Adam Harrison
SAME: Deformable Image Registration based on Self-supervised Anatomical Embeddings
Sep 23, 2021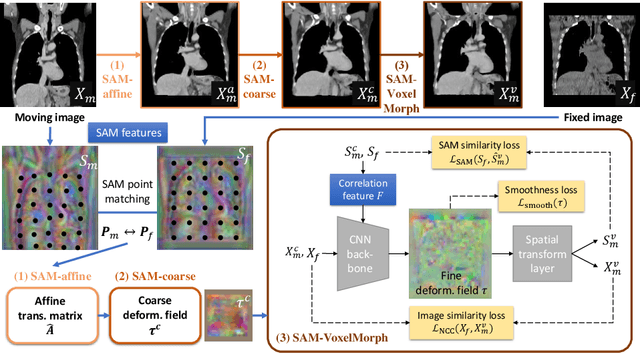
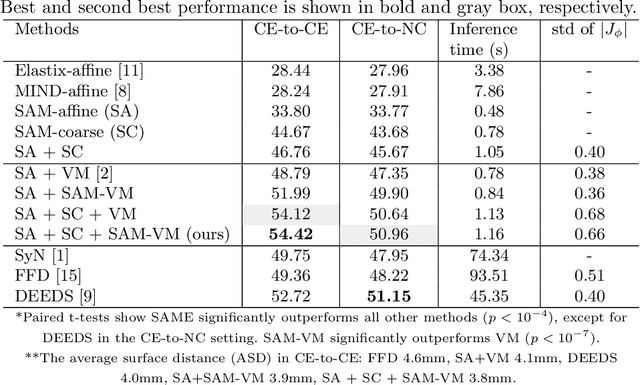


Abstract:In this work, we introduce a fast and accurate method for unsupervised 3D medical image registration. This work is built on top of a recent algorithm SAM, which is capable of computing dense anatomical/semantic correspondences between two images at the pixel level. Our method is named SAME, which breaks down image registration into three steps: affine transformation, coarse deformation, and deep deformable registration. Using SAM embeddings, we enhance these steps by finding more coherent correspondences, and providing features and a loss function with better semantic guidance. We collect a multi-phase chest computed tomography dataset with 35 annotated organs for each patient and conduct inter-subject registration for quantitative evaluation. Results show that SAME outperforms widely-used traditional registration techniques (Elastix FFD, ANTs SyN) and learning based VoxelMorph method by at least 4.7% and 2.7% in Dice scores for two separate tasks of within-contrast-phase and across-contrast-phase registration, respectively. SAME achieves the comparable performance to the best traditional registration method, DEEDS (from our evaluation), while being orders of magnitude faster (from 45 seconds to 1.2 seconds).
Scalable Semi-supervised Landmark Localization for X-ray Images using Few-shot Deep Adaptive Graph
Apr 29, 2021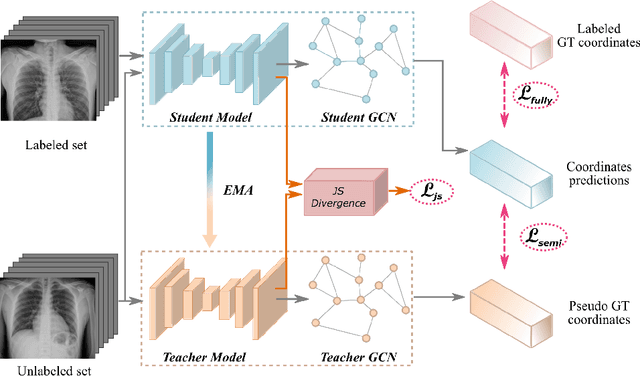


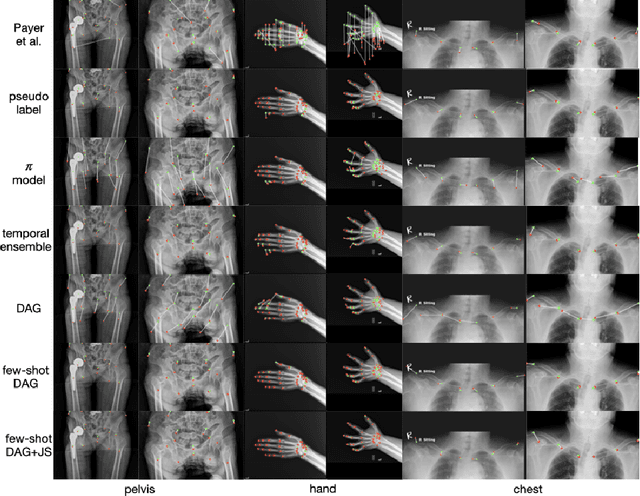
Abstract:Landmark localization plays an important role in medical image analysis. Learning based methods, including CNN and GCN, have demonstrated the state-of-the-art performance. However, most of these methods are fully-supervised and heavily rely on manual labeling of a large training dataset. In this paper, based on a fully-supervised graph-based method, DAG, we proposed a semi-supervised extension of it, termed few-shot DAG, \ie five-shot DAG. It first trains a DAG model on the labeled data and then fine-tunes the pre-trained model on the unlabeled data with a teacher-student SSL mechanism. In addition to the semi-supervised loss, we propose another loss using JS divergence to regulate the consistency of the intermediate feature maps. We extensively evaluated our method on pelvis, hand and chest landmark detection tasks. Our experiment results demonstrate consistent and significant improvements over previous methods.
Fully-Automated Liver Tumor Localization and Characterization from Multi-Phase MR Volumes Using Key-Slice ROI Parsing: A Physician-Inspired Approach
Dec 15, 2020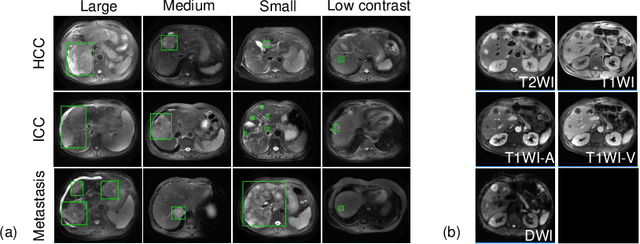
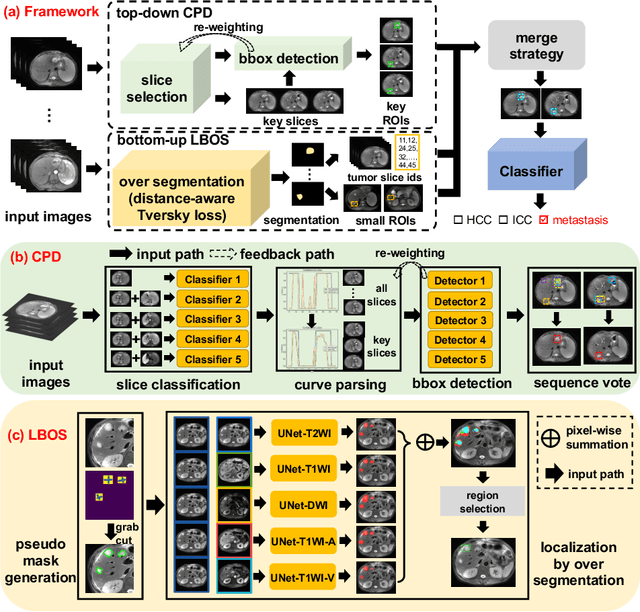
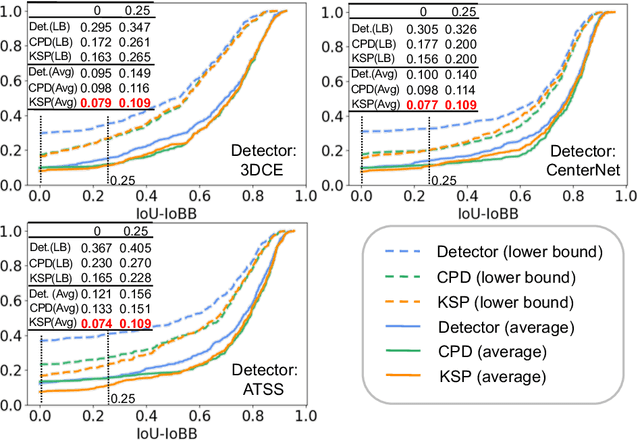
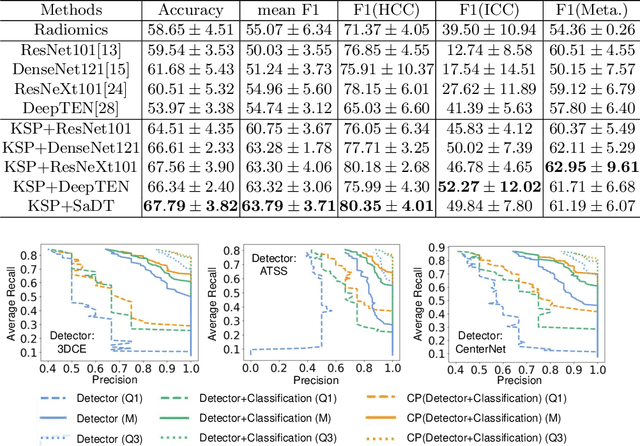
Abstract:Using radiological scans to identify liver tumors is crucial for proper patient treatment. This is highly challenging, as top radiologists only achieve F1 scores of roughly 80% (hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) vs. others) with only moderate inter-rater agreement, even when using multi-phase magnetic resonance (MR) imagery. Thus, there is great impetus for computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) solutions. A critical challengeis to reliably parse a 3D MR volume to localize diagnosable regions of interest (ROI). In this paper, we break down this problem using a key-slice parser (KSP), which emulates physician workflows by first identifying key slices and then localize their corresponding key ROIs. Because performance demands are so extreme, (not to miss any key ROI),our KSP integrates complementary modules--top-down classification-plus-detection (CPD) and bottom-up localization-by-over-segmentation(LBOS). The CPD uses a curve-parsing and detection confidence to re-weight classifier confidences. The LBOS uses over-segmentation to flag CPD failure cases and provides its own ROIs. For scalability, LBOS is only weakly trained on pseudo-masks using a new distance-aware Tversky loss. We evaluate our approach on the largest multi-phase MR liver lesion test dataset to date (430 biopsy-confirmed patients). Experiments demonstrate that our KSP can localize diagnosable ROIs with high reliability (85% patients have an average overlap of >= 40% with the ground truth). Moreover, we achieve an HCC vs. others F1 score of 0.804, providing a fully-automated CAD solution comparable with top human physicians.
Harvesting, Detecting, and Characterizing Liver Lesions from Large-scale Multi-phase CT Data via Deep Dynamic Texture Learning
Jun 28, 2020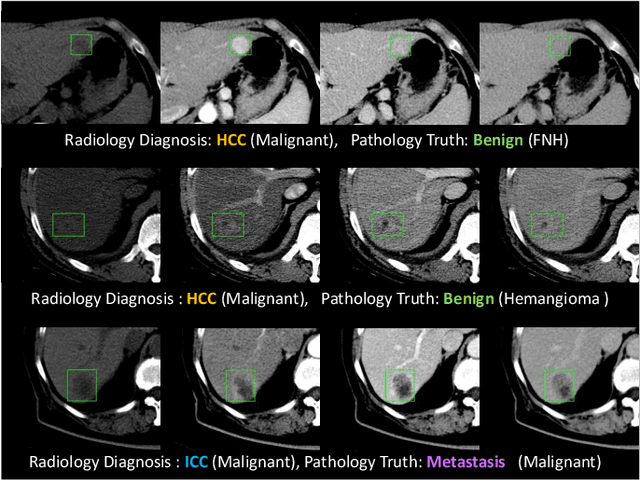
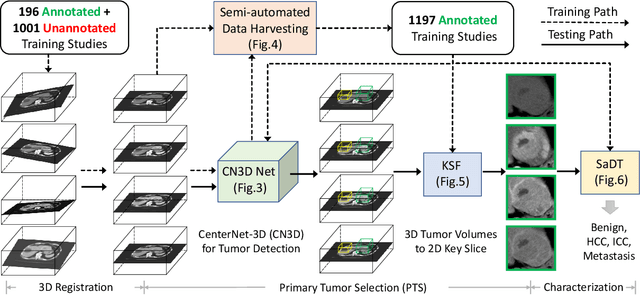
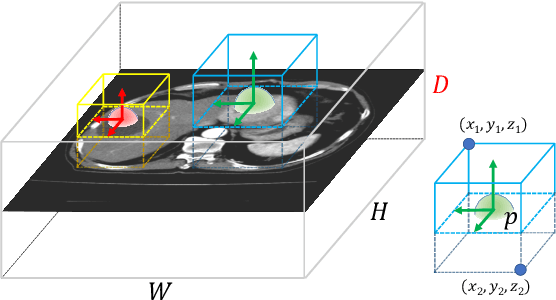
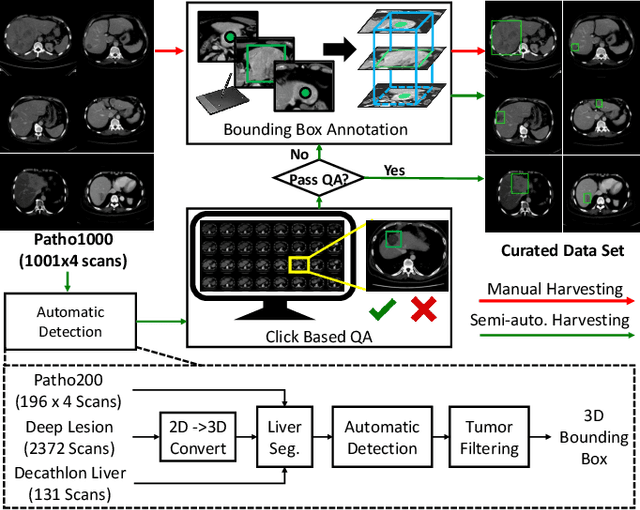
Abstract:Effective and non-invasive radiological imaging based tumor/lesion characterization (e.g., subtype classification) has long been a major aim in the oncology diagnosis and treatment procedures, with the hope of reducing needs for invasive surgical biopsies. Prior work are generally very restricted to a limited patient sample size, especially using patient studies with confirmed pathological reports as ground truth. In this work, we curate a patient cohort of 1305 dynamic contrast CT studies (i.e., 5220 multi-phase 3D volumes) with pathology confirmed ground truth. A novel fully-automated and multi-stage liver tumor characterization framework is proposed, comprising four steps of tumor proposal detection, tumor harvesting, primary tumor site selection, and deep texture-based characterization. More specifically, (1) we propose a 3D non-isotropic anchor-free lesion detection method; (2) we present and validate the use of multi-phase deep texture learning for precise liver lesion tissue characterization, named spatially adaptive deep texture (SaDT); (3) we leverage small-sized public datasets to semi-automatically curate our large-scale clinical dataset of 1305 patients where four main liver tumor subtypes of primary, secondary, metastasized and benign are presented. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our new data curation strategy, combined with the SaDT deep dynamic texture analysis, can effectively improve the mean F1 scores by >8.6% compared with baselines, in differentiating four major liver lesion types. This is a significant step towards the clinical goal.
Deep Lesion Graphs in the Wild: Relationship Learning and Organization of Significant Radiology Image Findings in a Diverse Large-scale Lesion Database
Jul 28, 2018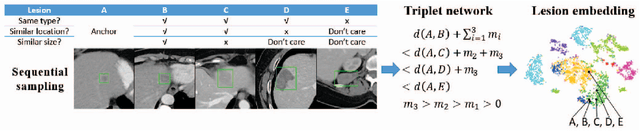
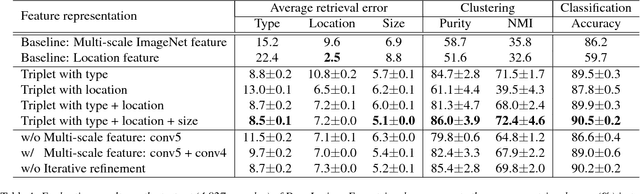
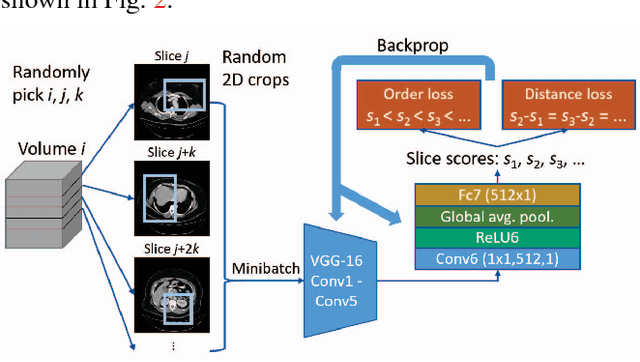
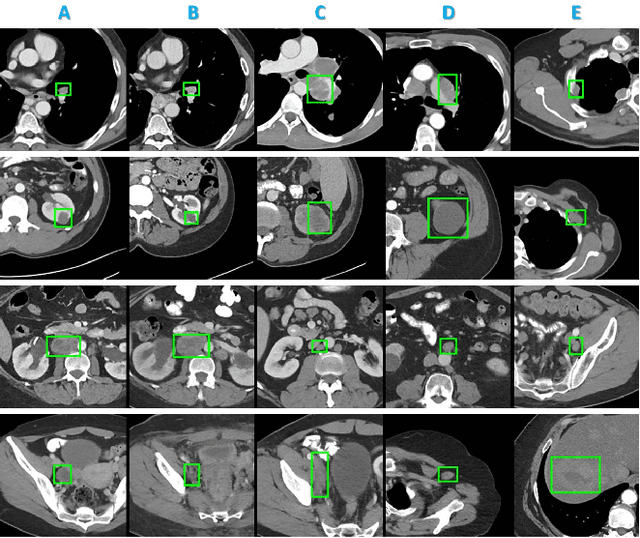
Abstract:Radiologists in their daily work routinely find and annotate significant abnormalities on a large number of radiology images. Such abnormalities, or lesions, have collected over years and stored in hospitals' picture archiving and communication systems. However, they are basically unsorted and lack semantic annotations like type and location. In this paper, we aim to organize and explore them by learning a deep feature representation for each lesion. A large-scale and comprehensive dataset, DeepLesion, is introduced for this task. DeepLesion contains bounding boxes and size measurements of over 32K lesions. To model their similarity relationship, we leverage multiple supervision information including types, self-supervised location coordinates and sizes. They require little manual annotation effort but describe useful attributes of the lesions. Then, a triplet network is utilized to learn lesion embeddings with a sequential sampling strategy to depict their hierarchical similarity structure. Experiments show promising qualitative and quantitative results on lesion retrieval, clustering, and classification. The learned embeddings can be further employed to build a lesion graph for various clinically useful applications. We propose algorithms for intra-patient lesion matching and missing annotation mining. Experimental results validate their effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge