Yuxuan Shi
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025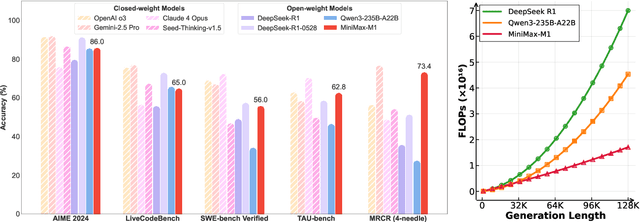
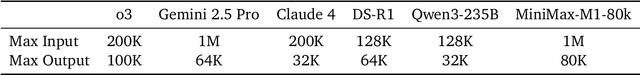
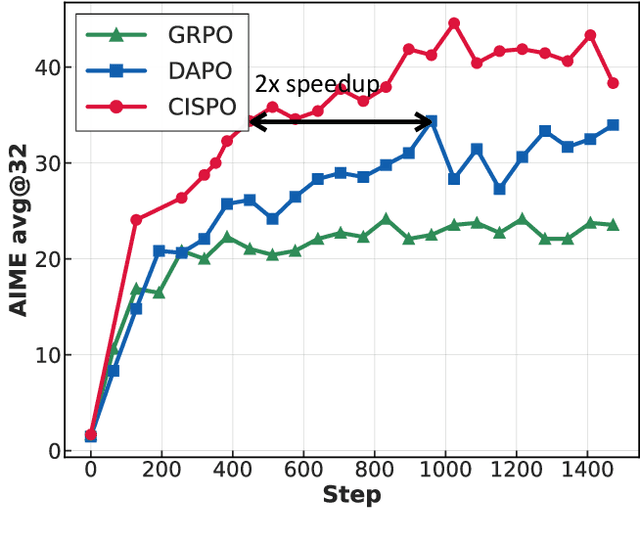
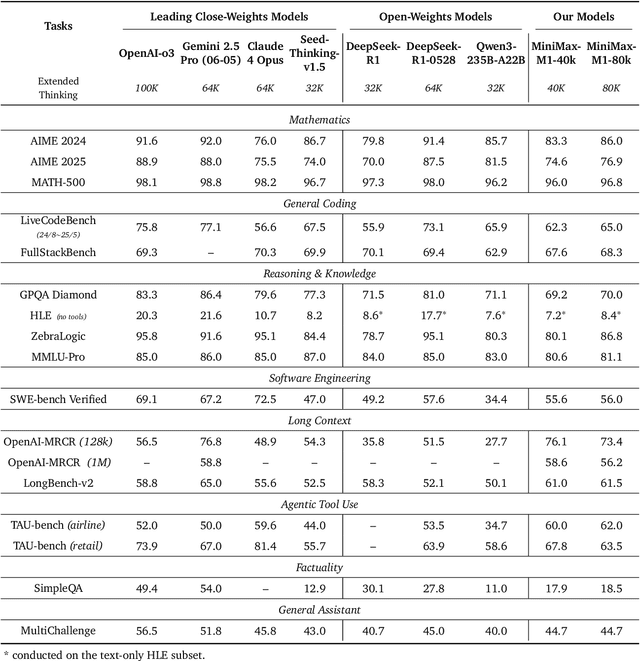
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
WVSC: Wireless Video Semantic Communication with Multi-frame Compensation
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Existing wireless video transmission schemes directly conduct video coding in pixel level, while neglecting the inner semantics contained in videos. In this paper, we propose a wireless video semantic communication framework, abbreviated as WVSC, which integrates the idea of semantic communication into wireless video transmission scenarios. WVSC first encodes original video frames as semantic frames and then conducts video coding based on such compact representations, enabling the video coding in semantic level rather than pixel level. Moreover, to further reduce the communication overhead, a reference semantic frame is introduced to substitute motion vectors of each frame in common video coding methods. At the receiver, multi-frame compensation (MFC) is proposed to produce compensated current semantic frame with a multi-frame fusion attention module. With both the reference frame transmission and MFC, the bandwidth efficiency improves with satisfying video transmission performance. Experimental results verify the performance gain of WVSC over other DL-based methods e.g. DVSC about 1 dB and traditional schemes about 2 dB in terms of PSNR.
Learnable Residual-based Latent Denoising in Semantic Communication
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:A latent denoising semantic communication (SemCom) framework is proposed for robust image transmission over noisy channels. By incorporating a learnable latent denoiser into the receiver, the received signals are preprocessed to effectively remove the channel noise and recover the semantic information, thereby enhancing the quality of the decoded images. Specifically, a latent denoising mapping is established by an iterative residual learning approach to improve the denoising efficiency while ensuring stable performance. Moreover, channel signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is utilized to estimate and predict the latent similarity score (SS) for conditional denoising, where the number of denoising steps is adapted based on the predicted SS sequence, further reducing the communication latency. Finally, simulations demonstrate that the proposed framework can effectively and efficiently remove the channel noise at various levels and reconstruct visual-appealing images.
WirelessGPT: A Generative Pre-trained Multi-task Learning Framework for Wireless Communication
Feb 08, 2025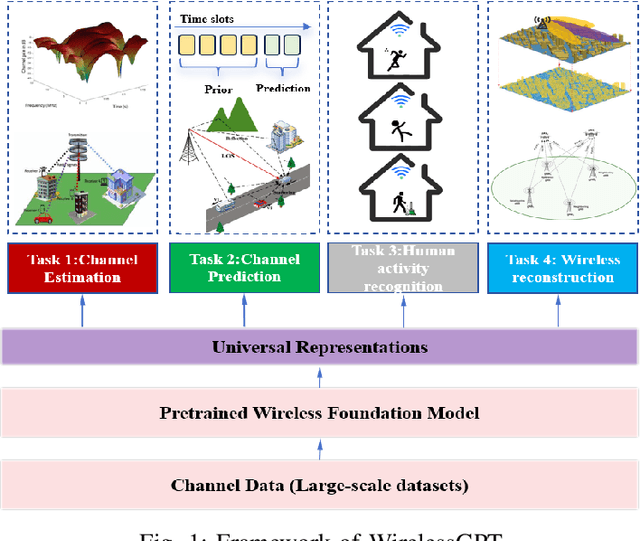
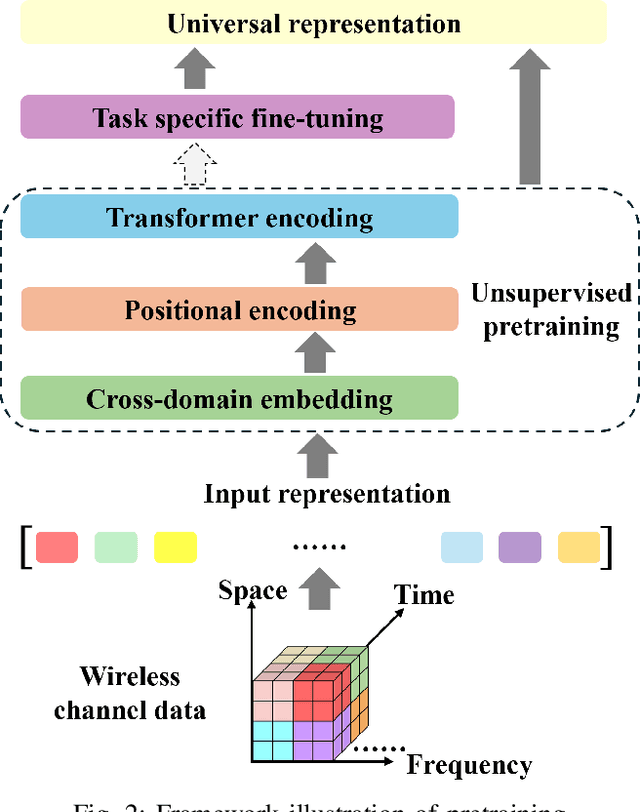
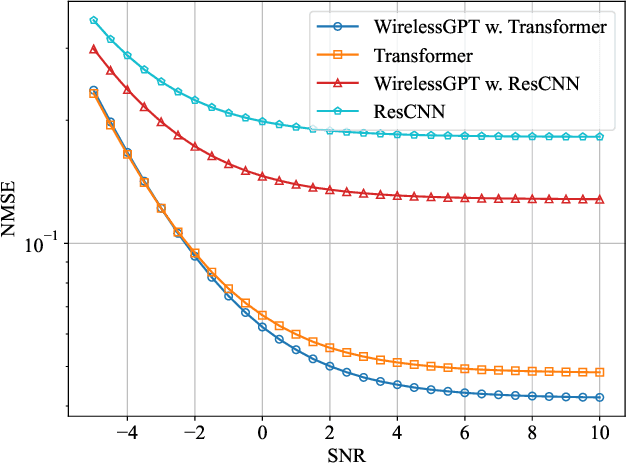
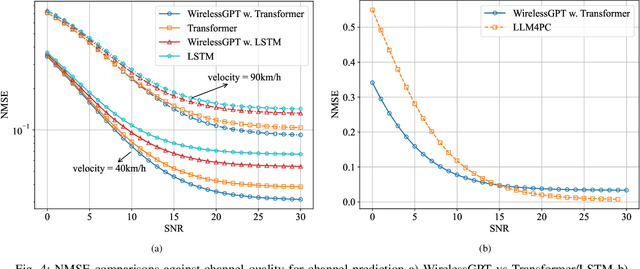
Abstract:This paper introduces WirelessGPT, a pioneering foundation model specifically designed for multi-task learning in wireless communication and sensing. Specifically, WirelessGPT leverages large-scale wireless channel datasets for unsupervised pretraining and extracting universal channel representations, which captures complex spatiotemporal dependencies. In fact,this task-agnostic design adapts WirelessGPT seamlessly to a wide range of downstream tasks, using a unified representation with minimal fine-tuning. By unifying communication and sensing functionalities, WirelessGPT addresses the limitations of task-specific models, offering a scalable and efficient solution for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). With an initial parameter size of around 80 million, WirelessGPT demonstrates significant improvements over conventional methods and smaller AI models, reducing reliance on large-scale labeled data. As the first foundation model capable of supporting diverse tasks across different domains, WirelessGPT establishes a new benchmark, paving the way for future advancements in multi-task wireless systems.
Reducing Fine-Tuning Memory Overhead by Approximate and Memory-Sharing Backpropagation
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Fine-tuning pretrained large models to downstream tasks is an important problem, which however suffers from huge memory overhead due to large-scale parameters. This work strives to reduce memory overhead in fine-tuning from perspectives of activation function and layer normalization. To this end, we propose the Approximate Backpropagation (Approx-BP) theory, which provides the theoretical feasibility of decoupling the forward and backward passes. We apply our Approx-BP theory to backpropagation training and derive memory-efficient alternatives of GELU and SiLU activation functions, which use derivative functions of ReLUs in the backward pass while keeping their forward pass unchanged. In addition, we introduce a Memory-Sharing Backpropagation strategy, which enables the activation memory to be shared by two adjacent layers, thereby removing activation memory usage redundancy. Our method neither induces extra computation nor reduces training efficiency. We conduct extensive experiments with pretrained vision and language models, and the results demonstrate that our proposal can reduce up to $\sim$$30\%$ of the peak memory usage. Our code is released at https://github.com/yyyyychen/LowMemoryBP.
Robust Image Semantic Coding with Learnable CSI Fusion Masking over MIMO Fading Channels
May 30, 2024



Abstract:Though achieving marvelous progress in various scenarios, existing semantic communication frameworks mainly consider single-input single-output Gaussian channels or Rayleigh fading channels, neglecting the widely-used multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channels, which hinders the application into practical systems. One common solution to combat MIMO fading is to utilize feedback MIMO channel state information (CSI). In this paper, we incorporate MIMO CSI into system designs from a new perspective and propose the learnable CSI fusion semantic communication (LCFSC) framework, where CSI is treated as side information by the semantic extractor to enhance the semantic coding. To avoid feature fusion due to abrupt combination of CSI with features, we present a non-invasive CSI fusion multi-head attention module inside the Swin Transformer. With the learned attention masking map determined by both source and channel states, more robust attention distribution could be generated. Furthermore, the percentage of mask elements could be flexibly adjusted by the learnable mask ratio, which is produced based on the conditional variational interference in an unsupervised manner. In this way, CSI-aware semantic coding is achieved through learnable CSI fusion masking. Experiment results testify the superiority of LCFSC over traditional schemes and state-of-the-art Swin Transformer-based semantic communication frameworks in MIMO fading channels.
DBDH: A Dual-Branch Dual-Head Neural Network for Invisible Embedded Regions Localization
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Embedding invisible hyperlinks or hidden codes in images to replace QR codes has become a hot topic recently. This technology requires first localizing the embedded region in the captured photos before decoding. Existing methods that train models to find the invisible embedded region struggle to obtain accurate localization results, leading to degraded decoding accuracy. This limitation is primarily because the CNN network is sensitive to low-frequency signals, while the embedded signal is typically in the high-frequency form. Based on this, this paper proposes a Dual-Branch Dual-Head (DBDH) neural network tailored for the precise localization of invisible embedded regions. Specifically, DBDH uses a low-level texture branch containing 62 high-pass filters to capture the high-frequency signals induced by embedding. A high-level context branch is used to extract discriminative features between the embedded and normal regions. DBDH employs a detection head to directly detect the four vertices of the embedding region. In addition, we introduce an extra segmentation head to segment the mask of the embedding region during training. The segmentation head provides pixel-level supervision for model learning, facilitating better learning of the embedded signals. Based on two state-of-the-art invisible offline-to-online messaging methods, we construct two datasets and augmentation strategies for training and testing localization models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed DBDH over existing methods.
MARformer: An Efficient Metal Artifact Reduction Transformer for Dental CBCT Images
Nov 16, 2023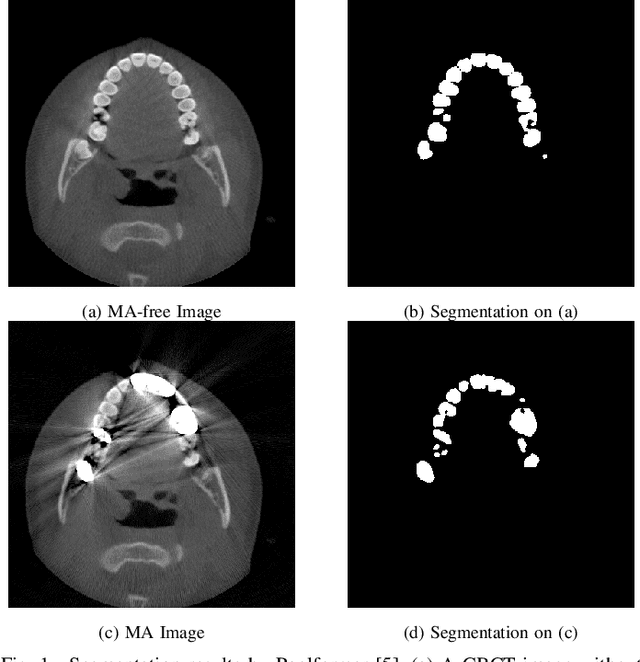
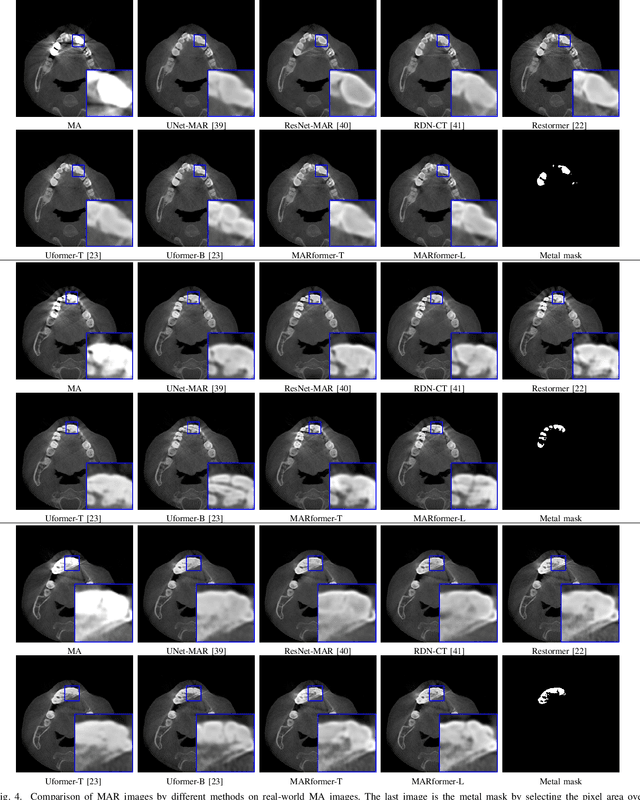
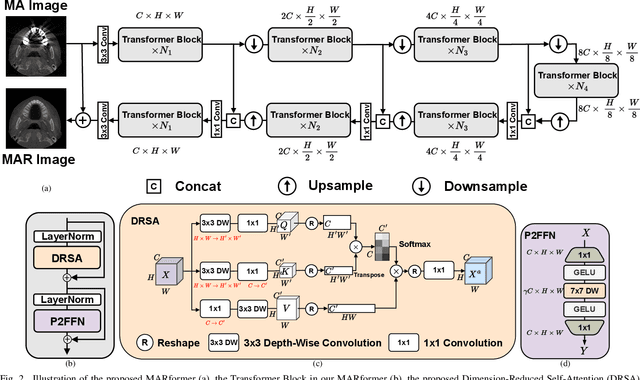
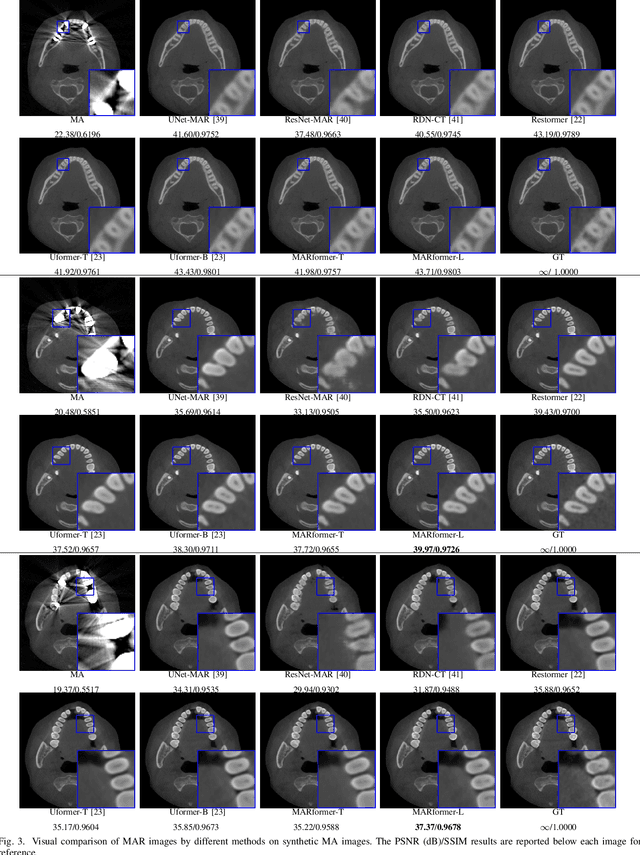

Abstract:Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) plays a key role in dental diagnosis and surgery. However, the metal teeth implants could bring annoying metal artifacts during the CBCT imaging process, interfering diagnosis and downstream processing such as tooth segmentation. In this paper, we develop an efficient Transformer to perform metal artifacts reduction (MAR) from dental CBCT images. The proposed MAR Transformer (MARformer) reduces computation complexity in the multihead self-attention by a new Dimension-Reduced Self-Attention (DRSA) module, based on that the CBCT images have globally similar structure. A Patch-wise Perceptive Feed Forward Network (P2FFN) is also proposed to perceive local image information for fine-grained restoration. Experimental results on CBCT images with synthetic and real-world metal artifacts show that our MARformer is efficient and outperforms previous MAR methods and two restoration Transformers.
Improving Visual Quality and Transferability of Adversarial Attacks on Face Recognition Simultaneously with Adversarial Restoration
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Adversarial face examples possess two critical properties: Visual Quality and Transferability. However, existing approaches rarely address these properties simultaneously, leading to subpar results. To address this issue, we propose a novel adversarial attack technique known as Adversarial Restoration (AdvRestore), which enhances both visual quality and transferability of adversarial face examples by leveraging a face restoration prior. In our approach, we initially train a Restoration Latent Diffusion Model (RLDM) designed for face restoration. Subsequently, we employ the inference process of RLDM to generate adversarial face examples. The adversarial perturbations are applied to the intermediate features of RLDM. Additionally, by treating RLDM face restoration as a sibling task, the transferability of the generated adversarial face examples is further improved. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed attack method.
Communication-Efficient Framework for Distributed Image Semantic Wireless Transmission
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Multi-node communication, which refers to the interaction among multiple devices, has attracted lots of attention in many Internet-of-Things (IoT) scenarios. However, its huge amounts of data flows and inflexibility for task extension have triggered the urgent requirement of communication-efficient distributed data transmission frameworks. In this paper, inspired by the great superiorities on bandwidth reduction and task adaptation of semantic communications, we propose a federated learning-based semantic communication (FLSC) framework for multi-task distributed image transmission with IoT devices. Federated learning enables the design of independent semantic communication link of each user while further improves the semantic extraction and task performance through global aggregation. Each link in FLSC is composed of a hierarchical vision transformer (HVT)-based extractor and a task-adaptive translator for coarse-to-fine semantic extraction and meaning translation according to specific tasks. In order to extend the FLSC into more realistic conditions, we design a channel state information-based multiple-input multiple-output transmission module to combat channel fading and noise. Simulation results show that the coarse semantic information can deal with a range of image-level tasks. Moreover, especially in low signal-to-noise ratio and channel bandwidth ratio regimes, FLSC evidently outperforms the traditional scheme, e.g. about 10 peak signal-to-noise ratio gain in the 3 dB channel condition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge