Neeraj Gaur
Schema Augmentation for Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation in Dialogue State Tracking
Oct 31, 2024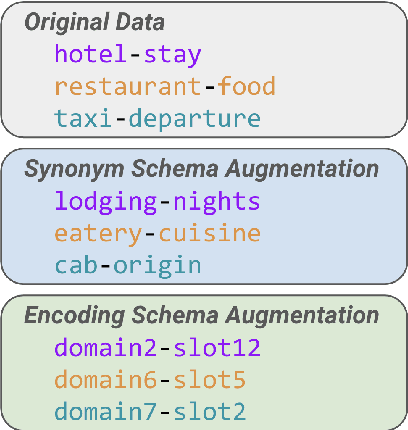
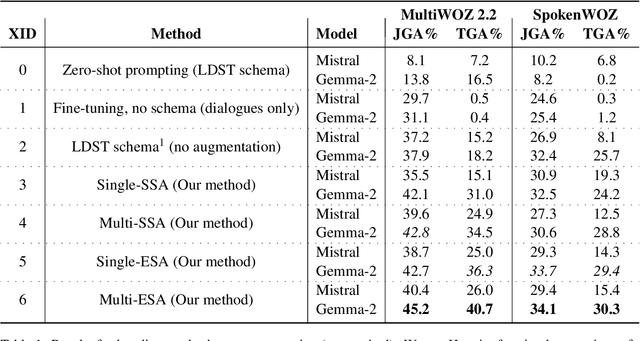
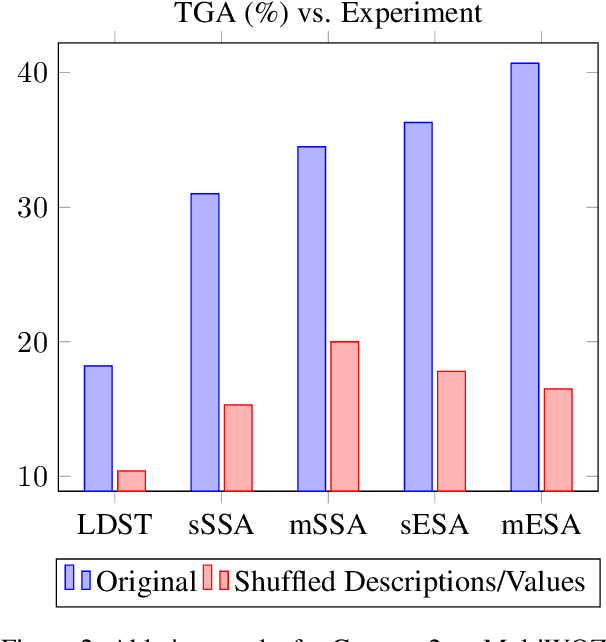
Abstract:Zero-shot domain adaptation for dialogue state tracking (DST) remains a challenging problem in task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems, where models must generalize to target domains unseen at training time. Current large language model approaches for zero-shot domain adaptation rely on prompting to introduce knowledge pertaining to the target domains. However, their efficacy strongly depends on prompt engineering, as well as the zero-shot ability of the underlying language model. In this work, we devise a novel data augmentation approach, Schema Augmentation, that improves the zero-shot domain adaptation of language models through fine-tuning. Schema Augmentation is a simple but effective technique that enhances generalization by introducing variations of slot names within the schema provided in the prompt. Experiments on MultiWOZ and SpokenWOZ showed that the proposed approach resulted in a substantial improvement over the baseline, in some experiments achieving over a twofold accuracy gain over unseen domains while maintaining equal or superior performance over all domains.
Speech Prefix-Tuning with RNNT Loss for Improving LLM Predictions
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we focus on addressing the constraints faced when applying LLMs to ASR. Recent works utilize prefixLM-type models, which directly apply speech as a prefix to LLMs for ASR. We have found that optimizing speech prefixes leads to better ASR performance and propose applying RNNT loss to perform speech prefix-tuning. This is a simple approach and does not increase the model complexity or alter the inference pipeline. We also propose language-based soft prompting to further improve with frozen LLMs. Empirical analysis on realtime testset from 10 Indic languages demonstrate that our proposed speech prefix-tuning yields improvements with both frozen and fine-tuned LLMs. Our recognition results on an average of 10 Indics show that the proposed prefix-tuning with RNNT loss results in a 12\% relative improvement in WER over the baseline with a fine-tuned LLM. Our proposed approches with the frozen LLM leads to a 31\% relative improvement over basic soft-prompting prefixLM.
ASTRA: Aligning Speech and Text Representations for Asr without Sampling
Jun 10, 2024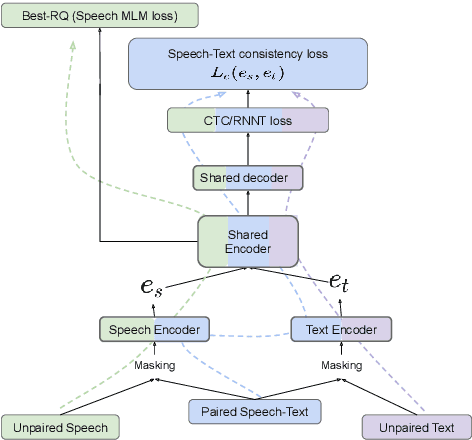



Abstract:This paper introduces ASTRA, a novel method for improving Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) through text injection.Unlike prevailing techniques, ASTRA eliminates the need for sampling to match sequence lengths between speech and text modalities. Instead, it leverages the inherent alignments learned within CTC/RNNT models. This approach offers the following two advantages, namely, avoiding potential misalignment between speech and text features that could arise from upsampling and eliminating the need for models to accurately predict duration of sub-word tokens. This novel formulation of modality (length) matching as a weighted RNNT objective matches the performance of the state-of-the-art duration-based methods on the FLEURS benchmark, while opening up other avenues of research in speech processing.
Audio-AdapterFusion: A Task-ID-free Approach for Efficient and Non-Destructive Multi-task Speech Recognition
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:Adapters are an efficient, composable alternative to full fine-tuning of pre-trained models and help scale the deployment of large ASR models to many tasks. In practice, a task ID is commonly prepended to the input during inference to route to single-task adapters for the specified task. However, one major limitation of this approach is that the task ID may not be known during inference, rendering it unsuitable for most multi-task settings. To address this, we propose three novel task-ID-free methods to combine single-task adapters in multi-task ASR and investigate two learning algorithms for training. We evaluate our methods on 10 test sets from 4 diverse ASR tasks and show that our methods are non-destructive and parameter-efficient. While only updating 17% of the model parameters, our methods can achieve an 8% mean WER improvement relative to full fine-tuning and are on-par with task-ID adapter routing.
Improving Rare Word Recognition with LM-aware MWER Training
Apr 15, 2022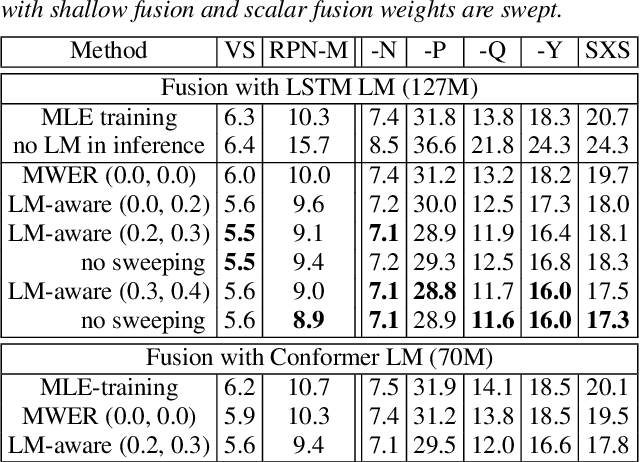
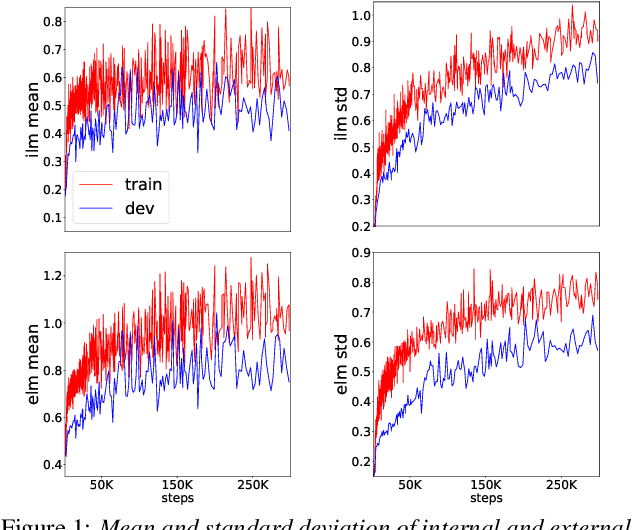

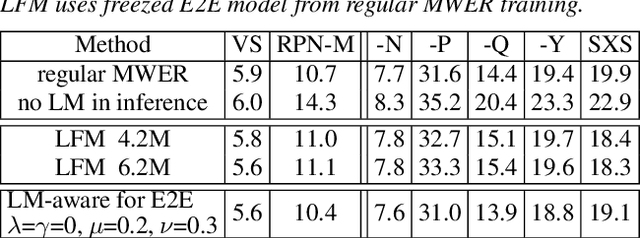
Abstract:Language models (LMs) significantly improve the recognition accuracy of end-to-end (E2E) models on words rarely seen during training, when used in either the shallow fusion or the rescoring setups. In this work, we introduce LMs in the learning of hybrid autoregressive transducer (HAT) models in the discriminative training framework, to mitigate the training versus inference gap regarding the use of LMs. For the shallow fusion setup, we use LMs during both hypotheses generation and loss computation, and the LM-aware MWER-trained model achieves 10\% relative improvement over the model trained with standard MWER on voice search test sets containing rare words. For the rescoring setup, we learn a small neural module to generate per-token fusion weights in a data-dependent manner. This model achieves the same rescoring WER as regular MWER-trained model, but without the need for sweeping fusion weights.
From Audio to Semantics: Approaches to end-to-end spoken language understanding
Sep 24, 2018
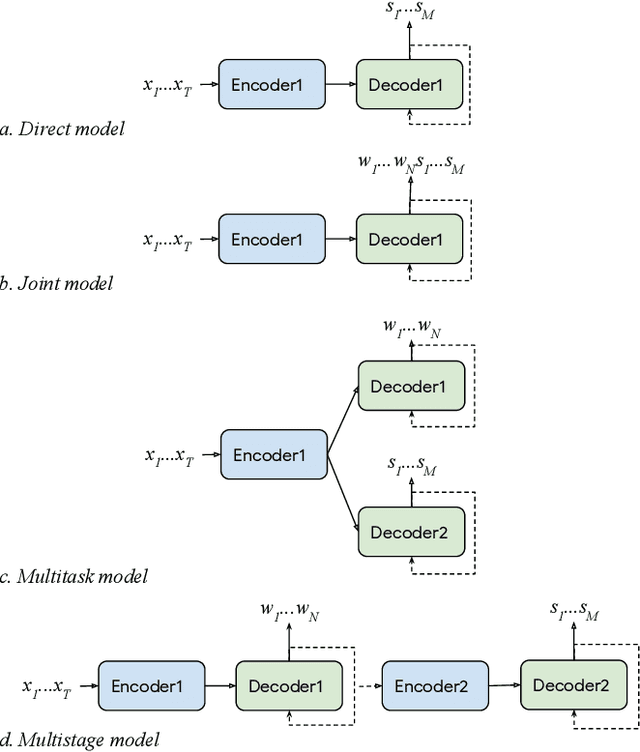
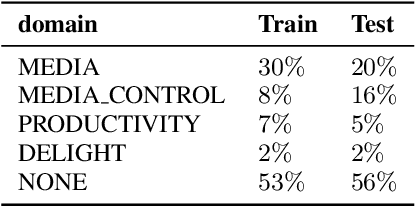
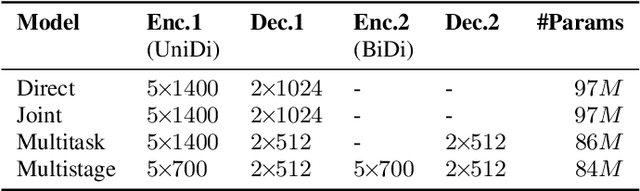
Abstract:Conventional spoken language understanding systems consist of two main components: an automatic speech recognition module that converts audio to a transcript, and a natural language understanding module that transforms the resulting text (or top N hypotheses) into a set of domains, intents, and arguments. These modules are typically optimized independently. In this paper, we formulate audio to semantic understanding as a sequence-to-sequence problem [1]. We propose and compare various encoder-decoder based approaches that optimize both modules jointly, in an end-to-end manner. Evaluations on a real-world task show that 1) having an intermediate text representation is crucial for the quality of the predicted semantics, especially the intent arguments and 2) jointly optimizing the full system improves overall accuracy of prediction. Compared to independently trained models, our best jointly trained model achieves similar domain and intent prediction F1 scores, but improves argument word error rate by 18% relative.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge