Tongzhou Chen
LegoSLM: Connecting LLM with Speech Encoder using CTC Posteriors
May 16, 2025Abstract:Recently, large-scale pre-trained speech encoders and Large Language Models (LLMs) have been released, which show state-of-the-art performance on a range of spoken language processing tasks including Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). To effectively combine both models for better performance, continuous speech prompts, and ASR error correction have been adopted. However, these methods are prone to suboptimal performance or are inflexible. In this paper, we propose a new paradigm, LegoSLM, that bridges speech encoders and LLMs using the ASR posterior matrices. The speech encoder is trained to generate Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) posteriors over the LLM vocabulary, which are used to reconstruct pseudo-audio embeddings by computing a weighted sum of the LLM input embeddings. These embeddings are concatenated with text embeddings in the LLM input space. Using the well-performing USM and Gemma models as an example, we demonstrate that our proposed LegoSLM method yields good performance on both ASR and speech translation tasks. By connecting USM with Gemma models, we can get an average of 49% WERR over the USM-CTC baseline on 8 MLS testsets. The trained model also exhibits modularity in a range of settings -- after fine-tuning the Gemma model weights, the speech encoder can be switched and combined with the LLM in a zero-shot fashion. Additionally, we propose to control the decode-time influence of the USM and LLM using a softmax temperature, which shows effectiveness in domain adaptation.
Multilingual and Fully Non-Autoregressive ASR with Large Language Model Fusion: A Comprehensive Study
Jan 23, 2024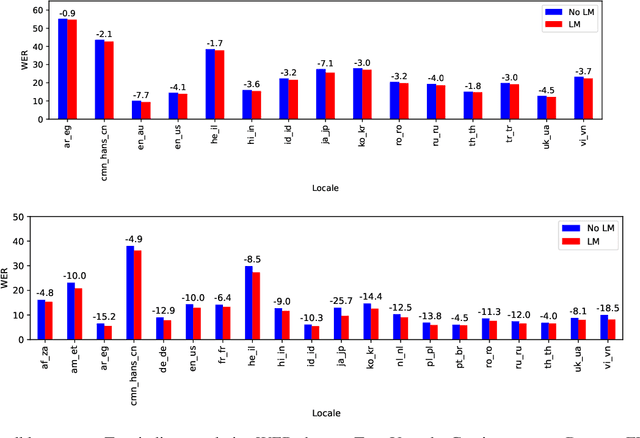
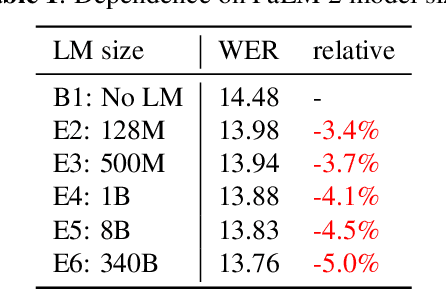
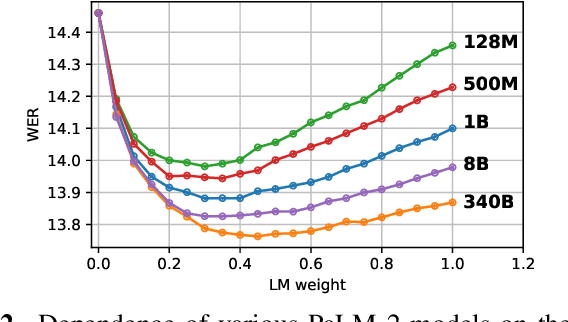
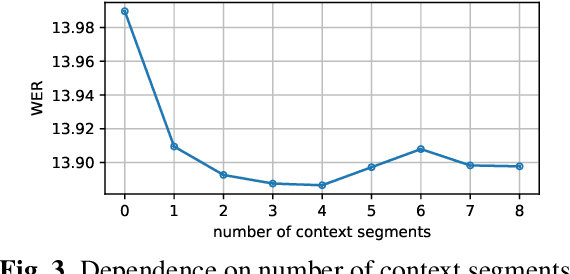
Abstract:In the era of large models, the autoregressive nature of decoding often results in latency serving as a significant bottleneck. We propose a non-autoregressive LM-fused ASR system that effectively leverages the parallelization capabilities of accelerator hardware. Our approach combines the Universal Speech Model (USM) and the PaLM 2 language model in per-segment scoring mode, achieving an average relative WER improvement across all languages of 10.8% on FLEURS and 3.6% on YouTube captioning. Furthermore, our comprehensive ablation study analyzes key parameters such as LLM size, context length, vocabulary size, fusion methodology. For instance, we explore the impact of LLM size ranging from 128M to 340B parameters on ASR performance. This study provides valuable insights into the factors influencing the effectiveness of practical large-scale LM-fused speech recognition systems.
Large-scale Language Model Rescoring on Long-form Data
Jun 13, 2023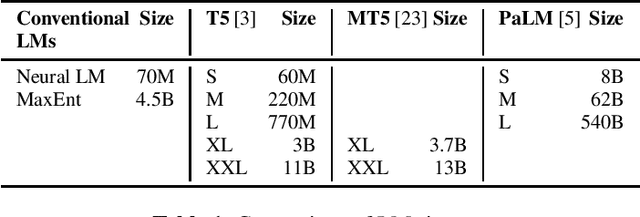
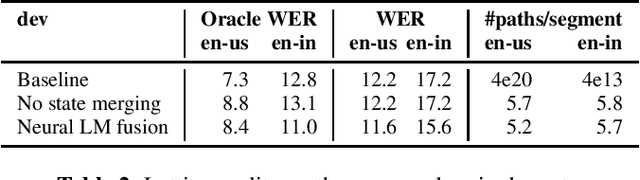

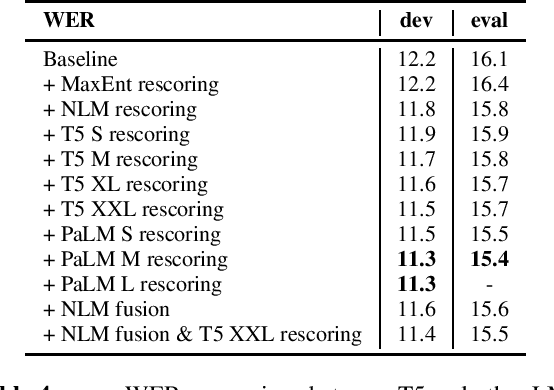
Abstract:In this work, we study the impact of Large-scale Language Models (LLM) on Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) of YouTube videos, which we use as a source for long-form ASR. We demonstrate up to 8\% relative reduction in Word Error Eate (WER) on US English (en-us) and code-switched Indian English (en-in) long-form ASR test sets and a reduction of up to 30\% relative on Salient Term Error Rate (STER) over a strong first-pass baseline that uses a maximum-entropy based language model. Improved lattice processing that results in a lattice with a proper (non-tree) digraph topology and carrying context from the 1-best hypothesis of the previous segment(s) results in significant wins in rescoring with LLMs. We also find that the gains in performance from the combination of LLMs trained on vast quantities of available data (such as C4) and conventional neural LMs is additive and significantly outperforms a strong first-pass baseline with a maximum entropy LM.
* 5 pages, accepted in ICASSP 2023
JEIT: Joint End-to-End Model and Internal Language Model Training for Speech Recognition
Feb 16, 2023



Abstract:We propose JEIT, a joint end-to-end (E2E) model and internal language model (ILM) training method to inject large-scale unpaired text into ILM during E2E training which improves rare-word speech recognition. With JEIT, the E2E model computes an E2E loss on audio-transcript pairs while its ILM estimates a cross-entropy loss on unpaired text. The E2E model is trained to minimize a weighted sum of E2E and ILM losses. During JEIT, ILM absorbs knowledge from unpaired text while the E2E training serves as regularization. Unlike ILM adaptation methods, JEIT does not require a separate adaptation step and avoids the need for Kullback-Leibler divergence regularization of ILM. We also show that modular hybrid autoregressive transducer (MHAT) performs better than HAT in the JEIT framework, and is much more robust than HAT during ILM adaptation. To push the limit of unpaired text injection, we further propose a combined JEIT and JOIST training (CJJT) that benefits from modality matching, encoder text injection and ILM training. Both JEIT and CJJT can foster a more effective LM fusion. With 100B unpaired sentences, JEIT/CJJT improves rare-word recognition accuracy by up to 16.4% over a model trained without unpaired text.
* 5 pages, 3 figures, in ICASSP 2023
Modular Hybrid Autoregressive Transducer
Oct 31, 2022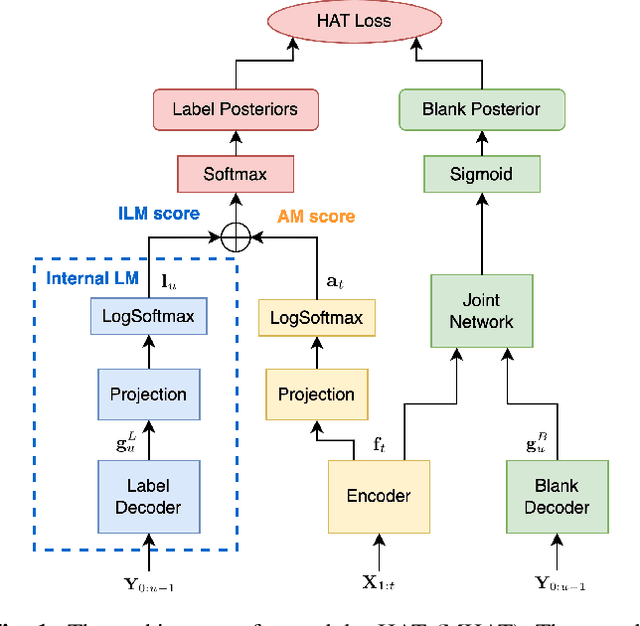
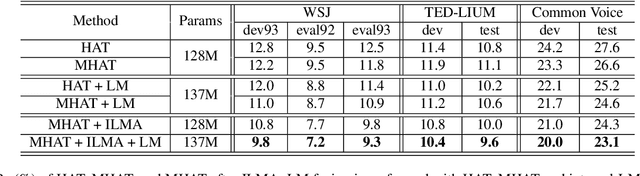
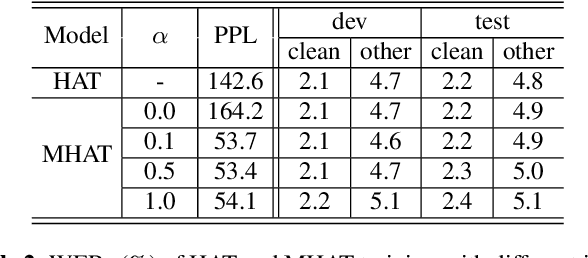
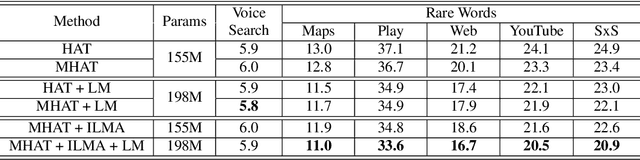
Abstract:Text-only adaptation of a transducer model remains challenging for end-to-end speech recognition since the transducer has no clearly separated acoustic model (AM), language model (LM) or blank model. In this work, we propose a modular hybrid autoregressive transducer (MHAT) that has structurally separated label and blank decoders to predict label and blank distributions, respectively, along with a shared acoustic encoder. The encoder and label decoder outputs are directly projected to AM and internal LM scores and then added to compute label posteriors. We train MHAT with an internal LM loss and a HAT loss to ensure that its internal LM becomes a standalone neural LM that can be effectively adapted to text. Moreover, text adaptation of MHAT fosters a much better LM fusion than internal LM subtraction-based methods. On Google's large-scale production data, a multi-domain MHAT adapted with 100B sentences achieves relative WER reductions of up to 12.4% without LM fusion and 21.5% with LM fusion from 400K-hour trained HAT.
* 8 pages, 1 figure, SLT 2022
Improving Rare Word Recognition with LM-aware MWER Training
Apr 15, 2022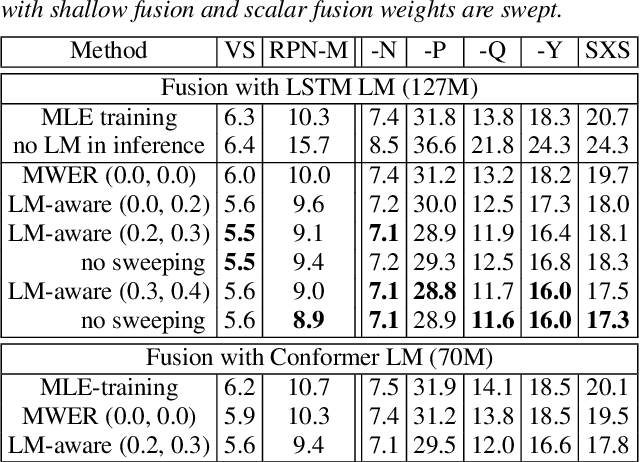
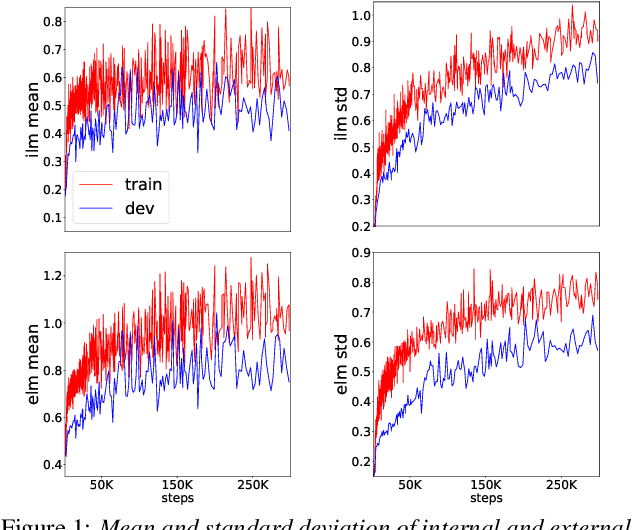

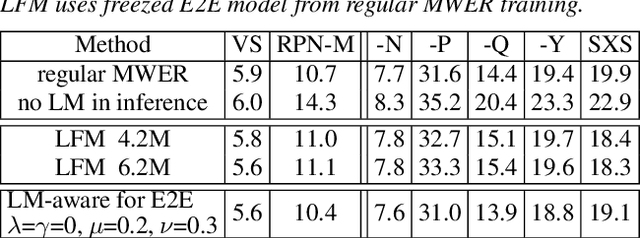
Abstract:Language models (LMs) significantly improve the recognition accuracy of end-to-end (E2E) models on words rarely seen during training, when used in either the shallow fusion or the rescoring setups. In this work, we introduce LMs in the learning of hybrid autoregressive transducer (HAT) models in the discriminative training framework, to mitigate the training versus inference gap regarding the use of LMs. For the shallow fusion setup, we use LMs during both hypotheses generation and loss computation, and the LM-aware MWER-trained model achieves 10\% relative improvement over the model trained with standard MWER on voice search test sets containing rare words. For the rescoring setup, we learn a small neural module to generate per-token fusion weights in a data-dependent manner. This model achieves the same rescoring WER as regular MWER-trained model, but without the need for sweeping fusion weights.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge