Allen Lin
Towards An Efficient LLM Training Paradigm for CTR Prediction
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated tremendous potential as the next-generation ranking-based recommendation system. Many recent works have shown that LLMs can significantly outperform conventional click-through-rate (CTR) prediction approaches. Despite such promising results, the computational inefficiency inherent in the current training paradigm makes it particularly challenging to train LLMs for ranking-based recommendation tasks on large datasets. To train LLMs for CTR prediction, most existing studies adopt the prevalent ''sliding-window'' paradigm. Given a sequence of $m$ user interactions, a unique training prompt is constructed for each interaction by designating it as the prediction target along with its preceding $n$ interactions serving as context. In turn, the sliding-window paradigm results in an overall complexity of $O(mn^2)$ that scales linearly with the length of user interactions. Consequently, a direct adoption to train LLMs with such strategy can result in prohibitively high training costs as the length of interactions grows. To alleviate the computational inefficiency, we propose a novel training paradigm, namely Dynamic Target Isolation (DTI), that structurally parallelizes the training of $k$ (where $k >> 1$) target interactions. Furthermore, we identify two major bottlenecks - hidden-state leakage and positional bias overfitting - that limit DTI to only scale up to a small value of $k$ (e.g., 5) then propose a computationally light solution to effectively tackle each. Through extensive experiments on three widely adopted public CTR datasets, we empirically show that DTI reduces training time by an average of $\textbf{92%}$ (e.g., from $70.5$ hrs to $5.31$ hrs), without compromising CTR prediction performance.
Federated Conversational Recommender System
Mar 02, 2025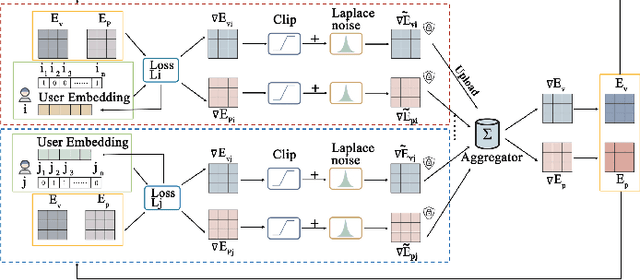
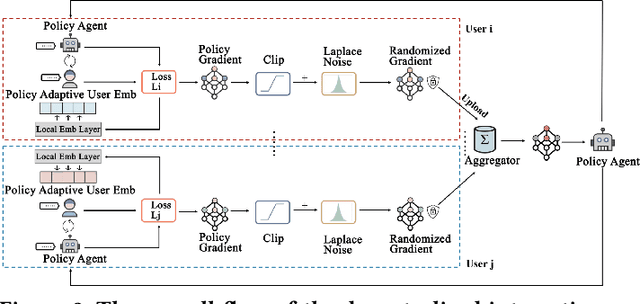
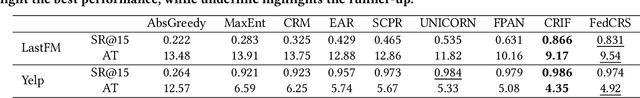
Abstract:Conversational Recommender Systems (CRSs) have become increasingly popular as a powerful tool for providing personalized recommendation experiences. By directly engaging with users in a conversational manner to learn their current and fine-grained preferences, a CRS can quickly derive recommendations that are relevant and justifiable. However, existing conversational recommendation systems (CRSs) typically rely on a centralized training and deployment process, which involves collecting and storing explicitly-communicated user preferences in a centralized repository. These fine-grained user preferences are completely human-interpretable and can easily be used to infer sensitive information (e.g., financial status, political stands, and health information) about the user, if leaked or breached. To address the user privacy concerns in CRS, we first define a set of privacy protection guidelines for preserving user privacy under the conversational recommendation setting. Based on these guidelines, we propose a novel federated conversational recommendation framework that effectively reduces the risk of exposing user privacy by (i) de-centralizing both the historical interests estimation stage and the interactive preference elicitation stage and (ii) strictly bounding privacy leakage by enforcing user-level differential privacy with meticulously selected privacy budgets. Through extensive experiments, we show that the proposed framework not only satisfies these user privacy protection guidelines, but also enables the system to achieve competitive recommendation performance even when compared to the state-of-the-art non-private conversational recommendation approach.
Cold-Start Recommendation towards the Era of Large Language Models (LLMs): A Comprehensive Survey and Roadmap
Jan 03, 2025
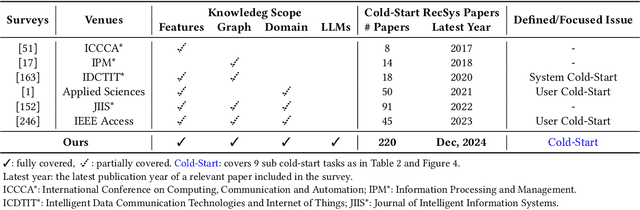
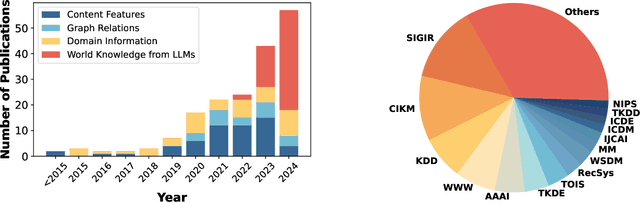
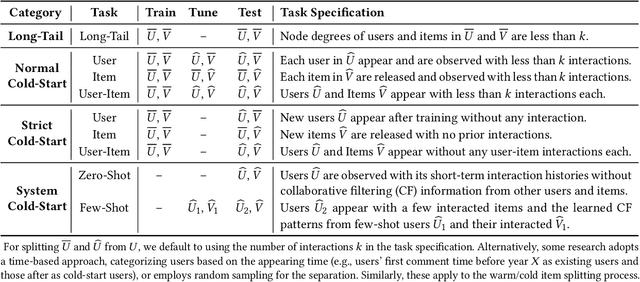
Abstract:Cold-start problem is one of the long-standing challenges in recommender systems, focusing on accurately modeling new or interaction-limited users or items to provide better recommendations. Due to the diversification of internet platforms and the exponential growth of users and items, the importance of cold-start recommendation (CSR) is becoming increasingly evident. At the same time, large language models (LLMs) have achieved tremendous success and possess strong capabilities in modeling user and item information, providing new potential for cold-start recommendations. However, the research community on CSR still lacks a comprehensive review and reflection in this field. Based on this, in this paper, we stand in the context of the era of large language models and provide a comprehensive review and discussion on the roadmap, related literature, and future directions of CSR. Specifically, we have conducted an exploration of the development path of how existing CSR utilizes information, from content features, graph relations, and domain information, to the world knowledge possessed by large language models, aiming to provide new insights for both the research and industrial communities on CSR. Related resources of cold-start recommendations are collected and continuously updated for the community in https://github.com/YuanchenBei/Awesome-Cold-Start-Recommendation.
Countering Mainstream Bias via End-to-End Adaptive Local Learning
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:Collaborative filtering (CF) based recommendations suffer from mainstream bias -- where mainstream users are favored over niche users, leading to poor recommendation quality for many long-tail users. In this paper, we identify two root causes of this mainstream bias: (i) discrepancy modeling, whereby CF algorithms focus on modeling mainstream users while neglecting niche users with unique preferences; and (ii) unsynchronized learning, where niche users require more training epochs than mainstream users to reach peak performance. Targeting these causes, we propose a novel end-To-end Adaptive Local Learning (TALL) framework to provide high-quality recommendations to both mainstream and niche users. TALL uses a loss-driven Mixture-of-Experts module to adaptively ensemble experts to provide customized local models for different users. Further, it contains an adaptive weight module to synchronize the learning paces of different users by dynamically adjusting weights in the loss. Extensive experiments demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of the proposed model. Code and data are provided at \url{https://github.com/JP-25/end-To-end-Adaptive-Local-Leanring-TALL-}
* ECIR 2024
NTIRE 2023 Quality Assessment of Video Enhancement Challenge
Jul 19, 2023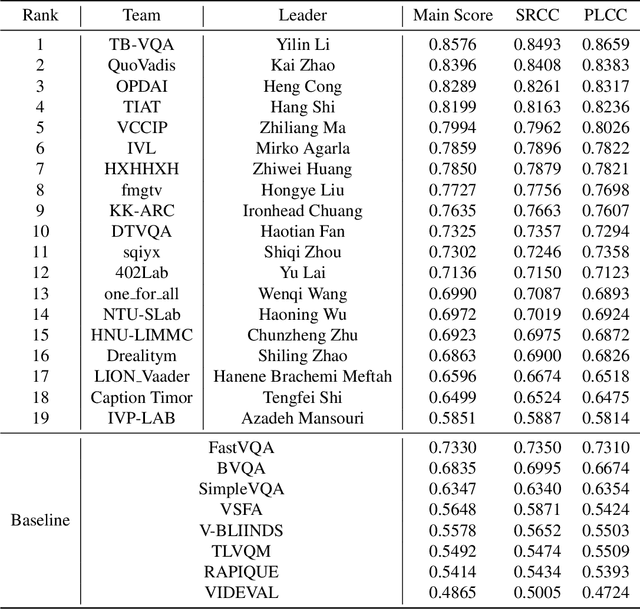
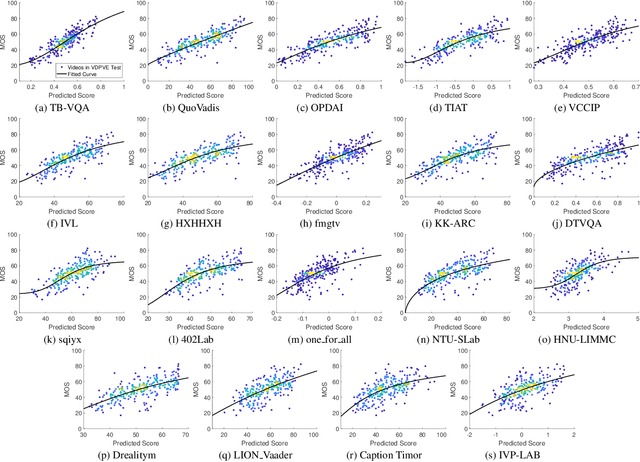

Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2023 Quality Assessment of Video Enhancement Challenge, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2023. This challenge is to address a major challenge in the field of video processing, namely, video quality assessment (VQA) for enhanced videos. The challenge uses the VQA Dataset for Perceptual Video Enhancement (VDPVE), which has a total of 1211 enhanced videos, including 600 videos with color, brightness, and contrast enhancements, 310 videos with deblurring, and 301 deshaked videos. The challenge has a total of 167 registered participants. 61 participating teams submitted their prediction results during the development phase, with a total of 3168 submissions. A total of 176 submissions were submitted by 37 participating teams during the final testing phase. Finally, 19 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets, and detailed the methods they used. Some methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods have demonstrated superior prediction performance.
Enhancing User Personalization in Conversational Recommenders
Feb 13, 2023



Abstract:Conversational recommenders are emerging as a powerful tool to personalize a user's recommendation experience. Through a back-and-forth dialogue, users can quickly hone in on just the right items. Many approaches to conversational recommendation, however, only partially explore the user preference space and make limiting assumptions about how user feedback can be best incorporated, resulting in long dialogues and poor recommendation performance. In this paper, we propose a novel conversational recommendation framework with two unique features: (i) a greedy NDCG attribute selector, to enhance user personalization in the interactive preference elicitation process by prioritizing attributes that most effectively represent the actual preference space of the user; and (ii) a user representation refiner, to effectively fuse together the user preferences collected from the interactive elicitation process to obtain a more personalized understanding of the user. Through extensive experiments on four frequently used datasets, we find the proposed framework not only outperforms all the state-of-the-art conversational recommenders (in terms of both recommendation performance and conversation efficiency), but also provides a more personalized experience for the user under the proposed multi-groundtruth multi-round conversational recommendation setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge