Pedro Moreno
Google USM: Scaling Automatic Speech Recognition Beyond 100 Languages
Mar 03, 2023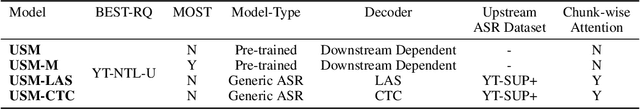
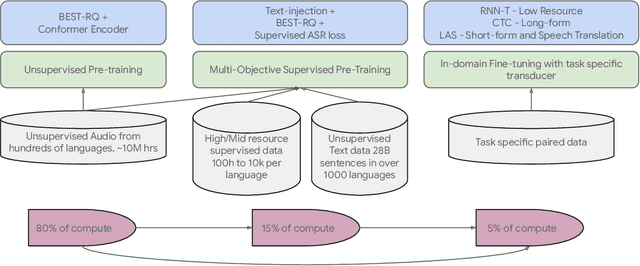
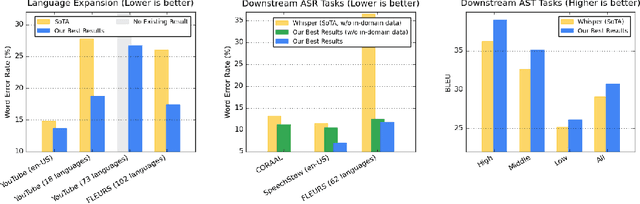
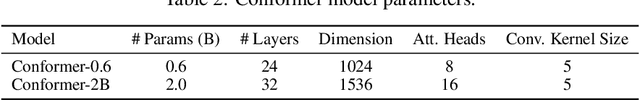
Abstract:We introduce the Universal Speech Model (USM), a single large model that performs automatic speech recognition (ASR) across 100+ languages. This is achieved by pre-training the encoder of the model on a large unlabeled multilingual dataset of 12 million (M) hours spanning over 300 languages, and fine-tuning on a smaller labeled dataset. We use multilingual pre-training with random-projection quantization and speech-text modality matching to achieve state-of-the-art performance on downstream multilingual ASR and speech-to-text translation tasks. We also demonstrate that despite using a labeled training set 1/7-th the size of that used for the Whisper model, our model exhibits comparable or better performance on both in-domain and out-of-domain speech recognition tasks across many languages.
Maestro-U: Leveraging joint speech-text representation learning for zero supervised speech ASR
Oct 18, 2022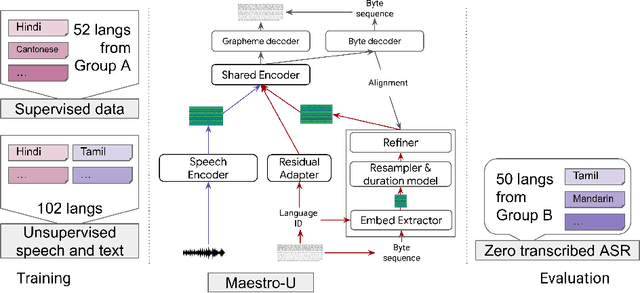
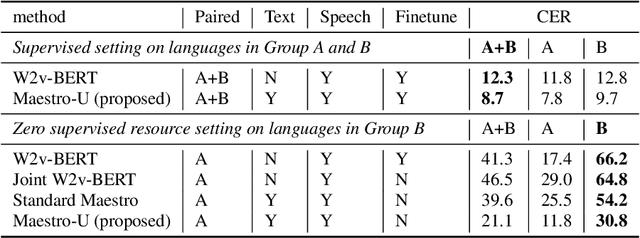
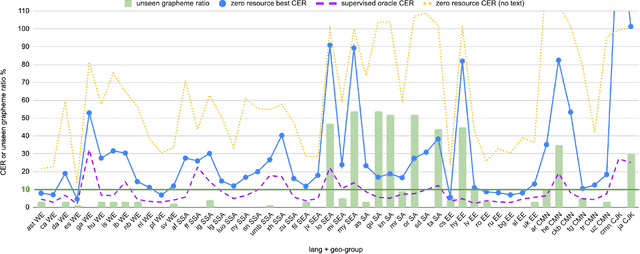
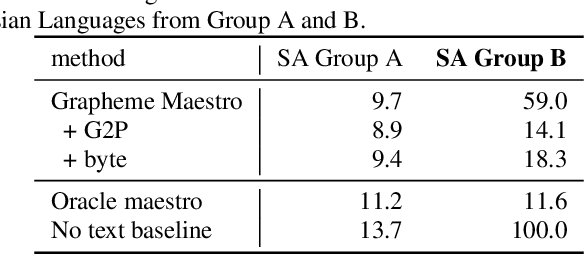
Abstract:Training state-of-the-art Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) models typically requires a substantial amount of transcribed speech. In this work, we demonstrate that a modality-matched joint speech and text model can be leveraged to train a massively multilingual ASR model without any supervised (manually transcribed) speech for some languages. This paper explores the use of jointly learnt speech and text representations in a massively multilingual, zero supervised speech, real-world setting to expand the set of languages covered by ASR with only unlabeled speech and text in the target languages. Using the FLEURS dataset, we define the task to cover $102$ languages, where transcribed speech is available in $52$ of these languages and can be used to improve end-to-end ASR quality on the remaining $50$. First, we show that by combining speech representations with byte-level text representations and use of language embeddings, we can dramatically reduce the Character Error Rate (CER) on languages with no supervised speech from 64.8\% to 30.8\%, a relative reduction of 53\%. Second, using a subset of South Asian languages we show that Maestro-U can promote knowledge transfer from languages with supervised speech even when there is limited to no graphemic overlap. Overall, Maestro-U closes the gap to oracle performance by 68.5\% relative and reduces the CER of 19 languages below 15\%.
MAESTRO: Matched Speech Text Representations through Modality Matching
Apr 07, 2022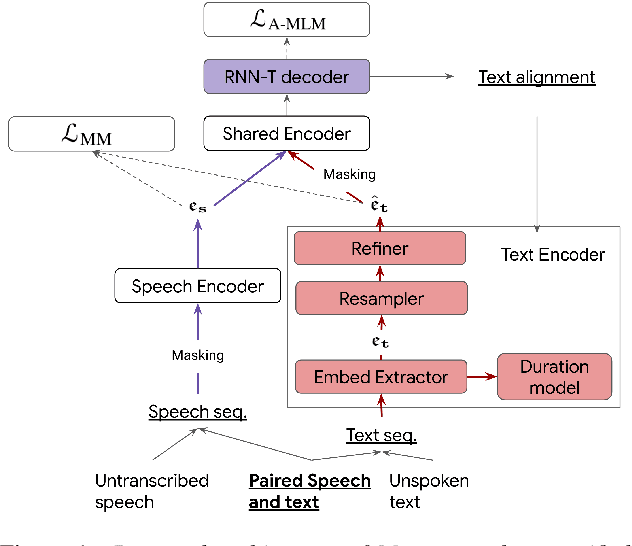
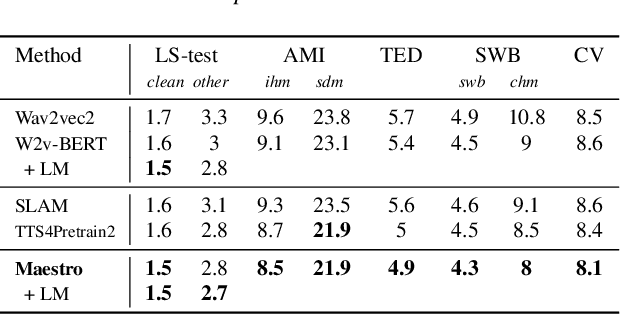
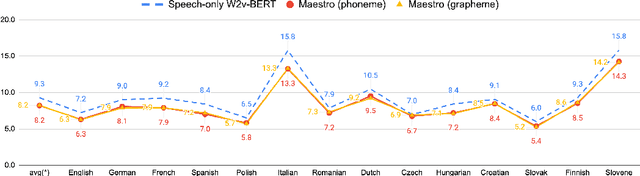
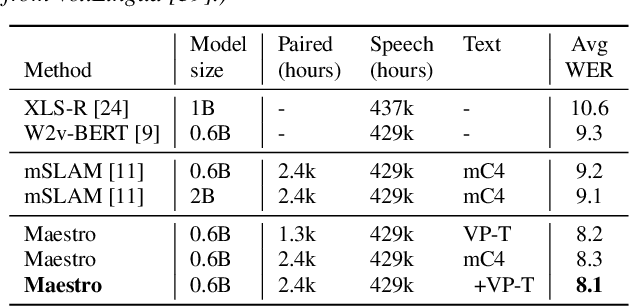
Abstract:We present Maestro, a self-supervised training method to unify representations learnt from speech and text modalities. Self-supervised learning from speech signals aims to learn the latent structure inherent in the signal, while self-supervised learning from text attempts to capture lexical information. Learning aligned representations from unpaired speech and text sequences is a challenging task. Previous work either implicitly enforced the representations learnt from these two modalities to be aligned in the latent space through multitasking and parameter sharing or explicitly through conversion of modalities via speech synthesis. While the former suffers from interference between the two modalities, the latter introduces additional complexity. In this paper, we propose Maestro, a novel algorithm to learn unified representations from both these modalities simultaneously that can transfer to diverse downstream tasks such as Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) and Speech Translation (ST). Maestro learns unified representations through sequence alignment, duration prediction and matching embeddings in the learned space through an aligned masked-language model loss. We establish a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) on VoxPopuli multilingual ASR with a 11% relative reduction in Word Error Rate (WER), multidomain SpeechStew ASR (3.7% relative) and 21 languages to English multilingual ST on CoVoST 2 with an improvement of 2.8 BLEU averaged over 21 languages.
Ask2Mask: Guided Data Selection for Masked Speech Modeling
Feb 24, 2022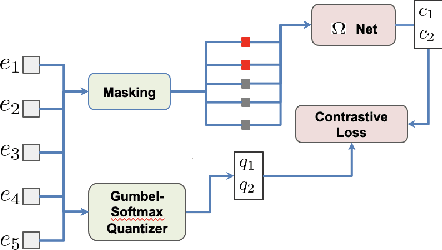
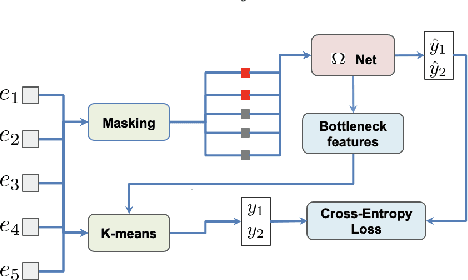
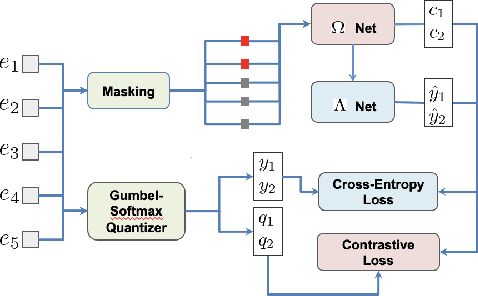
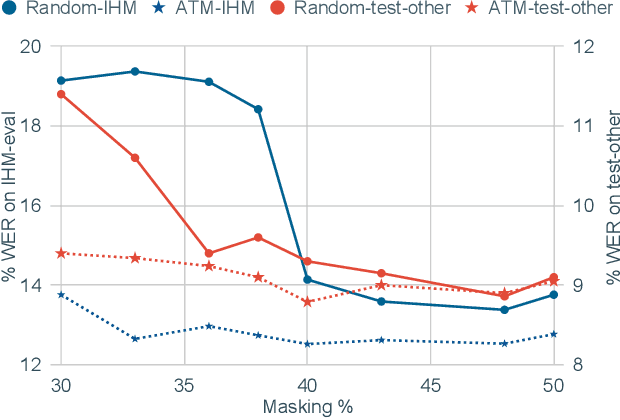
Abstract:Masked speech modeling (MSM) methods such as wav2vec2 or w2v-BERT learn representations over speech frames which are randomly masked within an utterance. While these methods improve performance of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems, they have one major limitation. They treat all unsupervised speech samples with equal weight, which hinders learning as not all samples have relevant information to learn meaningful representations. In this work, we address this limitation. We propose ask2mask (ATM), a novel approach to focus on specific samples during MSM pre-training. ATM employs an external ASR model or \textit{scorer} to weight unsupervised input samples in two different ways: 1) A fine-grained data selection is performed by masking over the highly confident input frames as chosen by the scorer. This allows the model to learn meaningful representations. 2) ATM is further extended to focus at utterance-level by weighting the final MSM loss with the utterance-level confidence score. We conduct fine-tuning experiments on two well-benchmarked corpora: LibriSpeech (matching the pre-training data) and Commonvoice, TED-LIUM, AMI and CHiME-6 (not matching the pre-training data). The results substantiate the efficacy of ATM on significantly improving the recognition performance under mismatched conditions (up to 11.6\% relative over published results and upto 4.46\% relative over our internal baseline) while still yielding modest improvements under matched conditions.
Injecting Text in Self-Supervised Speech Pretraining
Aug 27, 2021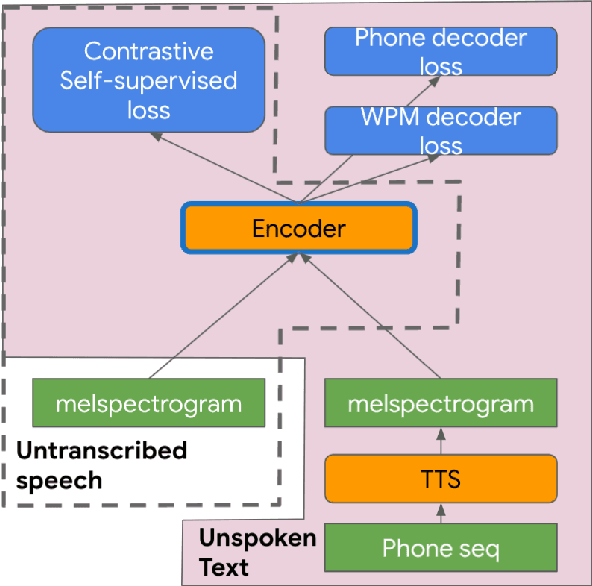

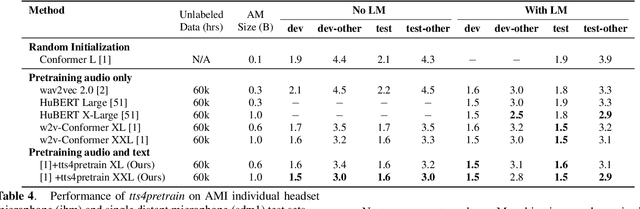
Abstract:Self-supervised pretraining for Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) has shown varied degrees of success. In this paper, we propose to jointly learn representations during pretraining from two different modalities: speech and text. The proposed method, tts4pretrain complements the power of contrastive learning in self-supervision with linguistic/lexical representations derived from synthesized speech, effectively learning from untranscribed speech and unspoken text. Lexical learning in the speech encoder is enforced through an additional sequence loss term that is coupled with contrastive loss during pretraining. We demonstrate that this novel pretraining method yields Word Error Rate (WER) reductions of 10% relative on the well-benchmarked, Librispeech task over a state-of-the-art baseline pretrained with wav2vec2.0 only. The proposed method also serves as an effective strategy to compensate for the lack of transcribed speech, effectively matching the performance of 5000 hours of transcribed speech with just 100 hours of transcribed speech on the AMI meeting transcription task. Finally, we demonstrate WER reductions of up to 15% on an in-house Voice Search task over traditional pretraining. Incorporating text into encoder pretraining is complimentary to rescoring with a larger or in-domain language model, resulting in additional 6% relative reduction in WER.
Speech Recognition with Augmented Synthesized Speech
Sep 25, 2019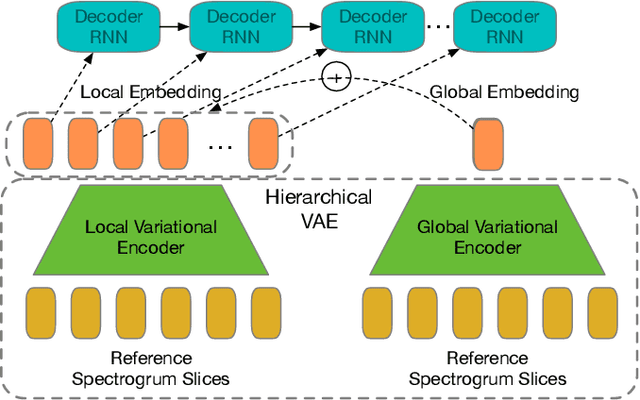
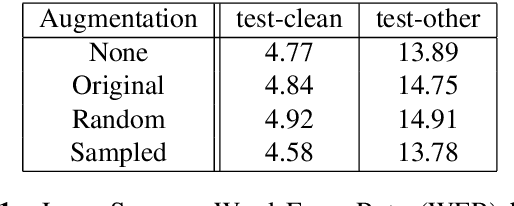
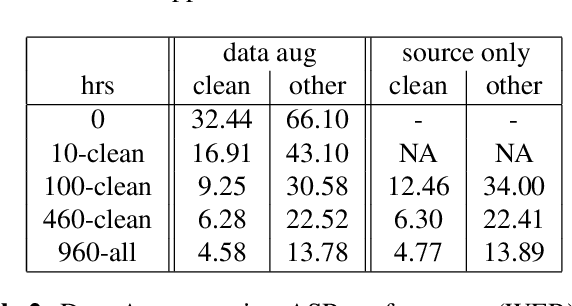
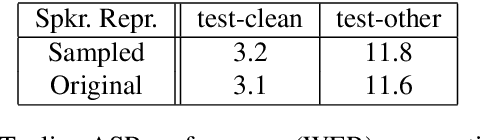
Abstract:Recent success of the Tacotron speech synthesis architecture and its variants in producing natural sounding multi-speaker synthesized speech has raised the exciting possibility of replacing expensive, manually transcribed, domain-specific, human speech that is used to train speech recognizers. The multi-speaker speech synthesis architecture can learn latent embedding spaces of prosody, speaker and style variations derived from input acoustic representations thereby allowing for manipulation of the synthesized speech. In this paper, we evaluate the feasibility of enhancing speech recognition performance using speech synthesis using two corpora from different domains. We explore algorithms to provide the necessary acoustic and lexical diversity needed for robust speech recognition. Finally, we demonstrate the feasibility of this approach as a data augmentation strategy for domain-transfer. We find that improvements to speech recognition performance is achievable by augmenting training data with synthesized material. However, there remains a substantial gap in performance between recognizers trained on human speech those trained on synthesized speech.
From Audio to Semantics: Approaches to end-to-end spoken language understanding
Sep 24, 2018
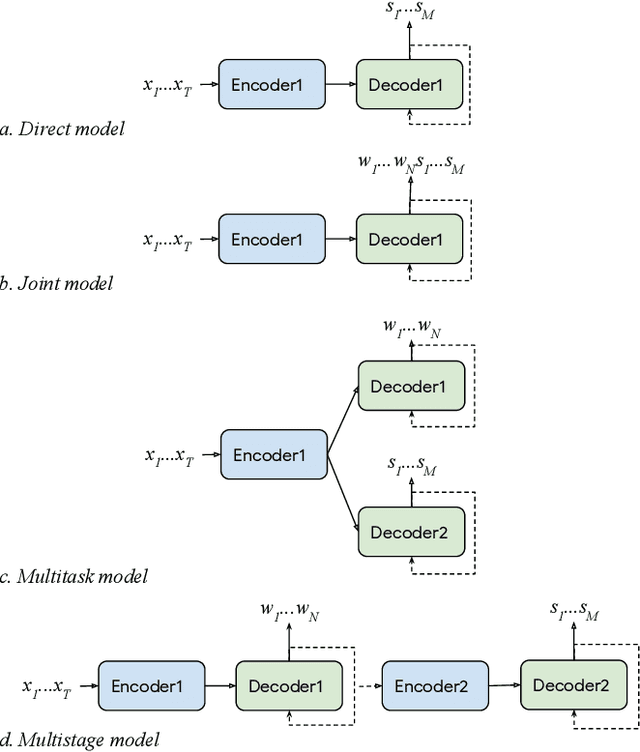
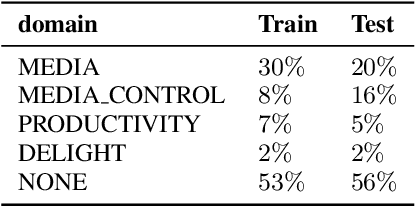
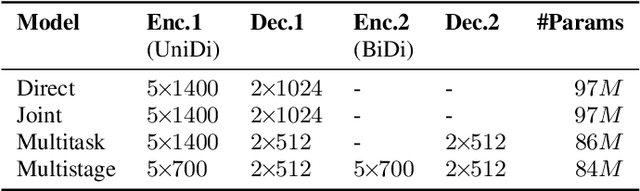
Abstract:Conventional spoken language understanding systems consist of two main components: an automatic speech recognition module that converts audio to a transcript, and a natural language understanding module that transforms the resulting text (or top N hypotheses) into a set of domains, intents, and arguments. These modules are typically optimized independently. In this paper, we formulate audio to semantic understanding as a sequence-to-sequence problem [1]. We propose and compare various encoder-decoder based approaches that optimize both modules jointly, in an end-to-end manner. Evaluations on a real-world task show that 1) having an intermediate text representation is crucial for the quality of the predicted semantics, especially the intent arguments and 2) jointly optimizing the full system improves overall accuracy of prediction. Compared to independently trained models, our best jointly trained model achieves similar domain and intent prediction F1 scores, but improves argument word error rate by 18% relative.
Multilingual Speech Recognition With A Single End-To-End Model
Feb 15, 2018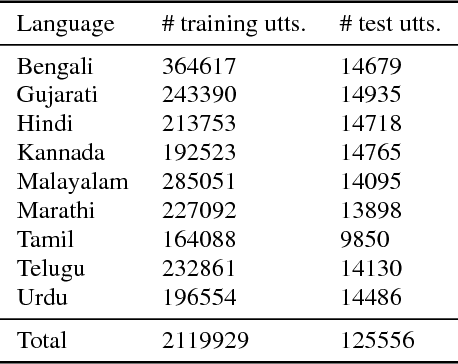
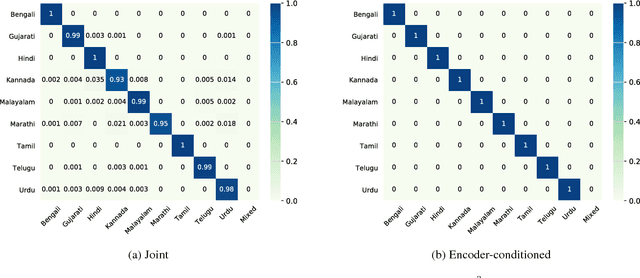
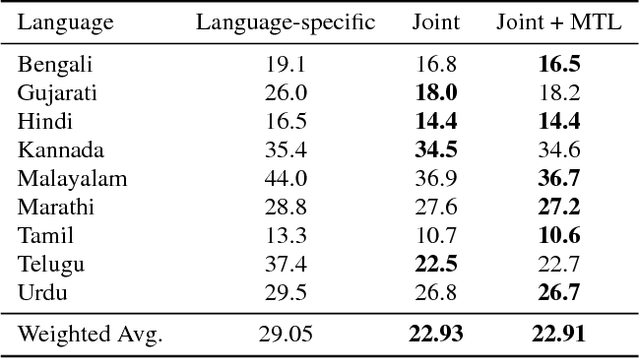
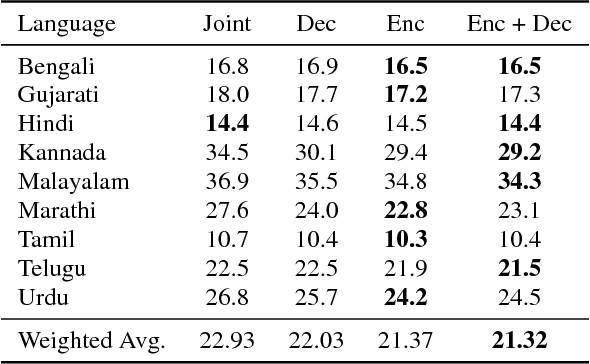
Abstract:Training a conventional automatic speech recognition (ASR) system to support multiple languages is challenging because the sub-word unit, lexicon and word inventories are typically language specific. In contrast, sequence-to-sequence models are well suited for multilingual ASR because they encapsulate an acoustic, pronunciation and language model jointly in a single network. In this work we present a single sequence-to-sequence ASR model trained on 9 different Indian languages, which have very little overlap in their scripts. Specifically, we take a union of language-specific grapheme sets and train a grapheme-based sequence-to-sequence model jointly on data from all languages. We find that this model, which is not explicitly given any information about language identity, improves recognition performance by 21% relative compared to analogous sequence-to-sequence models trained on each language individually. By modifying the model to accept a language identifier as an additional input feature, we further improve performance by an additional 7% relative and eliminate confusion between different languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge