Zhenchang Xing
Data61, CSIRO
DeMark: A Query-Free Black-Box Attack on Deepfake Watermarking Defenses
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:The rapid proliferation of realistic deepfakes has raised urgent concerns over their misuse, motivating the use of defensive watermarks in synthetic images for reliable detection and provenance tracking. However, this defense paradigm assumes such watermarks are inherently resistant to removal. We challenge this assumption with DeMark, a query-free black-box attack framework that targets defensive image watermarking schemes for deepfakes. DeMark exploits latent-space vulnerabilities in encoder-decoder watermarking models through a compressive sensing based sparsification process, suppressing watermark signals while preserving perceptual and structural realism appropriate for deepfakes. Across eight state-of-the-art watermarking schemes, DeMark reduces watermark detection accuracy from 100% to 32.9% on average while maintaining natural visual quality, outperforming existing attacks. We further evaluate three defense strategies, including image super resolution, sparse watermarking, and adversarial training, and find them largely ineffective. These results demonstrate that current encoder decoder watermarking schemes remain vulnerable to latent-space manipulations, underscoring the need for more robust watermarking methods to safeguard against deepfakes.
Environment-Aware Code Generation: How far are We?
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has improved code generation, but most evaluations still test isolated, small-scale code (e.g., a single function) under default or unspecified software environments. As a result, it is unclear whether LLMs can reliably generate executable code tailored to a user's specific environment. We present the first systematic study of Environment-Aware Code Generation (EACG), where generated code must be functionally correct and directly executable under arbitrary software configurations. To enable realistic evaluation, we introduce VersiBCB, a benchmark that is multi-package, execution-verified, and deprecation-aware, capturing complex and evolving environments that prior datasets often overlook. Using VersiBCB, we investigate three complementary adaptation axes: data, parameters, and cache, and develop representative strategies for each. Our results show that current LLMs struggle with environment-specific code generation, while our adaptations improve environment compatibility and executability. These findings highlight key challenges and opportunities for deploying LLMs in practical software engineering workflows.
Ensembling LLM-Induced Decision Trees for Explainable and Robust Error Detection
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Error detection (ED), which aims to identify incorrect or inconsistent cell values in tabular data, is important for ensuring data quality. Recent state-of-the-art ED methods leverage the pre-trained knowledge and semantic capability embedded in large language models (LLMs) to directly label whether a cell is erroneous. However, this LLM-as-a-labeler pipeline (1) relies on the black box, implicit decision process, thus failing to provide explainability for the detection results, and (2) is highly sensitive to prompts, yielding inconsistent outputs due to inherent model stochasticity, therefore lacking robustness. To address these limitations, we propose an LLM-as-an-inducer framework that adopts LLM to induce the decision tree for ED (termed TreeED) and further ensembles multiple such trees for consensus detection (termed ForestED), thereby improving explainability and robustness. Specifically, based on prompts derived from data context, decision tree specifications and output requirements, TreeED queries the LLM to induce the decision tree skeleton, whose root-to-leaf decision paths specify the stepwise procedure for evaluating a given sample. Each tree contains three types of nodes: (1) rule nodes that perform simple validation checks (e.g., format or range), (2) Graph Neural Network (GNN) nodes that capture complex patterns (e.g., functional dependencies), and (3) leaf nodes that output the final decision types (error or clean). Furthermore, ForestED employs uncertainty-based sampling to obtain multiple row subsets, constructing a decision tree for each subset using TreeED. It then leverages an Expectation-Maximization-based algorithm that jointly estimates tree reliability and optimizes the consensus ED prediction. Extensive xperiments demonstrate that our methods are accurate, explainable and robust, achieving an average F1-score improvement of 16.1% over the best baseline.
Rethinking Testing for LLM Applications: Characteristics, Challenges, and a Lightweight Interaction Protocol
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Applications of Large Language Models~(LLMs) have evolved from simple text generators into complex software systems that integrate retrieval augmentation, tool invocation, and multi-turn interactions. Their inherent non-determinism, dynamism, and context dependence pose fundamental challenges for quality assurance. This paper decomposes LLM applications into a three-layer architecture: \textbf{\textit{System Shell Layer}}, \textbf{\textit{Prompt Orchestration Layer}}, and \textbf{\textit{LLM Inference Core}}. We then assess the applicability of traditional software testing methods in each layer: directly applicable at the shell layer, requiring semantic reinterpretation at the orchestration layer, and necessitating paradigm shifts at the inference core. A comparative analysis of Testing AI methods from the software engineering community and safety analysis techniques from the AI community reveals structural disconnects in testing unit abstraction, evaluation metrics, and lifecycle management. We identify four fundamental differences that underlie 6 core challenges. To address these, we propose four types of collaborative strategies (\emph{Retain}, \emph{Translate}, \emph{Integrate}, and \emph{Runtime}) and explore a closed-loop, trustworthy quality assurance framework that combines pre-deployment validation with runtime monitoring. Based on these strategies, we offer practical guidance and a protocol proposal to support the standardization and tooling of LLM application testing. We propose a protocol \textbf{\textit{Agent Interaction Communication Language}} (AICL) that is used to communicate between AI agents. AICL has the test-oriented features and is easily integrated in the current agent framework.
When Prompt Engineering Meets Software Engineering: CNL-P as Natural and Robust "APIs'' for Human-AI Interaction
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:With the growing capabilities of large language models (LLMs), they are increasingly applied in areas like intelligent customer service, code generation, and knowledge management. Natural language (NL) prompts act as the ``APIs'' for human-LLM interaction. To improve prompt quality, best practices for prompt engineering (PE) have been developed, including writing guidelines and templates. Building on this, we propose Controlled NL for Prompt (CNL-P), which not only incorporates PE best practices but also draws on key principles from software engineering (SE). CNL-P introduces precise grammar structures and strict semantic norms, further eliminating NL's ambiguity, allowing for a declarative but structured and accurate expression of user intent. This helps LLMs better interpret and execute the prompts, leading to more consistent and higher-quality outputs. We also introduce an NL2CNL-P conversion tool based on LLMs, enabling users to write prompts in NL, which are then transformed into CNL-P format, thus lowering the learning curve of CNL-P. In particular, we develop a linting tool that checks CNL-P prompts for syntactic and semantic accuracy, applying static analysis techniques to NL for the first time. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CNL-P enhances the quality of LLM responses through the novel and organic synergy of PE and SE. We believe that CNL-P can bridge the gap between emerging PE and traditional SE, laying the foundation for a new programming paradigm centered around NL.
Deployability-Centric Infrastructure-as-Code Generation: An LLM-based Iterative Framework
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) generation holds significant promise for automating cloud infrastructure provisioning. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) present a promising opportunity to democratize IaC development by generating deployable infrastructure templates from natural language descriptions, but current evaluation focuses on syntactic correctness while ignoring deployability, the fatal measure of IaC template utility. We address this gap through two contributions: (1) IaCGen, an LLM-based deployability-centric framework that uses iterative feedback mechanism to generate IaC templates, and (2) DPIaC-Eval, a deployability-centric IaC template benchmark consists of 153 real-world scenarios that can evaluate syntax, deployment, user intent, and security. Our evaluation reveals that state-of-the-art LLMs initially performed poorly, with Claude-3.5 and Claude-3.7 achieving only 30.2% and 26.8% deployment success on the first attempt respectively. However, IaCGen transforms this performance dramatically: all evaluated models reach over 90% passItr@25, with Claude-3.5 and Claude-3.7 achieving 98% success rate. Despite these improvements, critical challenges remain in user intent alignment (25.2% accuracy) and security compliance (8.4% pass rate), highlighting areas requiring continued research. Our work provides the first comprehensive assessment of deployability-centric IaC template generation and establishes a foundation for future research.
LLM-based HSE Compliance Assessment: Benchmark, Performance, and Advancements
May 29, 2025Abstract:Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) compliance assessment demands dynamic real-time decision-making under complicated regulations and complex human-machine-environment interactions. While large language models (LLMs) hold significant potential for decision intelligence and contextual dialogue, their capacity for domain-specific knowledge in HSE and structured legal reasoning remains underexplored. We introduce HSE-Bench, the first benchmark dataset designed to evaluate the HSE compliance assessment capabilities of LLM. HSE-Bench comprises over 1,000 manually curated questions drawn from regulations, court cases, safety exams, and fieldwork videos, and integrates a reasoning flow based on Issue spotting, rule Recall, rule Application, and rule Conclusion (IRAC) to assess the holistic reasoning pipeline. We conduct extensive evaluations on different prompting strategies and more than 10 LLMs, including foundation models, reasoning models and multimodal vision models. The results show that, although current LLMs achieve good performance, their capabilities largely rely on semantic matching rather than principled reasoning grounded in the underlying HSE compliance context. Moreover, their native reasoning trace lacks the systematic legal reasoning required for rigorous HSE compliance assessment. To alleviate these, we propose a new prompting technique, Reasoning of Expert (RoE), which guides LLMs to simulate the reasoning process of different experts for compliance assessment and reach a more accurate unified decision. We hope our study highlights reasoning gaps in LLMs for HSE compliance and inspires further research on related tasks.
REPA-E: Unlocking VAE for End-to-End Tuning with Latent Diffusion Transformers
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:In this paper we tackle a fundamental question: "Can we train latent diffusion models together with the variational auto-encoder (VAE) tokenizer in an end-to-end manner?" Traditional deep-learning wisdom dictates that end-to-end training is often preferable when possible. However, for latent diffusion transformers, it is observed that end-to-end training both VAE and diffusion-model using standard diffusion-loss is ineffective, even causing a degradation in final performance. We show that while diffusion loss is ineffective, end-to-end training can be unlocked through the representation-alignment (REPA) loss -- allowing both VAE and diffusion model to be jointly tuned during the training process. Despite its simplicity, the proposed training recipe (REPA-E) shows remarkable performance; speeding up diffusion model training by over 17x and 45x over REPA and vanilla training recipes, respectively. Interestingly, we observe that end-to-end tuning with REPA-E also improves the VAE itself; leading to improved latent space structure and downstream generation performance. In terms of final performance, our approach sets a new state-of-the-art; achieving FID of 1.26 and 1.83 with and without classifier-free guidance on ImageNet 256 x 256. Code is available at https://end2end-diffusion.github.io.
FactFlow: Automatic Fact Sheet Generation and Customization from Tabular Dataset via AI Chain Design & Implementation
Feb 25, 2025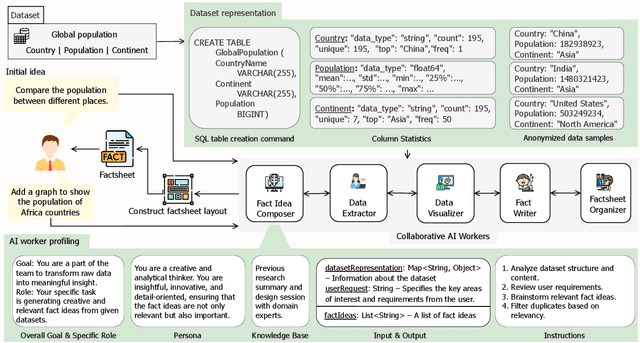
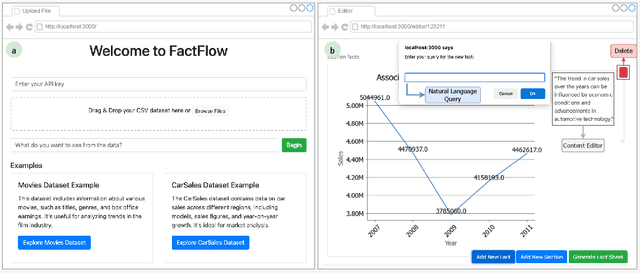
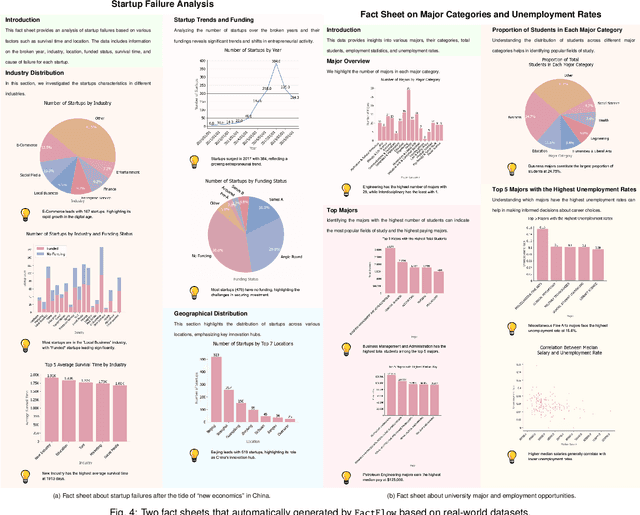
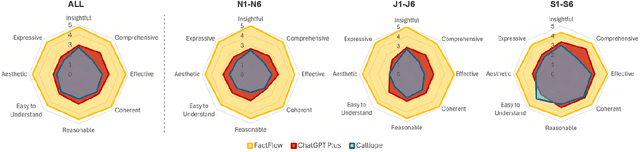
Abstract:With the proliferation of data across various domains, there is a critical demand for tools that enable non-experts to derive meaningful insights without deep data analysis skills. To address this need, existing automatic fact sheet generation tools offer heuristic-based solutions to extract facts and generate stories. However, they inadequately grasp the semantics of data and struggle to generate narratives that fully capture the semantics of the dataset or align the fact sheet with specific user needs. Addressing these shortcomings, this paper introduces \tool, a novel tool designed for the automatic generation and customisation of fact sheets. \tool applies the concept of collaborative AI workers to transform raw tabular dataset into comprehensive, visually compelling fact sheets. We define effective taxonomy to profile AI worker for specialised tasks. Furthermore, \tool empowers users to refine these fact sheets through intuitive natural language commands, ensuring the final outputs align closely with individual preferences and requirements. Our user evaluation with 18 participants confirms that \tool not only surpasses state-of-the-art baselines in automated fact sheet production but also provides a positive user experience during customization tasks.
Explore-Construct-Filter: An Automated Framework for Rich and Reliable API Knowledge Graph Construction
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:The API Knowledge Graph (API KG) is a structured network that models API entities and their relations, providing essential semantic insights for tasks such as API recommendation, code generation, and API misuse detection. However, constructing a knowledge-rich and reliable API KG presents several challenges. Existing schema-based methods rely heavily on manual annotations to design KG schemas, leading to excessive manual overhead. On the other hand, schema-free methods, due to the lack of schema guidance, are prone to introducing noise, reducing the KG's reliability. To address these issues, we propose the Explore-Construct-Filter framework, an automated approach for API KG construction based on large language models (LLMs). This framework consists of three key modules: 1) KG exploration: LLMs simulate the workflow of annotators to automatically design a schema with comprehensive type triples, minimizing human intervention; 2) KG construction: Guided by the schema, LLMs extract instance triples to construct a rich yet unreliable API KG; 3) KG filtering: Removing invalid type triples and suspicious instance triples to construct a rich and reliable API KG. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses the state-of-the-art method, achieving a 25.2% improvement in F1 score. Moreover, the Explore-Construct-Filter framework proves effective, with the KG exploration module increasing KG richness by 133.6% and the KG filtering module improving reliability by 26.6%. Finally, cross-model experiments confirm the generalizability of our framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge