Yong Qi
Forgetting Through Transforming: Enabling Federated Unlearning via Class-Aware Representation Transformation
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Federated Unlearning (FU) enables clients to selectively remove the influence of specific data from a trained federated learning model, addressing privacy concerns and regulatory requirements. However, existing FU methods often struggle to balance effective erasure with model utility preservation, especially for class-level unlearning in non-IID settings. We propose Federated Unlearning via Class-aware Representation Transformation (FUCRT), a novel method that achieves unlearning through class-aware representation transformation. FUCRT employs two key components: (1) a transformation class selection strategy to identify optimal forgetting directions, and (2) a transformation alignment technique using dual class-aware contrastive learning to ensure consistent transformations across clients. Extensive experiments on four datasets demonstrate FUCRT's superior performance in terms of erasure guarantee, model utility preservation, and efficiency. FUCRT achieves complete (100\%) erasure of unlearning classes while maintaining or improving performance on remaining classes, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines across both IID and Non-IID settings. Analysis of the representation space reveals FUCRT's ability to effectively merge unlearning class representations with the transformation class from remaining classes, closely mimicking the model retrained from scratch.
Contribution Evaluation of Heterogeneous Participants in Federated Learning via Prototypical Representations
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:Contribution evaluation in federated learning (FL) has become a pivotal research area due to its applicability across various domains, such as detecting low-quality datasets, enhancing model robustness, and designing incentive mechanisms. Existing contribution evaluation methods, which primarily rely on data volume, model similarity, and auxiliary test datasets, have shown success in diverse scenarios. However, their effectiveness often diminishes due to the heterogeneity of data distributions, presenting a significant challenge to their applicability. In response, this paper explores contribution evaluation in FL from an entirely new perspective of representation. In this work, we propose a new method for the contribution evaluation of heterogeneous participants in federated learning (FLCE), which introduces a novel indicator \emph{class contribution momentum} to conduct refined contribution evaluation. Our core idea is the construction and application of the class contribution momentum indicator from individual, relative, and holistic perspectives, thereby achieving an effective and efficient contribution evaluation of heterogeneous participants without relying on an auxiliary test dataset. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method in terms of fidelity, effectiveness, efficiency, and heterogeneity across various scenarios.
Safety Control of Service Robots with LLMs and Embodied Knowledge Graphs
May 28, 2024Abstract:Safety limitations in service robotics across various industries have raised significant concerns about the need for robust mechanisms ensuring that robots adhere to safe practices, thereby preventing actions that might harm humans or cause property damage. Despite advances, including the integration of Knowledge Graphs (KGs) with Large Language Models (LLMs), challenges in ensuring consistent safety in autonomous robot actions persist. In this paper, we propose a novel integration of Large Language Models with Embodied Robotic Control Prompts (ERCPs) and Embodied Knowledge Graphs (EKGs) to enhance the safety framework for service robots. ERCPs are designed as predefined instructions that ensure LLMs generate safe and precise responses. These responses are subsequently validated by EKGs, which provide a comprehensive knowledge base ensuring that the actions of the robot are continuously aligned with safety protocols, thereby promoting safer operational practices in varied contexts. Our experimental setup involved diverse real-world tasks, where robots equipped with our framework demonstrated significantly higher compliance with safety standards compared to traditional methods. This integration fosters secure human-robot interactions and positions our methodology at the forefront of AI-driven safety innovations in service robotics.
Saliency-Aware Automatic Buddhas Statue Recognition
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Buddha statues, as a symbol of many religions, have significant cultural implications that are crucial for understanding the culture and history of different regions, and the recognition of Buddha statues is therefore the pivotal link in the field of Buddha study. However, the Buddha statue recognition requires extensive time and effort from knowledgeable professionals, making it a costly task to perform. Convolution neural networks (CNNs) are inherently efficient at processing visual information, but CNNs alone are likely to make inaccurate classification decisions when subjected to the class imbalance problem. Therefore, this paper proposes an end-to-end automatic Buddha statue recognition model based on saliency map sampling. The proposed Grid-Wise Local Self-Attention Module (GLSA) provides extra salient features which can serve to enrich the dataset and allow CNNs to observe in a much more comprehensive way. Eventually, our model is evaluated on a Buddha dataset collected with the aid of Buddha experts and outperforms state-of-the-art networks in terms of Top-1 accuracy by 4.63\% on average, while only marginally increasing MUL-ADD.
Robot Learning in the Era of Foundation Models: A Survey
Nov 24, 2023Abstract:The proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has s fueled a shift in robot learning from automation towards general embodied Artificial Intelligence (AI). Adopting foundation models together with traditional learning methods to robot learning has increasingly gained recent interest research community and showed potential for real-life application. However, there are few literatures comprehensively reviewing the relatively new technologies combined with robotics. The purpose of this review is to systematically assess the state-of-the-art foundation model techniques in the robot learning and to identify future potential areas. Specifically, we first summarized the technical evolution of robot learning and identified the necessary preliminary preparations for foundation models including the simulators, datasets, foundation model framework. In addition, we focused on the following four mainstream areas of robot learning including manipulation, navigation, planning, and reasoning and demonstrated how the foundation model techniques can be adopted in the above scenarios. Furthermore, critical issues which are neglected in the current literatures including robot hardware and software decoupling, dynamic data, generalization performance with the presence of human, etc. were discussed. This review highlights the state-of-the-art progress of foundation models in robot learning and future research should focus on multimodal interaction especially dynamics data, exclusive foundation models for robots, and AI alignment, etc.
Dual Class-Aware Contrastive Federated Semi-Supervised Learning
Nov 16, 2022Abstract:Federated semi-supervised learning (FSSL), facilitates labeled clients and unlabeled clients jointly training a global model without sharing private data. Existing FSSL methods mostly focus on pseudo-labeling and consistency regularization to leverage the knowledge of unlabeled data, which have achieved substantial success on raw data utilization. However, their training procedures suffer from the large deviation from local models of labeled clients and unlabeled clients and the confirmation bias induced by noisy pseudo labels, which seriously damage the performance of the global model. In this paper, we propose a novel FSSL method, named Dual Class-aware Contrastive Federated Semi-Supervised Learning (DCCFSSL), which considers the local class-aware distribution of individual client's data and the global class-aware distribution of all clients' data simultaneously in the feature space. By introducing a dual class-aware contrastive module, DCCFSSL builds a common training goal for different clients to reduce the large deviation and introduces contrastive information in the feature space to alleviate the confirmation bias. Meanwhile, DCCFSSL presents an authentication-reweighted aggregation method to enhance the robustness of the server's aggregation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DCCFSSL not only outperforms state-of-the-art methods on three benchmarked datasets, but also surpasses the FedAvg with relabeled unlabeled clients on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets. To our best knowledge, we are the first to present the FSSL method that utilizes only 10\% labeled clients of all clients to achieve better performance than the standard federated supervised learning that uses all clients with labeled data.
FedMCSA: Personalized Federated Learning via Model Components Self-Attention
Aug 23, 2022



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) facilitates multiple clients to jointly train a machine learning model without sharing their private data. However, Non-IID data of clients presents a tough challenge for FL. Existing personalized FL approaches rely heavily on the default treatment of one complete model as a basic unit and ignore the significance of different layers on Non-IID data of clients. In this work, we propose a new framework, federated model components self-attention (FedMCSA), to handle Non-IID data in FL, which employs model components self-attention mechanism to granularly promote cooperation between different clients. This mechanism facilitates collaboration between similar model components while reducing interference between model components with large differences. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate that FedMCSA outperforms the previous methods on four benchmark datasets. Furthermore, we empirically show the effectiveness of the model components self-attention mechanism, which is complementary to existing personalized FL and can significantly improve the performance of FL.
Research on Gender-related Fingerprint Features
Aug 18, 2021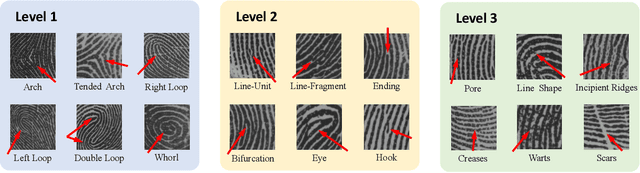
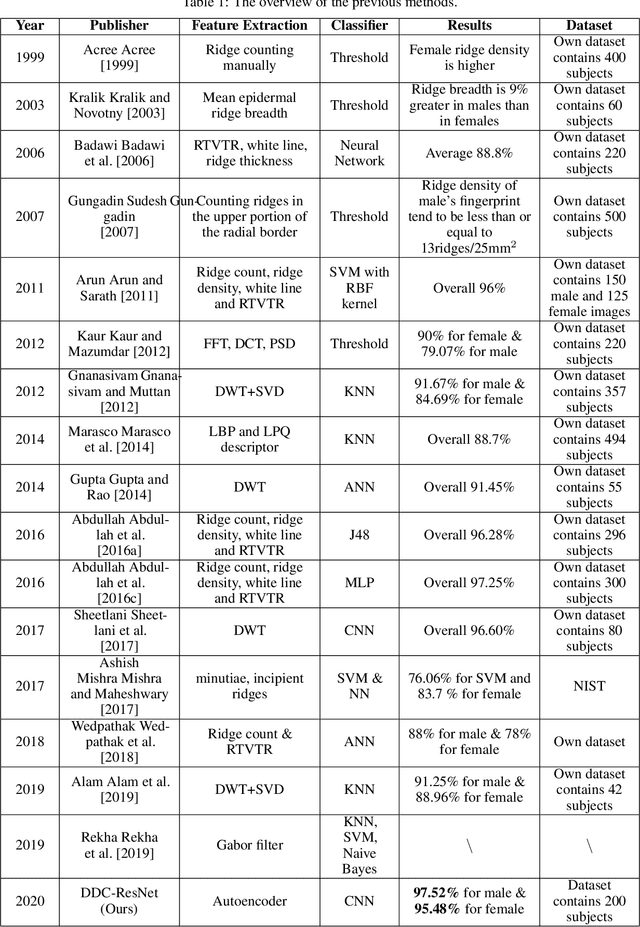
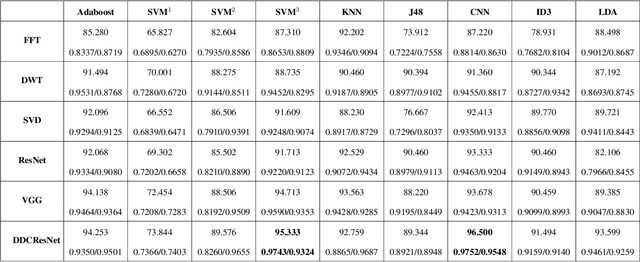
Abstract:Fingerprint is an important biological feature of human body, which contains abundant gender information. At present, the academic research of fingerprint gender characteristics is generally at the level of understanding, while the standardization research is quite limited. In this work, we propose a more robust method, Dense Dilated Convolution ResNet (DDC-ResNet) to extract valid gender information from fingerprints. By replacing the normal convolution operations with the atrous convolution in the backbone, prior knowledge is provided to keep the edge details and the global reception field can be extended. We explored the results in 3 ways: 1) The efficiency of the DDC-ResNet. 6 typical methods of automatic feature extraction coupling with 9 mainstream classifiers are evaluated in our dataset with fair implementation details. Experimental results demonstrate that the combination of our approach outperforms other combinations in terms of average accuracy and separate-gender accuracy. It reaches 96.5% for average and 0.9752 (males)/0.9548 (females) for separate-gender accuracy. 2) The effect of fingers. It is found that the best performance of classifying gender with separate fingers is achieved by the right ring finger. 3) The effect of specific features. Based on the observations of the concentrations of fingerprints visualized by our approach, it can be inferred that loops and whorls (level 1), bifurcations (level 2), as well as line shapes (level 3) are connected with gender. Finally, we will open source the dataset that contains 6000 fingerprint images
Stochastic Batch Augmentation with An Effective Distilled Dynamic Soft Label Regularizer
Jun 27, 2020



Abstract:Data augmentation have been intensively used in training deep neural network to improve the generalization, whether in original space (e.g., image space) or representation space. Although being successful, the connection between the synthesized data and the original data is largely ignored in training, without considering the distribution information that the synthesized samples are surrounding the original sample in training. Hence, the behavior of the network is not optimized for this. However, that behavior is crucially important for generalization, even in the adversarial setting, for the safety of the deep learning system. In this work, we propose a framework called Stochastic Batch Augmentation (SBA) to address these problems. SBA stochastically decides whether to augment at iterations controlled by the batch scheduler and in which a ''distilled'' dynamic soft label regularization is introduced by incorporating the similarity in the vicinity distribution respect to raw samples. The proposed regularization provides direct supervision by the KL-Divergence between the output soft-max distributions of original and virtual data. Our experiments on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet show that SBA can improve the generalization of the neural networks and speed up the convergence of network training.
Multi-view Point Cloud Registration with Adaptive Convergence Threshold and its Application on 3D Model Retrieval
Nov 25, 2018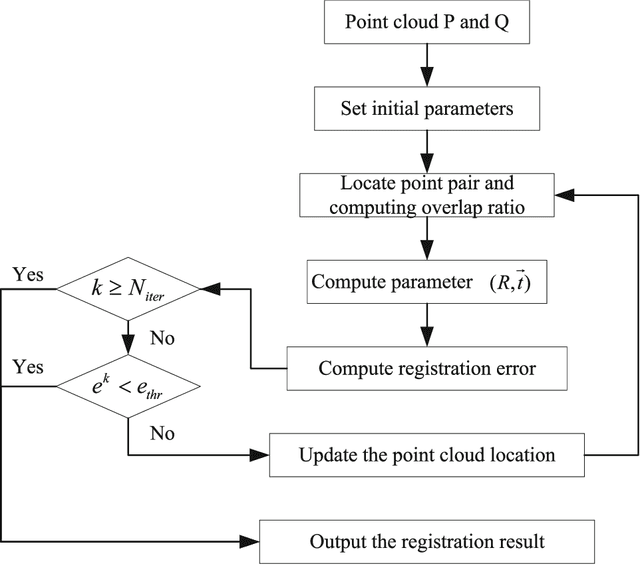
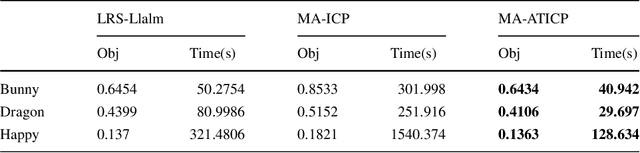

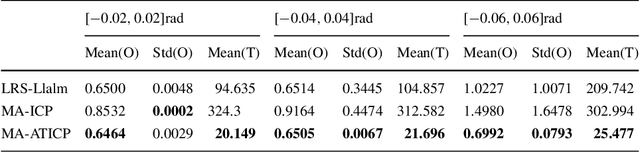
Abstract:Multi-view point cloud registration is a hot topic in the communities of multimedia technology and artificial intelligence (AI). In this paper, we propose a framework to reconstruct the 3D models by the multi-view point cloud registration algorithm with adaptive convergence threshold, and subsequently apply it to 3D model retrieval. The iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is implemented combining with the motion average algorithm for the registration of multi-view point clouds. After the registration process, we design applications for 3D model retrieval. The geometric saliency map is computed based on the vertex curvature. The test facial triangle is then generated based on the saliency map, which is applied to compare with the standard facial triangle. The face and non-face models are then discriminated. The experiments and comparisons prove the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge