Zexin He
Neural LightRig: Unlocking Accurate Object Normal and Material Estimation with Multi-Light Diffusion
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Recovering the geometry and materials of objects from a single image is challenging due to its under-constrained nature. In this paper, we present Neural LightRig, a novel framework that boosts intrinsic estimation by leveraging auxiliary multi-lighting conditions from 2D diffusion priors. Specifically, 1) we first leverage illumination priors from large-scale diffusion models to build our multi-light diffusion model on a synthetic relighting dataset with dedicated designs. This diffusion model generates multiple consistent images, each illuminated by point light sources in different directions. 2) By using these varied lighting images to reduce estimation uncertainty, we train a large G-buffer model with a U-Net backbone to accurately predict surface normals and materials. Extensive experiments validate that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, enabling accurate surface normal and PBR material estimation with vivid relighting effects. Code and dataset are available on our project page at https://projects.zxhezexin.com/neural-lightrig.
Phidias: A Generative Model for Creating 3D Content from Text, Image, and 3D Conditions with Reference-Augmented Diffusion
Sep 17, 2024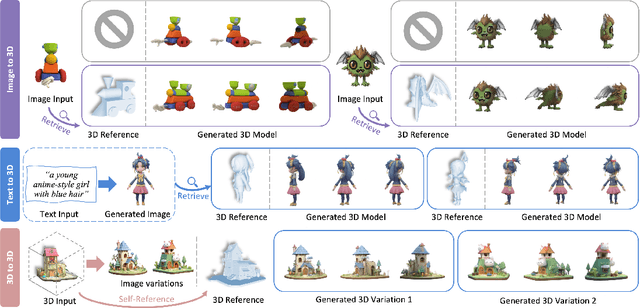
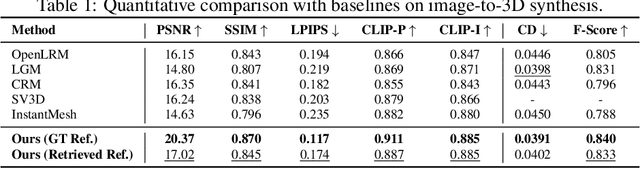
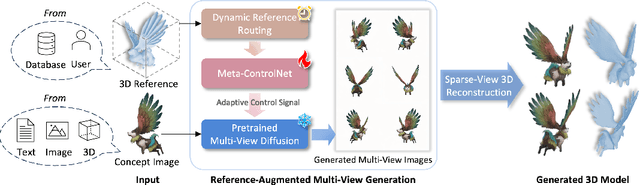
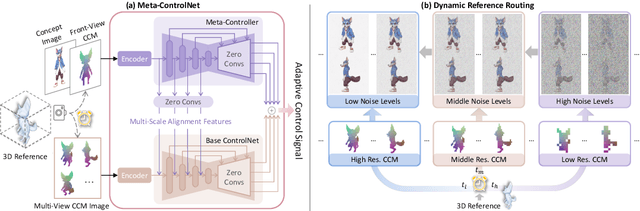
Abstract:In 3D modeling, designers often use an existing 3D model as a reference to create new ones. This practice has inspired the development of Phidias, a novel generative model that uses diffusion for reference-augmented 3D generation. Given an image, our method leverages a retrieved or user-provided 3D reference model to guide the generation process, thereby enhancing the generation quality, generalization ability, and controllability. Our model integrates three key components: 1) meta-ControlNet that dynamically modulates the conditioning strength, 2) dynamic reference routing that mitigates misalignment between the input image and 3D reference, and 3) self-reference augmentations that enable self-supervised training with a progressive curriculum. Collectively, these designs result in a clear improvement over existing methods. Phidias establishes a unified framework for 3D generation using text, image, and 3D conditions with versatile applications.
Rethinking Out-of-distribution (OOD) Detection: Masked Image Modeling is All You Need
Feb 06, 2023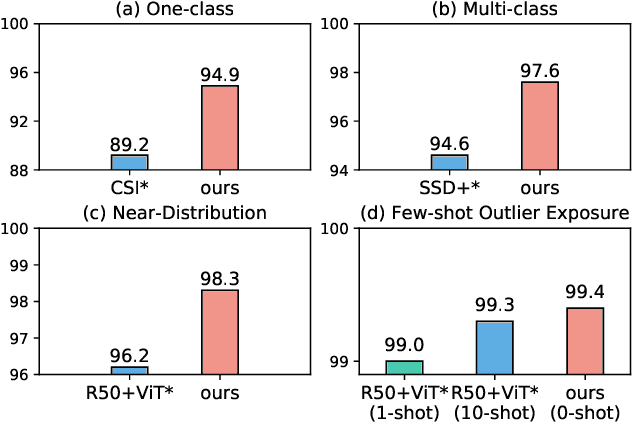
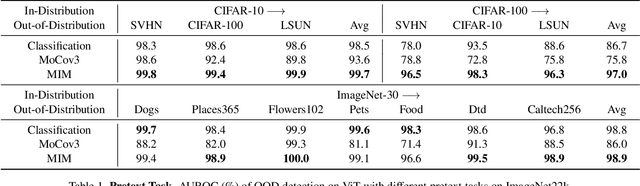
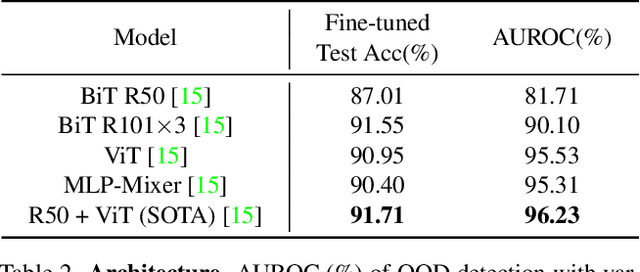
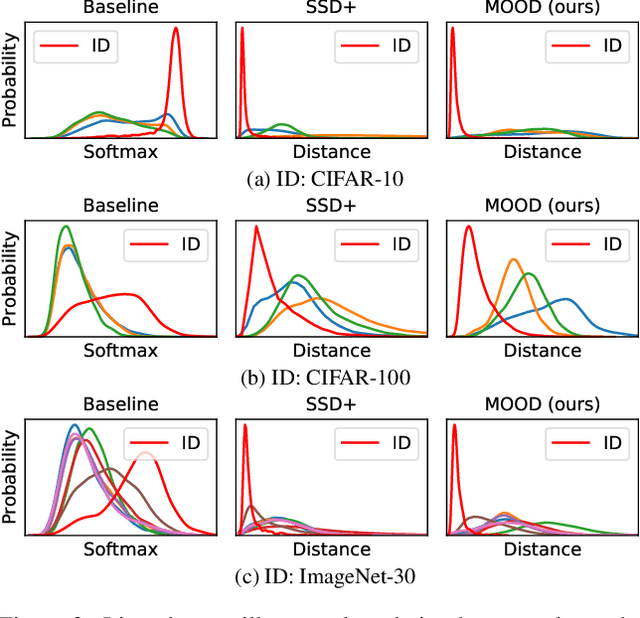
Abstract:The core of out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is to learn the in-distribution (ID) representation, which is distinguishable from OOD samples. Previous work applied recognition-based methods to learn the ID features, which tend to learn shortcuts instead of comprehensive representations. In this work, we find surprisingly that simply using reconstruction-based methods could boost the performance of OOD detection significantly. We deeply explore the main contributors of OOD detection and find that reconstruction-based pretext tasks have the potential to provide a generally applicable and efficacious prior, which benefits the model in learning intrinsic data distributions of the ID dataset. Specifically, we take Masked Image Modeling as a pretext task for our OOD detection framework (MOOD). Without bells and whistles, MOOD outperforms previous SOTA of one-class OOD detection by 5.7%, multi-class OOD detection by 3.0%, and near-distribution OOD detection by 2.1%. It even defeats the 10-shot-per-class outlier exposure OOD detection, although we do not include any OOD samples for our detection
Ref-NPR: Reference-Based Non-Photorealistic Radiance Fields
Dec 06, 2022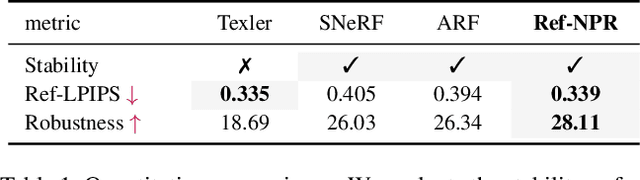
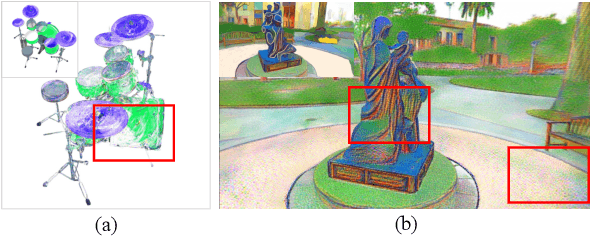
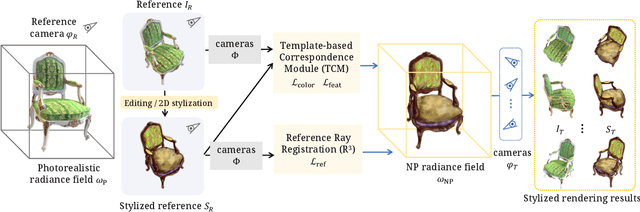
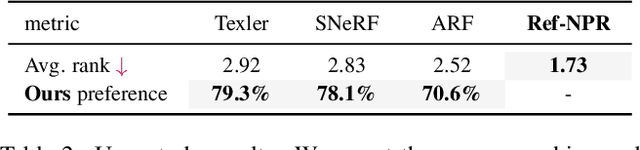
Abstract:Existing 3D scene stylization methods employ an arbitrary style reference to transfer textures and colors as styles without establishing meaningful semantic correspondences. We present Reference-Based Non-Photorealistic Radiance Fields, i.e., Ref-NPR. It is a controllable scene stylization method utilizing radiance fields to stylize a 3D scene, with a single stylized 2D view taken as reference. To achieve decent results, we propose a ray registration process based on the stylized reference view to obtain pseudo-ray supervision in novel views, and exploit the semantic correspondence in content images to fill occluded regions with perceptually similar styles. Combining these operations, Ref-NPR generates non-photorealistic and continuous novel view sequences with a single reference while obtaining reasonable stylization in occluded regions. Experiments show that Ref-NPR significantly outperforms other scene and video stylization methods in terms of both visual quality and semantic correspondence. Code and data will be made publicly available.
Bamboo: Building Mega-Scale Vision Dataset Continually with Human-Machine Synergy
Mar 15, 2022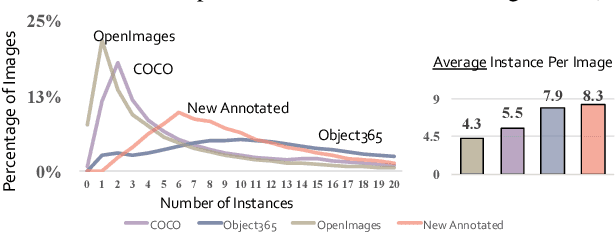

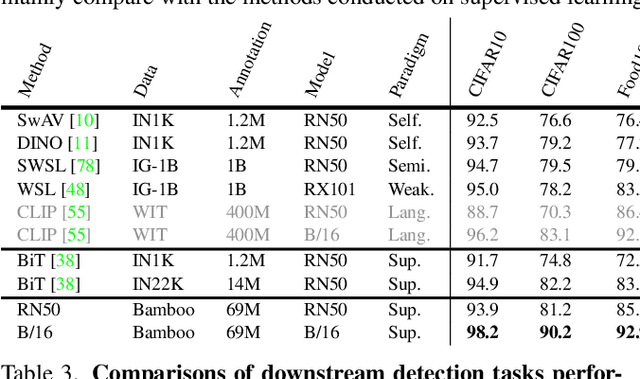
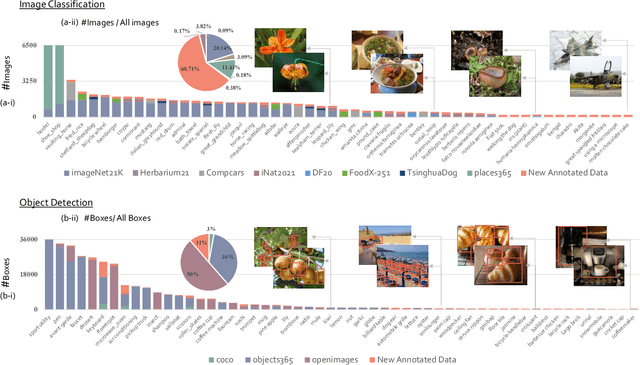
Abstract:Large-scale datasets play a vital role in computer vision. Existing datasets are either collected according to heuristic label systems or annotated blindly without differentiation to samples, making them inefficient and unscalable. How to systematically collect, annotate and build a mega-scale dataset remains an open question. In this work, we advocate building a high-quality vision dataset actively and continually on a comprehensive label system. Specifically, we contribute Bamboo Dataset, a mega-scale and information-dense dataset for both classification and detection. Bamboo aims to populate the comprehensive categories with 69M image classification annotations and 170,586 object bounding box annotations. Compared to ImageNet22K and Objects365, models pre-trained on Bamboo achieve superior performance among various downstream tasks (6.2% gains on classification and 2.1% gains on detection). In addition, we provide valuable observations regarding large-scale pre-training from over 1,000 experiments. Due to its scalable nature on both label system and annotation pipeline, Bamboo will continue to grow and benefit from the collective efforts of the community, which we hope would pave the way for more general vision models.
Video Background Music Generation with Controllable Music Transformer
Nov 16, 2021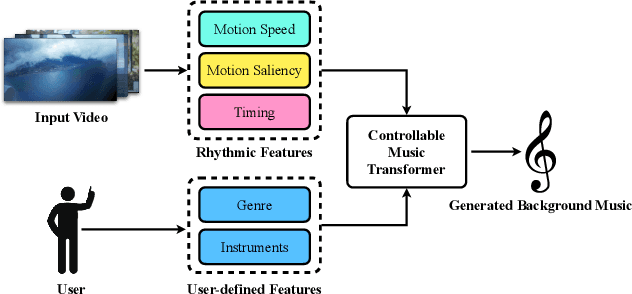
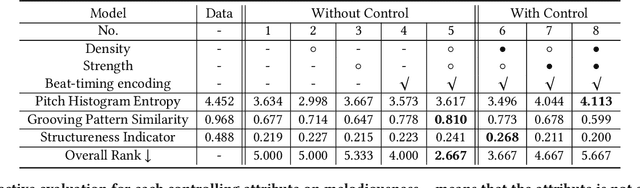
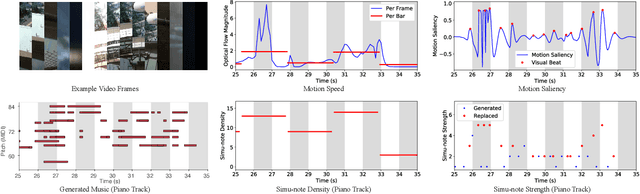
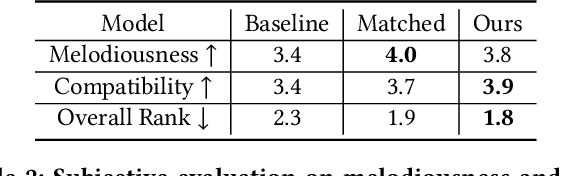
Abstract:In this work, we address the task of video background music generation. Some previous works achieve effective music generation but are unable to generate melodious music tailored to a particular video, and none of them considers the video-music rhythmic consistency. To generate the background music that matches the given video, we first establish the rhythmic relations between video and background music. In particular, we connect timing, motion speed, and motion saliency from video with beat, simu-note density, and simu-note strength from music, respectively. We then propose CMT, a Controllable Music Transformer that enables local control of the aforementioned rhythmic features and global control of the music genre and instruments. Objective and subjective evaluations show that the generated background music has achieved satisfactory compatibility with the input videos, and at the same time, impressive music quality. Code and models are available at https://github.com/wzk1015/video-bgm-generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge