Alex Waibel
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Policies and Evaluation for Online Meeting Summarization
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:With more and more meetings moving to a digital domain, meeting summarization has recently gained interest in both academic and commercial research. However, prior academic research focuses on meeting summarization as an offline task, performed after the meeting concludes. In this paper, we perform the first systematic study of online meeting summarization. For this purpose, we propose several policies for conducting online summarization. We discuss the unique challenges of this task compared to the offline setting and define novel metrics to evaluate latency and partial summary quality. The experiments on the AutoMin dataset show that 1) online models can produce strong summaries, 2) our metrics allow a detailed analysis of different systems' quality-latency trade-off, also taking into account intermediate outputs and 3) adaptive policies perform better than fixed scheduled ones. These findings provide a starting point for the wider research community to explore this important task.
PIER: A Novel Metric for Evaluating What Matters in Code-Switching
Jan 16, 2025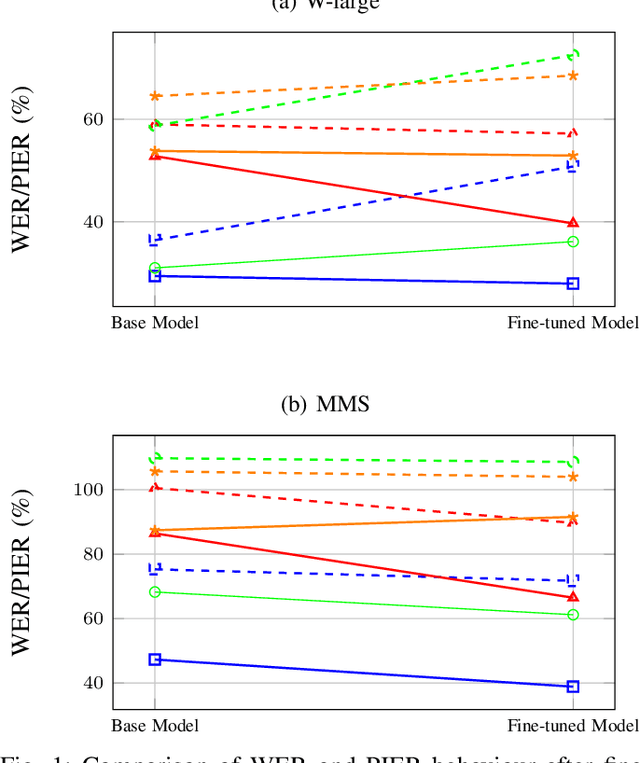
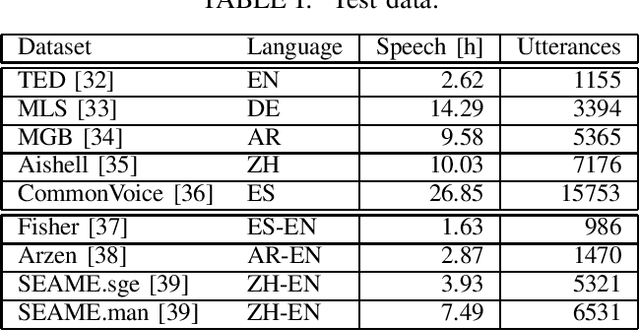
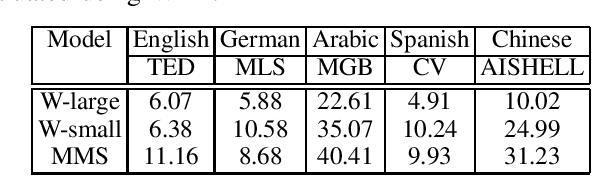
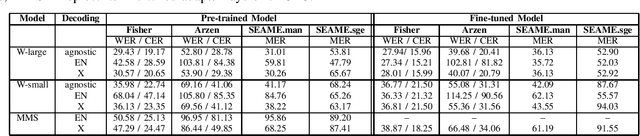
Abstract:Code-switching, the alternation of languages within a single discourse, presents a significant challenge for Automatic Speech Recognition. Despite the unique nature of the task, performance is commonly measured with established metrics such as Word-Error-Rate (WER). However, in this paper, we question whether these general metrics accurately assess performance on code-switching. Specifically, using both Connectionist-Temporal-Classification and Encoder-Decoder models, we show fine-tuning on non-code-switched data from both matrix and embedded language improves classical metrics on code-switching test sets, although actual code-switched words worsen (as expected). Therefore, we propose Point-of-Interest Error Rate (PIER), a variant of WER that focuses only on specific words of interest. We instantiate PIER on code-switched utterances and show that this more accurately describes the code-switching performance, showing huge room for improvement in future work. This focused evaluation allows for a more precise assessment of model performance, particularly in challenging aspects such as inter-word and intra-word code-switching.
Findings of the IWSLT 2024 Evaluation Campaign
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:This paper reports on the shared tasks organized by the 21st IWSLT Conference. The shared tasks address 7 scientific challenges in spoken language translation: simultaneous and offline translation, automatic subtitling and dubbing, speech-to-speech translation, dialect and low-resource speech translation, and Indic languages. The shared tasks attracted 18 teams whose submissions are documented in 26 system papers. The growing interest towards spoken language translation is also witnessed by the constantly increasing number of shared task organizers and contributors to the overview paper, almost evenly distributed across industry and academia.
Episodic Memory Verbalization using Hierarchical Representations of Life-Long Robot Experience
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Verbalization of robot experience, i.e., summarization of and question answering about a robot's past, is a crucial ability for improving human-robot interaction. Previous works applied rule-based systems or fine-tuned deep models to verbalize short (several-minute-long) streams of episodic data, limiting generalization and transferability. In our work, we apply large pretrained models to tackle this task with zero or few examples, and specifically focus on verbalizing life-long experiences. For this, we derive a tree-like data structure from episodic memory (EM), with lower levels representing raw perception and proprioception data, and higher levels abstracting events to natural language concepts. Given such a hierarchical representation built from the experience stream, we apply a large language model as an agent to interactively search the EM given a user's query, dynamically expanding (initially collapsed) tree nodes to find the relevant information. The approach keeps computational costs low even when scaling to months of robot experience data. We evaluate our method on simulated household robot data, human egocentric videos, and real-world robot recordings, demonstrating its flexibility and scalability.
Incremental Blockwise Beam Search for Simultaneous Speech Translation with Controllable Quality-Latency Tradeoff
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:Blockwise self-attentional encoder models have recently emerged as one promising end-to-end approach to simultaneous speech translation. These models employ a blockwise beam search with hypothesis reliability scoring to determine when to wait for more input speech before translating further. However, this method maintains multiple hypotheses until the entire speech input is consumed -- this scheme cannot directly show a single \textit{incremental} translation to users. Further, this method lacks mechanisms for \textit{controlling} the quality vs. latency tradeoff. We propose a modified incremental blockwise beam search incorporating local agreement or hold-$n$ policies for quality-latency control. We apply our framework to models trained for online or offline translation and demonstrate that both types can be effectively used in online mode. Experimental results on MuST-C show 0.6-3.6 BLEU improvement without changing latency or 0.8-1.4 s latency improvement without changing quality.
* Accepted at INTERSPEECH 2023
Incremental Learning of Humanoid Robot Behavior from Natural Interaction and Large Language Models
Sep 08, 2023



Abstract:Natural-language dialog is key for intuitive human-robot interaction. It can be used not only to express humans' intents, but also to communicate instructions for improvement if a robot does not understand a command correctly. Of great importance is to endow robots with the ability to learn from such interaction experience in an incremental way to allow them to improve their behaviors or avoid mistakes in the future. In this paper, we propose a system to achieve incremental learning of complex behavior from natural interaction, and demonstrate its implementation on a humanoid robot. Building on recent advances, we present a system that deploys Large Language Models (LLMs) for high-level orchestration of the robot's behavior, based on the idea of enabling the LLM to generate Python statements in an interactive console to invoke both robot perception and action. The interaction loop is closed by feeding back human instructions, environment observations, and execution results to the LLM, thus informing the generation of the next statement. Specifically, we introduce incremental prompt learning, which enables the system to interactively learn from its mistakes. For that purpose, the LLM can call another LLM responsible for code-level improvements of the current interaction based on human feedback. The improved interaction is then saved in the robot's memory, and thus retrieved on similar requests. We integrate the system in the robot cognitive architecture of the humanoid robot ARMAR-6 and evaluate our methods both quantitatively (in simulation) and qualitatively (in simulation and real-world) by demonstrating generalized incrementally-learned knowledge.
Train Global, Tailor Local: Minimalist Multilingual Translation into Endangered Languages
May 05, 2023Abstract:In many humanitarian scenarios, translation into severely low resource languages often does not require a universal translation engine, but a dedicated text-specific translation engine. For example, healthcare records, hygienic procedures, government communication, emergency procedures and religious texts are all limited texts. While generic translation engines for all languages do not exist, translation of multilingually known limited texts into new, endangered languages may be possible and reduce human translation effort. We attempt to leverage translation resources from many rich resource languages to efficiently produce best possible translation quality for a well known text, which is available in multiple languages, in a new, severely low resource language. We examine two approaches: 1. best selection of seed sentences to jump start translations in a new language in view of best generalization to the remainder of a larger targeted text(s), and 2. we adapt large general multilingual translation engines from many other languages to focus on a specific text in a new, unknown language. We find that adapting large pretrained multilingual models to the domain/text first and then to the severely low resource language works best. If we also select a best set of seed sentences, we can improve average chrF performance on new test languages from a baseline of 21.9 to 50.7, while reducing the number of seed sentences to only around 1,000 in the new, unknown language.
Adaptive multilingual speech recognition with pretrained models
May 24, 2022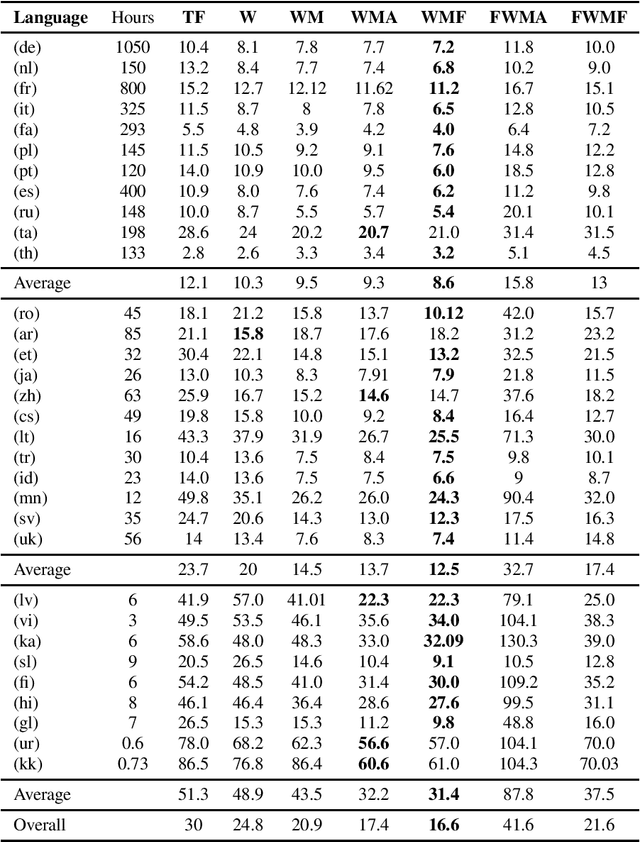
Abstract:Multilingual speech recognition with supervised learning has achieved great results as reflected in recent research. With the development of pretraining methods on audio and text data, it is imperative to transfer the knowledge from unsupervised multilingual models to facilitate recognition, especially in many languages with limited data. Our work investigated the effectiveness of using two pretrained models for two modalities: wav2vec 2.0 for audio and MBART50 for text, together with the adaptive weight techniques to massively improve the recognition quality on the public datasets containing CommonVoice and Europarl. Overall, we noticed an 44% improvement over purely supervised learning, and more importantly, each technique provides a different reinforcement in different languages. We also explore other possibilities to potentially obtain the best model by slightly adding either depth or relative attention to the architecture.
Active Learning for Massively Parallel Translation of Constrained Text into Low Resource Languages
Aug 16, 2021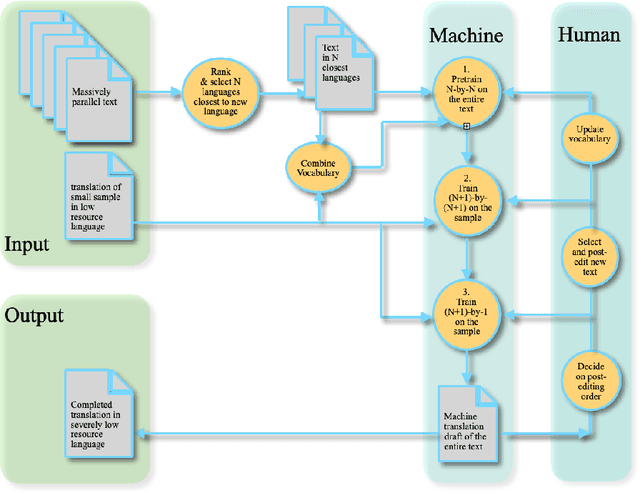
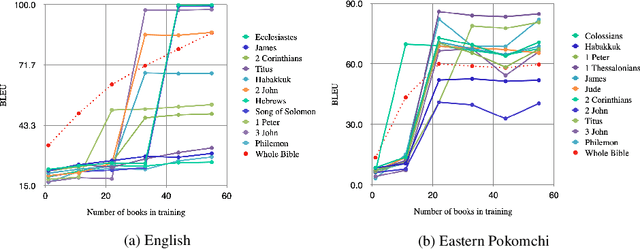
Abstract:We translate a closed text that is known in advance and available in many languages into a new and severely low resource language. Most human translation efforts adopt a portion-based approach to translate consecutive pages/chapters in order, which may not suit machine translation. We compare the portion-based approach that optimizes coherence of the text locally with the random sampling approach that increases coverage of the text globally. Our results show that the random sampling approach performs better. When training on a seed corpus of ~1,000 lines from the Bible and testing on the rest of the Bible (~30,000 lines), random sampling gives a performance gain of +11.0 BLEU using English as a simulated low resource language, and +4.9 BLEU using Eastern Pokomchi, a Mayan language. Furthermore, we compare three ways of updating machine translation models with increasing amount of human post-edited data through iterations. We find that adding newly post-edited data to training after vocabulary update without self-supervision performs the best. We propose an algorithm for human and machine to work together seamlessly to translate a closed text into a severely low resource language.
Family of Origin and Family of Choice: Massively Parallel Lexiconized Iterative Pretraining for Severely Low Resource Machine Translation
Apr 28, 2021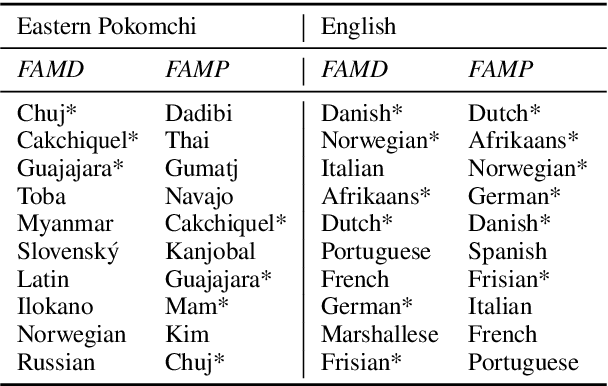
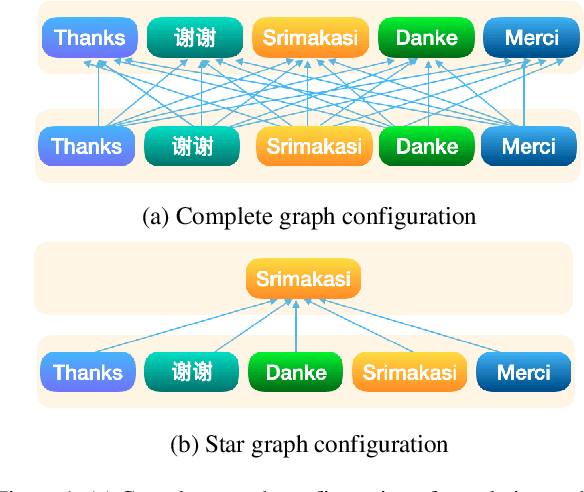


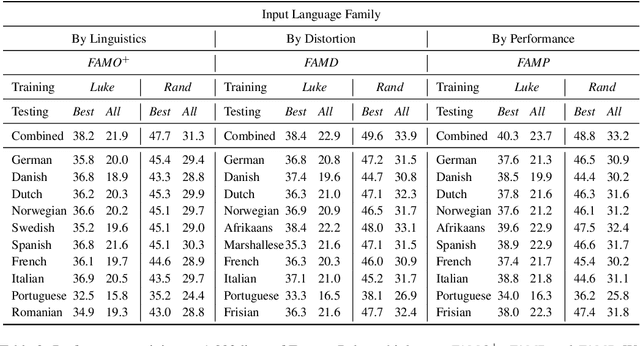
Abstract:We translate a closed text that is known in advance into a severely low resource language by leveraging massive source parallelism. In other words, given a text in 124 source languages, we translate it into a severely low resource language using only ~1,000 lines of low resource data without any external help. Firstly, we propose a systematic method to rank and choose source languages that are close to the low resource language. We call the linguistic definition of language family Family of Origin (FAMO), and we call the empirical definition of higher-ranked languages using our metrics Family of Choice (FAMC). Secondly, we build an Iteratively Pretrained Multilingual Order-preserving Lexiconized Transformer (IPML) to train on ~1,000 lines (~3.5%) of low resource data. To translate named entities correctly, we build a massive lexicon table for 2,939 Bible named entities in 124 source languages, and include many that occur once and covers more than 66 severely low resource languages. Moreover, we also build a novel method of combining translations from different source languages into one. Using English as a hypothetical low resource language, we get a +23.9 BLEU increase over a multilingual baseline, and a +10.3 BLEU increase over our asymmetric baseline in the Bible dataset. We get a 42.8 BLEU score for Portuguese-English translation on the medical EMEA dataset. We also have good results for a real severely low resource Mayan language, Eastern Pokomchi.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge