Liwen Jing
WirelessGPT: A Generative Pre-trained Multi-task Learning Framework for Wireless Communication
Feb 08, 2025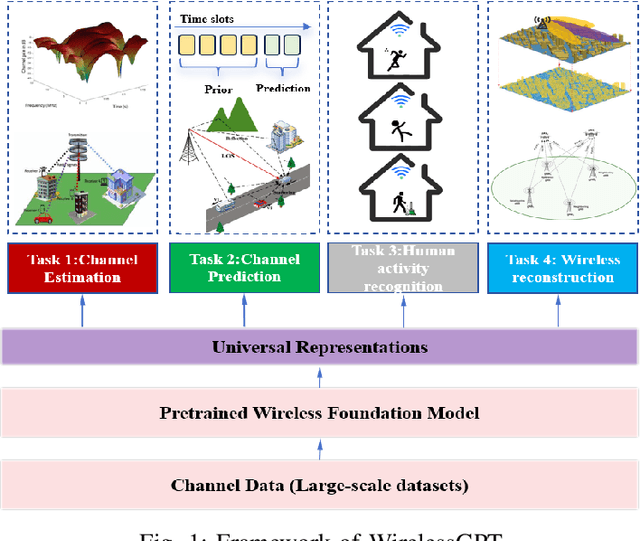
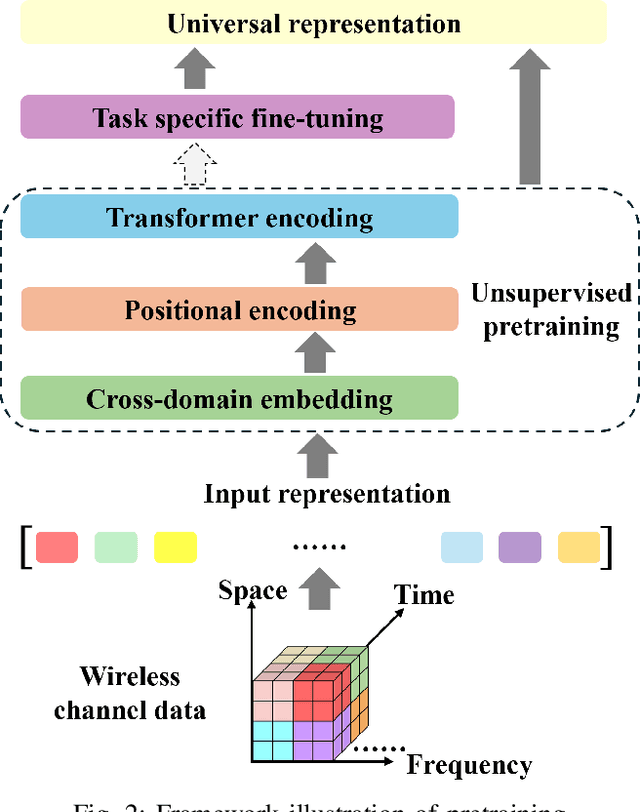
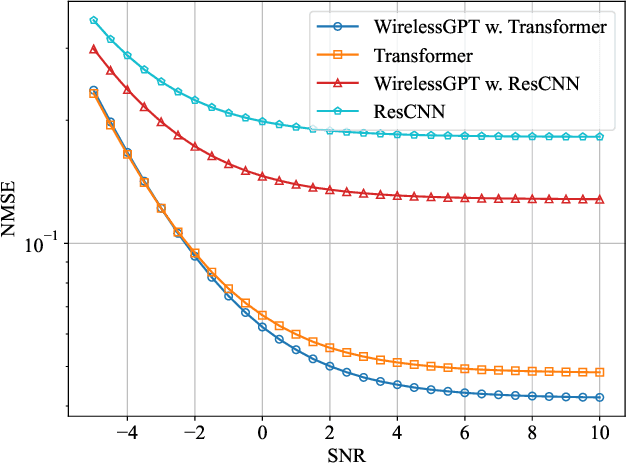
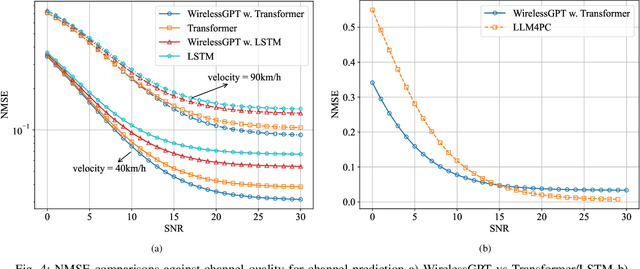
Abstract:This paper introduces WirelessGPT, a pioneering foundation model specifically designed for multi-task learning in wireless communication and sensing. Specifically, WirelessGPT leverages large-scale wireless channel datasets for unsupervised pretraining and extracting universal channel representations, which captures complex spatiotemporal dependencies. In fact,this task-agnostic design adapts WirelessGPT seamlessly to a wide range of downstream tasks, using a unified representation with minimal fine-tuning. By unifying communication and sensing functionalities, WirelessGPT addresses the limitations of task-specific models, offering a scalable and efficient solution for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). With an initial parameter size of around 80 million, WirelessGPT demonstrates significant improvements over conventional methods and smaller AI models, reducing reliance on large-scale labeled data. As the first foundation model capable of supporting diverse tasks across different domains, WirelessGPT establishes a new benchmark, paving the way for future advancements in multi-task wireless systems.
EDDA: A Encoder-Decoder Data Augmentation Framework for Zero-Shot Stance Detection
Mar 23, 2024



Abstract:Stance detection aims to determine the attitude expressed in text towards a given target. Zero-shot stance detection (ZSSD) has emerged to classify stances towards unseen targets during inference. Recent data augmentation techniques for ZSSD increase transferable knowledge between targets through text or target augmentation. However, these methods exhibit limitations. Target augmentation lacks logical connections between generated targets and source text, while text augmentation relies solely on training data, resulting in insufficient generalization. To address these issues, we propose an encoder-decoder data augmentation (EDDA) framework. The encoder leverages large language models and chain-of-thought prompting to summarize texts into target-specific if-then rationales, establishing logical relationships. The decoder generates new samples based on these expressions using a semantic correlation word replacement strategy to increase syntactic diversity. We also analyze the generated expressions to develop a rationale-enhanced network that fully utilizes the augmented data. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate our approach substantially improves over state-of-the-art ZSSD techniques. The proposed EDDA framework increases semantic relevance and syntactic variety in augmented texts while enabling interpretable rationale-based learning.
Vision Reimagined: AI-Powered Breakthroughs in WiFi Indoor Imaging
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Indoor imaging is a critical task for robotics and internet-of-things. WiFi as an omnipresent signal is a promising candidate for carrying out passive imaging and synchronizing the up-to-date information to all connected devices. This is the first research work to consider WiFi indoor imaging as a multi-modal image generation task that converts the measured WiFi power into a high-resolution indoor image. Our proposed WiFi-GEN network achieves a shape reconstruction accuracy that is 275% of that achieved by physical model-based inversion methods. Additionally, the Frechet Inception Distance score has been significantly reduced by 82%. To examine the effectiveness of models for this task, the first large-scale dataset is released containing 80,000 pairs of WiFi signal and imaging target. Our model absorbs challenges for the model-based methods including the non-linearity, ill-posedness and non-certainty into massive parameters of our generative AI network. The network is also designed to best fit measured WiFi signals and the desired imaging output. For reproducibility, we will release the data and code upon acceptance.
Cross-target Stance Detection by Exploiting Target Analytical Perspectives
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Cross-target stance detection (CTSD) is an important task, which infers the attitude of the destination target by utilizing annotated data derived from the source target. One important approach in CTSD is to extract domain-invariant features to bridge the knowledge gap between multiple targets. However, the analysis of informal and short text structure, and implicit expressions, complicate the extraction of domain-invariant knowledge. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Perspective Prompt-Tuning (MPPT) model for CTSD that uses the analysis perspective as a bridge to transfer knowledge. First, we develop a two-stage instruct-based chain-of-thought method (TsCoT) to elicit target analysis perspectives and provide natural language explanations (NLEs) from multiple viewpoints by formulating instructions based on large language model (LLM). Second, we propose a multi-perspective prompt-tuning framework (MultiPLN) to fuse the NLEs into the stance predictor. Extensive experiments results demonstrate the superiority of MPPT against the state-of-the-art baseline methods.
A Logically Consistent Chain-of-Thought Approach for Stance Detection
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Zero-shot stance detection (ZSSD) aims to detect stances toward unseen targets. Incorporating background knowledge to enhance transferability between seen and unseen targets constitutes the primary approach of ZSSD. However, these methods often struggle with a knowledge-task disconnect and lack logical consistency in their predictions. To address these issues, we introduce a novel approach named Logically Consistent Chain-of-Thought (LC-CoT) for ZSSD, which improves stance detection by ensuring relevant and logically sound knowledge extraction. LC-CoT employs a three-step process. Initially, it assesses whether supplementary external knowledge is necessary. Subsequently, it uses API calls to retrieve this knowledge, which can be processed by a separate LLM. Finally, a manual exemplar guides the LLM to infer stance categories, using an if-then logical structure to maintain relevance and logical coherence. This structured approach to eliciting background knowledge enhances the model's capability, outperforming traditional supervised methods without relying on labeled data.
Investigating Chain-of-thought with ChatGPT for Stance Detection on Social Media
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:Stance detection predicts attitudes towards targets in texts and has gained attention with the rise of social media. Traditional approaches include conventional machine learning, early deep neural networks, and pre-trained fine-tuning models. However, with the evolution of very large pre-trained language models (VLPLMs) like ChatGPT (GPT-3.5), traditional methods face deployment challenges. The parameter-free Chain-of-Thought (CoT) approach, not requiring backpropagation training, has emerged as a promising alternative. This paper examines CoT's effectiveness in stance detection tasks, demonstrating its superior accuracy and discussing associated challenges.
How would Stance Detection Techniques Evolve after the Launch of ChatGPT?
Dec 30, 2022



Abstract:Stance detection refers to the task of extracting the standpoint (Favor, Against or Neither) towards a target in given texts. Such research gains increasing attention with the proliferation of social media contents. The conventional framework of handling stance detection is converting it into text classification tasks. Deep learning models have already replaced rule-based models and traditional machine learning models in solving such problems. Current deep neural networks are facing two main challenges which are insufficient labeled data and information in social media posts and the unexplainable nature of deep learning models. A new pre-trained language model chatGPT was launched on Nov 30, 2022. For the stance detection tasks, our experiments show that ChatGPT can achieve SOTA or similar performance for commonly used datasets including SemEval-2016 and P-Stance. At the same time, ChatGPT can provide explanation for its own prediction, which is beyond the capability of any existing model. The explanations for the cases it cannot provide classification results are especially useful. ChatGPT has the potential to be the best AI model for stance detection tasks in NLP, or at least change the research paradigm of this field. ChatGPT also opens up the possibility of building explanatory AI for stance detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge