Andrew Rosenberg
Zero-shot Cross-lingual Voice Transfer for TTS
Sep 20, 2024

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a zero-shot Voice Transfer (VT) module that can be seamlessly integrated into a multi-lingual Text-to-speech (TTS) system to transfer an individual's voice across languages. Our proposed VT module comprises a speaker-encoder that processes reference speech, a bottleneck layer, and residual adapters, connected to preexisting TTS layers. We compare the performance of various configurations of these components and report Mean Opinion Score (MOS) and Speaker Similarity across languages. Using a single English reference speech per speaker, we achieve an average voice transfer similarity score of 73% across nine target languages. Vocal characteristics contribute significantly to the construction and perception of individual identity. The loss of one's voice, due to physical or neurological conditions, can lead to a profound sense of loss, impacting one's core identity. As a case study, we demonstrate that our approach can not only transfer typical speech but also restore the voices of individuals with dysarthria, even when only atypical speech samples are available - a valuable utility for those who have never had typical speech or banked their voice. Cross-lingual typical audio samples, plus videos demonstrating voice restoration for dysarthric speakers are available here (google.github.io/tacotron/publications/zero_shot_voice_transfer).
STAB: Speech Tokenizer Assessment Benchmark
Sep 04, 2024
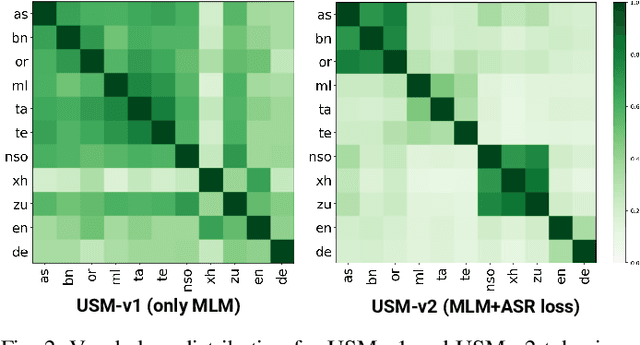
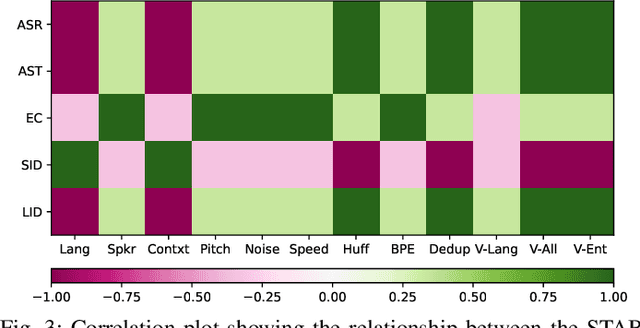
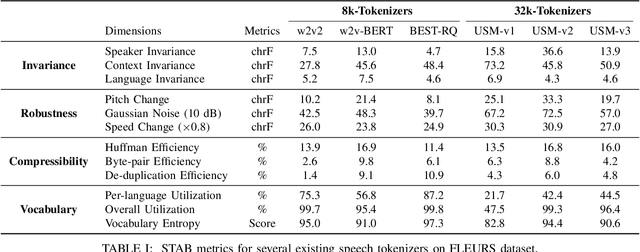
Abstract:Representing speech as discrete tokens provides a framework for transforming speech into a format that closely resembles text, thus enabling the use of speech as an input to the widely successful large language models (LLMs). Currently, while several speech tokenizers have been proposed, there is ambiguity regarding the properties that are desired from a tokenizer for specific downstream tasks and its overall generalizability. Evaluating the performance of tokenizers across different downstream tasks is a computationally intensive effort that poses challenges for scalability. To circumvent this requirement, we present STAB (Speech Tokenizer Assessment Benchmark), a systematic evaluation framework designed to assess speech tokenizers comprehensively and shed light on their inherent characteristics. This framework provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms of speech tokenization, thereby offering a valuable resource for expediting the advancement of future tokenizer models and enabling comparative analysis using a standardized benchmark. We evaluate the STAB metrics and correlate this with downstream task performance across a range of speech tasks and tokenizer choices.
Adversarial training of Keyword Spotting to Minimize TTS Data Overfitting
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:The keyword spotting (KWS) problem requires large amounts of real speech training data to achieve high accuracy across diverse populations. Utilizing large amounts of text-to-speech (TTS) synthesized data can reduce the cost and time associated with KWS development. However, TTS data may contain artifacts not present in real speech, which the KWS model can exploit (overfit), leading to degraded accuracy on real speech. To address this issue, we propose applying an adversarial training method to prevent the KWS model from learning TTS-specific features when trained on large amounts of TTS data. Experimental results demonstrate that KWS model accuracy on real speech data can be improved by up to 12% when adversarial loss is used in addition to the original KWS loss. Surprisingly, we also observed that the adversarial setup improves accuracy by up to 8%, even when trained solely on TTS and real negative speech data, without any real positive examples.
Utilizing TTS Synthesized Data for Efficient Development of Keyword Spotting Model
Jul 26, 2024
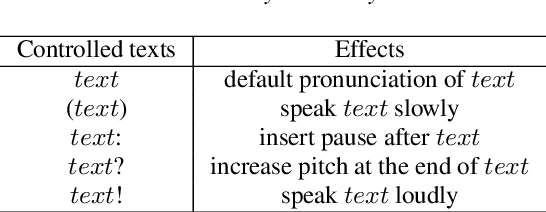
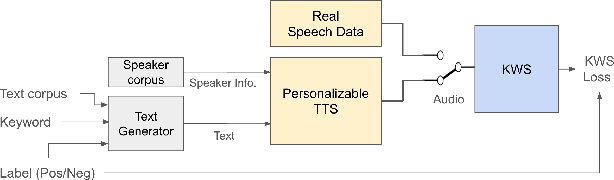
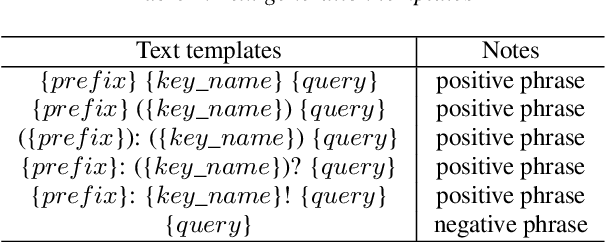
Abstract:This paper explores the use of TTS synthesized training data for KWS (keyword spotting) task while minimizing development cost and time. Keyword spotting models require a huge amount of training data to be accurate, and obtaining such training data can be costly. In the current state of the art, TTS models can generate large amounts of natural-sounding data, which can help reducing cost and time for KWS model development. Still, TTS generated data can be lacking diversity compared to real data. To pursue maximizing KWS model accuracy under the constraint of limited resources and current TTS capability, we explored various strategies to mix TTS data and real human speech data, with a focus on minimizing real data use and maximizing diversity of TTS output. Our experimental results indicate that relatively small amounts of real audio data with speaker diversity (100 speakers, 2k utterances) and large amounts of TTS synthesized data can achieve reasonably high accuracy (within 3x error rate of baseline), compared to the baseline (trained with 3.8M real positive utterances).
Speculative Speech Recognition by Audio-Prefixed Low-Rank Adaptation of Language Models
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores speculative speech recognition (SSR), where we empower conventional automatic speech recognition (ASR) with speculation capabilities, allowing the recognizer to run ahead of audio. We introduce a metric for measuring SSR performance and we propose a model which does SSR by combining a RNN-Transducer-based ASR system with an audio-prefixed language model (LM). The ASR system transcribes ongoing audio and feeds the resulting transcripts, along with an audio-dependent prefix, to the LM, which speculates likely completions for the transcriptions. We experiment with a variety of ASR datasets on which show the efficacy our method and the feasibility of SSR as a method of reducing ASR latency.
Speech Prefix-Tuning with RNNT Loss for Improving LLM Predictions
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we focus on addressing the constraints faced when applying LLMs to ASR. Recent works utilize prefixLM-type models, which directly apply speech as a prefix to LLMs for ASR. We have found that optimizing speech prefixes leads to better ASR performance and propose applying RNNT loss to perform speech prefix-tuning. This is a simple approach and does not increase the model complexity or alter the inference pipeline. We also propose language-based soft prompting to further improve with frozen LLMs. Empirical analysis on realtime testset from 10 Indic languages demonstrate that our proposed speech prefix-tuning yields improvements with both frozen and fine-tuned LLMs. Our recognition results on an average of 10 Indics show that the proposed prefix-tuning with RNNT loss results in a 12\% relative improvement in WER over the baseline with a fine-tuned LLM. Our proposed approches with the frozen LLM leads to a 31\% relative improvement over basic soft-prompting prefixLM.
ASTRA: Aligning Speech and Text Representations for Asr without Sampling
Jun 10, 2024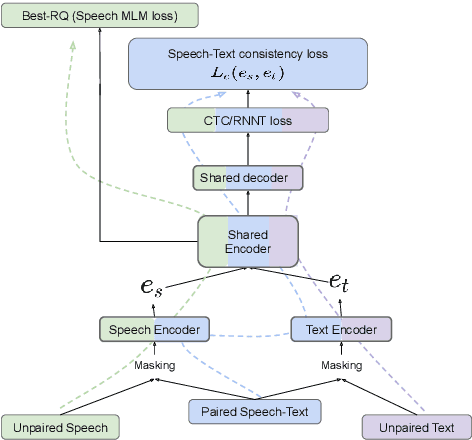



Abstract:This paper introduces ASTRA, a novel method for improving Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) through text injection.Unlike prevailing techniques, ASTRA eliminates the need for sampling to match sequence lengths between speech and text modalities. Instead, it leverages the inherent alignments learned within CTC/RNNT models. This approach offers the following two advantages, namely, avoiding potential misalignment between speech and text features that could arise from upsampling and eliminating the need for models to accurately predict duration of sub-word tokens. This novel formulation of modality (length) matching as a weighted RNNT objective matches the performance of the state-of-the-art duration-based methods on the FLEURS benchmark, while opening up other avenues of research in speech processing.
Extending Multilingual Speech Synthesis to 100+ Languages without Transcribed Data
Feb 29, 2024



Abstract:Collecting high-quality studio recordings of audio is challenging, which limits the language coverage of text-to-speech (TTS) systems. This paper proposes a framework for scaling a multilingual TTS model to 100+ languages using found data without supervision. The proposed framework combines speech-text encoder pretraining with unsupervised training using untranscribed speech and unspoken text data sources, thereby leveraging massively multilingual joint speech and text representation learning. Without any transcribed speech in a new language, this TTS model can generate intelligible speech in >30 unseen languages (CER difference of <10% to ground truth). With just 15 minutes of transcribed, found data, we can reduce the intelligibility difference to 1% or less from the ground-truth, and achieve naturalness scores that match the ground-truth in several languages.
High-precision Voice Search Query Correction via Retrievable Speech-text Embedings
Jan 08, 2024Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems can suffer from poor recall for various reasons, such as noisy audio, lack of sufficient training data, etc. Previous work has shown that recall can be improved by retrieving rewrite candidates from a large database of likely, contextually-relevant alternatives to the hypothesis text using nearest-neighbors search over embeddings of the ASR hypothesis text to correct and candidate corrections. However, ASR-hypothesis-based retrieval can yield poor precision if the textual hypotheses are too phonetically dissimilar to the transcript truth. In this paper, we eliminate the hypothesis-audio mismatch problem by querying the correction database directly using embeddings derived from the utterance audio; the embeddings of the utterance audio and candidate corrections are produced by multimodal speech-text embedding networks trained to place the embedding of the audio of an utterance and the embedding of its corresponding textual transcript close together. After locating an appropriate correction candidate using nearest-neighbor search, we score the candidate with its speech-text embedding distance before adding the candidate to the original n-best list. We show a relative word error rate (WER) reduction of 6% on utterances whose transcripts appear in the candidate set, without increasing WER on general utterances.
O-1: Self-training with Oracle and 1-best Hypothesis
Aug 14, 2023
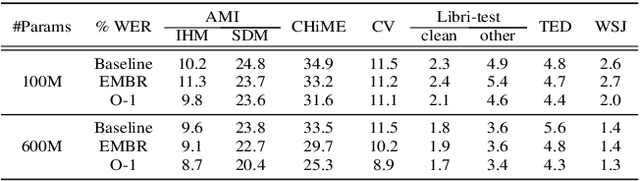

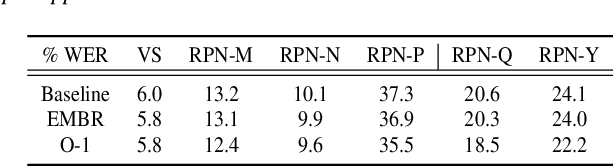
Abstract:We introduce O-1, a new self-training objective to reduce training bias and unify training and evaluation metrics for speech recognition. O-1 is a faster variant of Expected Minimum Bayes Risk (EMBR), that boosts the oracle hypothesis and can accommodate both supervised and unsupervised data. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in terms of recognition on publicly available SpeechStew datasets and a large-scale, in-house data set. On Speechstew, the O-1 objective closes the gap between the actual and oracle performance by 80\% relative compared to EMBR which bridges the gap by 43\% relative. O-1 achieves 13\% to 25\% relative improvement over EMBR on the various datasets that SpeechStew comprises of, and a 12\% relative gap reduction with respect to the oracle WER over EMBR training on the in-house dataset. Overall, O-1 results in a 9\% relative improvement in WER over EMBR, thereby speaking to the scalability of the proposed objective for large-scale datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge