concurrent, and cascaded-concurrency for XR use cases. Finally, we emphasize the need for new metrics that capture the requirements properly. We hope that our work will stimulate research and lead to the development of a new generation of ML systems for XR use cases.
MLPerf Inference Benchmark
Nov 06, 2019
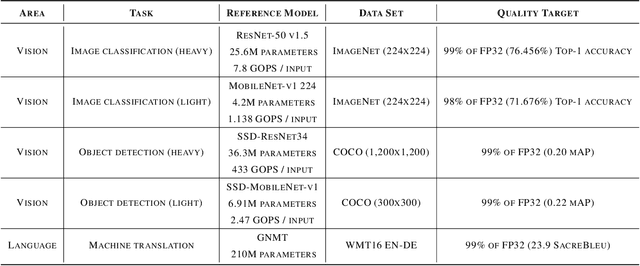
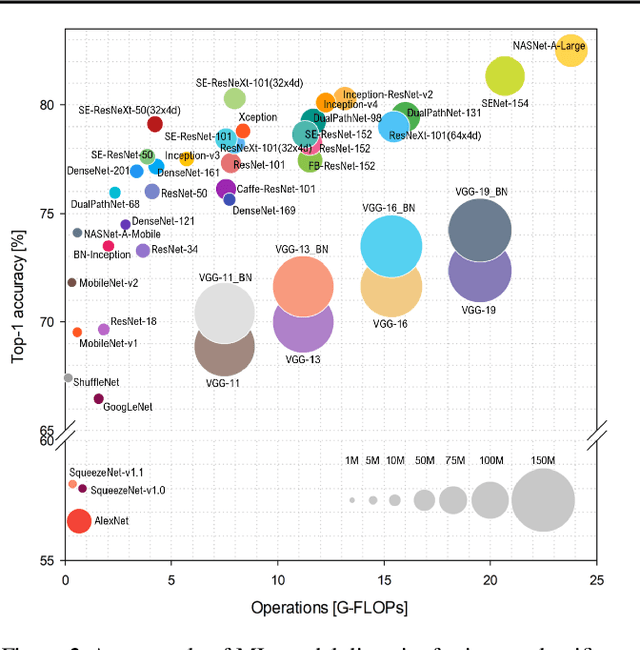
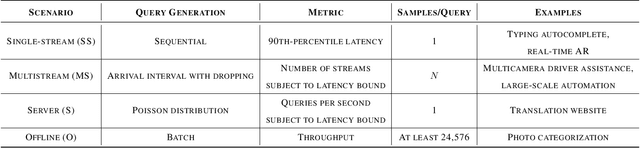
Abstract:Machine-learning (ML) hardware and software system demand is burgeoning. Driven by ML applications, the number of different ML inference systems has exploded. Over 100 organizations are building ML inference chips, and the systems that incorporate existing models span at least three orders of magnitude in power consumption and four orders of magnitude in performance; they range from embedded devices to data-center solutions. Fueling the hardware are a dozen or more software frameworks and libraries. The myriad combinations of ML hardware and ML software make assessing ML-system performance in an architecture-neutral, representative, and reproducible manner challenging. There is a clear need for industry-wide standard ML benchmarking and evaluation criteria. MLPerf Inference answers that call. Driven by more than 30 organizations as well as more than 200 ML engineers and practitioners, MLPerf implements a set of rules and practices to ensure comparability across systems with wildly differing architectures. In this paper, we present the method and design principles of the initial MLPerf Inference release. The first call for submissions garnered more than 600 inference-performance measurements from 14 organizations, representing over 30 systems that show a range of capabilities.
Quantizing Convolutional Neural Networks for Low-Power High-Throughput Inference Engines
May 21, 2018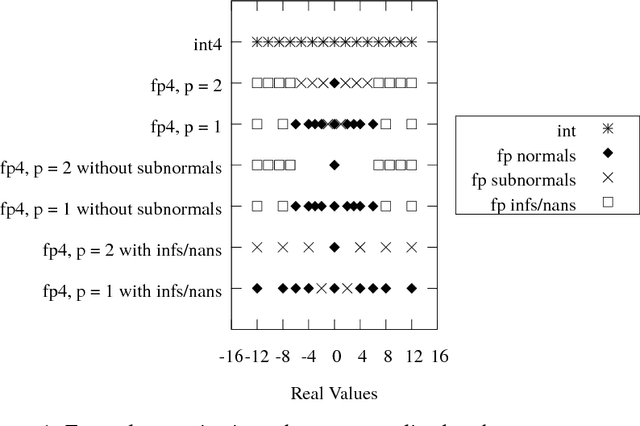
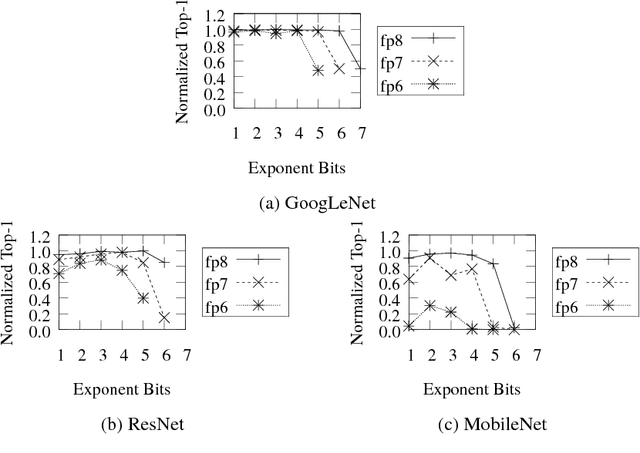
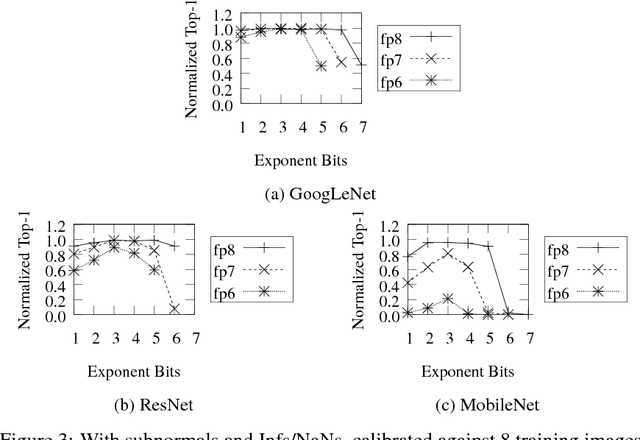
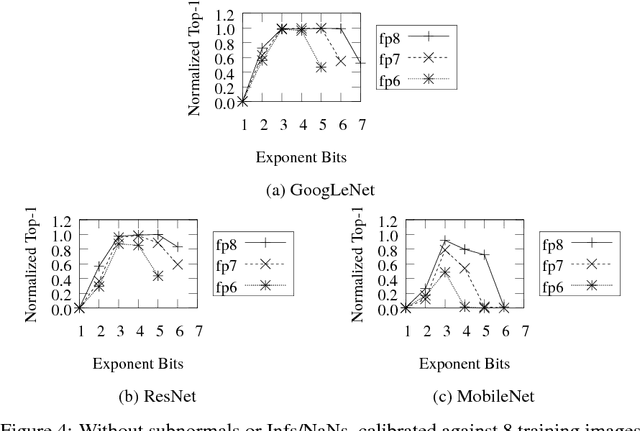
Abstract:Deep learning as a means to inferencing has proliferated thanks to its versatility and ability to approach or exceed human-level accuracy. These computational models have seemingly insatiable appetites for computational resources not only while training, but also when deployed at scales ranging from data centers all the way down to embedded devices. As such, increasing consideration is being made to maximize the computational efficiency given limited hardware and energy resources and, as a result, inferencing with reduced precision has emerged as a viable alternative to the IEEE 754 Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic. We propose a quantization scheme that allows inferencing to be carried out using arithmetic that is fundamentally more efficient when compared to even half-precision floating-point. Our quantization procedure is significant in that we determine our quantization scheme parameters by calibrating against its reference floating-point model using a single inference batch rather than (re)training and achieve end-to-end post quantization accuracies comparable to the reference model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge