Yingyu Chen
FedPalm: A General Federated Learning Framework for Closed- and Open-Set Palmprint Verification
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Current deep learning (DL)-based palmprint verification models rely on centralized training with large datasets, which raises significant privacy concerns due to biometric data's sensitive and immutable nature. Federated learning~(FL), a privacy-preserving distributed learning paradigm, offers a compelling alternative by enabling collaborative model training without the need for data sharing. However, FL-based palmprint verification faces critical challenges, including data heterogeneity from diverse identities and the absence of standardized evaluation benchmarks. This paper addresses these gaps by establishing a comprehensive benchmark for FL-based palmprint verification, which explicitly defines and evaluates two practical scenarios: closed-set and open-set verification. We propose FedPalm, a unified FL framework that balances local adaptability with global generalization. Each client trains a personalized textural expert tailored to local data and collaboratively contributes to a shared global textural expert for extracting generalized features. To further enhance verification performance, we introduce a Textural Expert Interaction Module that dynamically routes textural features among experts to generate refined side textural features. Learnable parameters are employed to model relationships between original and side features, fostering cross-texture-expert interaction and improving feature discrimination. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of FedPalm, demonstrating robust performance across both scenarios and providing a promising foundation for advancing FL-based palmprint verification research.
Patient-Level Anatomy Meets Scanning-Level Physics: Personalized Federated Low-Dose CT Denoising Empowered by Large Language Model
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Reducing radiation doses benefits patients, however, the resultant low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) images often suffer from clinically unacceptable noise and artifacts. While deep learning (DL) shows promise in LDCT reconstruction, it requires large-scale data collection from multiple clients, raising privacy concerns. Federated learning (FL) has been introduced to address these privacy concerns; however, current methods are typically tailored to specific scanning protocols, which limits their generalizability and makes them less effective for unseen protocols. To address these issues, we propose SCAN-PhysFed, a novel SCanning- and ANatomy-level personalized Physics-Driven Federated learning paradigm for LDCT reconstruction. Since the noise distribution in LDCT data is closely tied to scanning protocols and anatomical structures being scanned, we design a dual-level physics-informed way to address these challenges. Specifically, we incorporate physical and anatomical prompts into our physics-informed hypernetworks to capture scanning- and anatomy-specific information, enabling dual-level physics-driven personalization of imaging features. These prompts are derived from the scanning protocol and the radiology report generated by a medical large language model (MLLM), respectively. Subsequently, client-specific decoders project these dual-level personalized imaging features back into the image domain. Besides, to tackle the challenge of unseen data, we introduce a novel protocol vector-quantization strategy (PVQS), which ensures consistent performance across new clients by quantifying the unseen scanning code as one of the codes in the scanning codebook. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of SCAN-PhysFed on public datasets.
Double Banking on Knowledge: Customized Modulation and Prototypes for Multi-Modality Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Oct 23, 2024



Abstract:Multi-modality (MM) semi-supervised learning (SSL) based medical image segmentation has recently gained increasing attention for its ability to utilize MM data and reduce reliance on labeled images. However, current methods face several challenges: (1) Complex network designs hinder scalability to scenarios with more than two modalities. (2) Focusing solely on modality-invariant representation while neglecting modality-specific features, leads to incomplete MM learning. (3) Leveraging unlabeled data with generative methods can be unreliable for SSL. To address these problems, we propose Double Bank Dual Consistency (DBDC), a novel MM-SSL approach for medical image segmentation. To address challenge (1), we propose a modality all-in-one segmentation network that accommodates data from any number of modalities, removing the limitation on modality count. To address challenge (2), we design two learnable plug-in banks, Modality-Level Modulation bank (MLMB) and Modality-Level Prototype (MLPB) bank, to capture both modality-invariant and modality-specific knowledge. These banks are updated using our proposed Modality Prototype Contrastive Learning (MPCL). Additionally, we design Modality Adaptive Weighting (MAW) to dynamically adjust learning weights for each modality, ensuring balanced MM learning as different modalities learn at different rates. Finally, to address challenge (3), we introduce a Dual Consistency (DC) strategy that enforces consistency at both the image and feature levels without relying on generative methods. We evaluate our method on a 2-to-4 modality segmentation task using three open-source datasets, and extensive experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
SynFacePAD 2023: Competition on Face Presentation Attack Detection Based on Privacy-aware Synthetic Training Data
Nov 09, 2023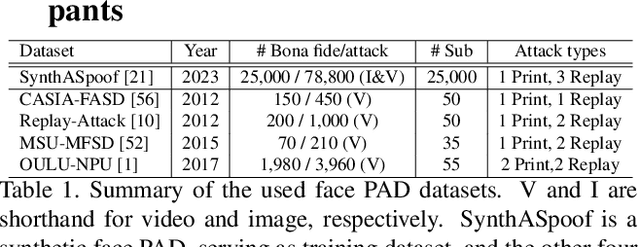

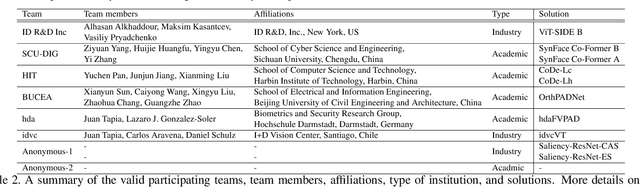
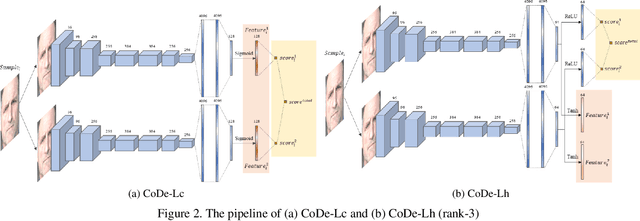
Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the Competition on Face Presentation Attack Detection Based on Privacy-aware Synthetic Training Data (SynFacePAD 2023) held at the 2023 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB 2023). The competition attracted a total of 8 participating teams with valid submissions from academia and industry. The competition aimed to motivate and attract solutions that target detecting face presentation attacks while considering synthetic-based training data motivated by privacy, legal and ethical concerns associated with personal data. To achieve that, the training data used by the participants was limited to synthetic data provided by the organizers. The submitted solutions presented innovations and novel approaches that led to outperforming the considered baseline in the investigated benchmarks.
EVIL: Evidential Inference Learning for Trustworthy Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 18, 2023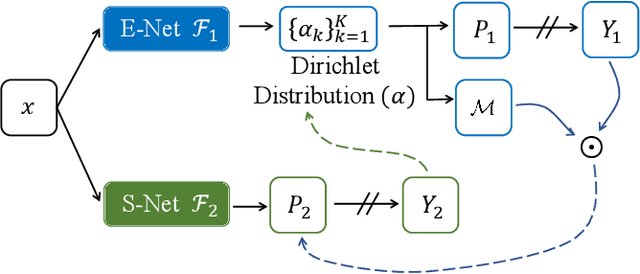
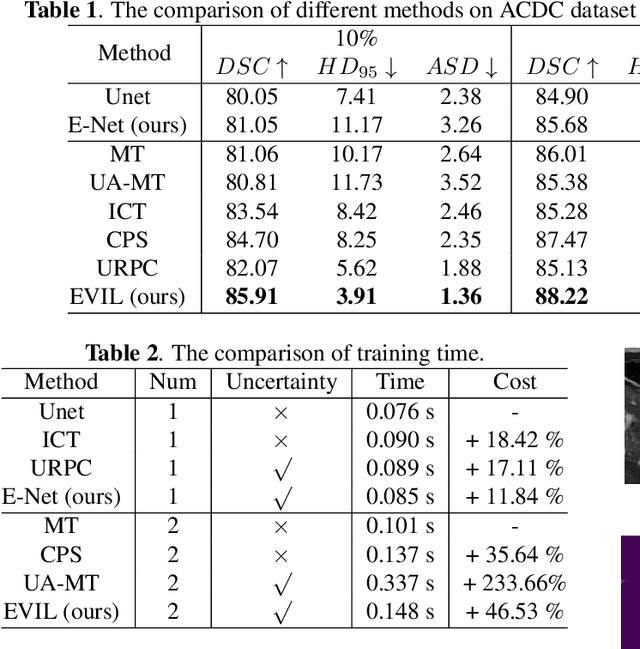
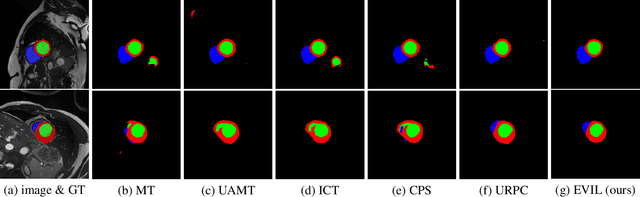
Abstract:Recently, uncertainty-aware methods have attracted increasing attention in semi-supervised medical image segmentation. However, current methods usually suffer from the drawback that it is difficult to balance the computational cost, estimation accuracy, and theoretical support in a unified framework. To alleviate this problem, we introduce the Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence (DST) into semi-supervised medical image segmentation, dubbed Evidential Inference Learning (EVIL). EVIL provides a theoretically guaranteed solution to infer accurate uncertainty quantification in a single forward pass. Trustworthy pseudo labels on unlabeled data are generated after uncertainty estimation. The recently proposed consistency regularization-based training paradigm is adopted in our framework, which enforces the consistency on the perturbed predictions to enhance the generalization with few labeled data. Experimental results show that EVIL achieves competitive performance in comparison with several state-of-the-art methods on the public dataset.
Robust Split Federated Learning for U-shaped Medical Image Networks
Dec 13, 2022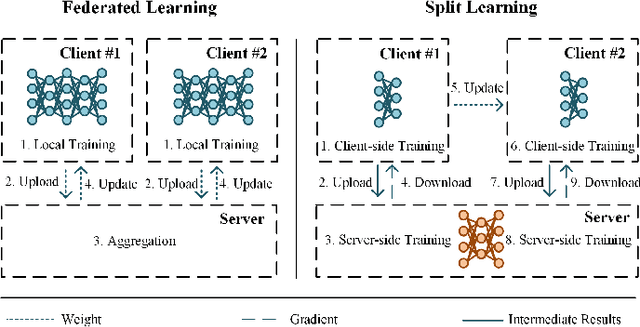
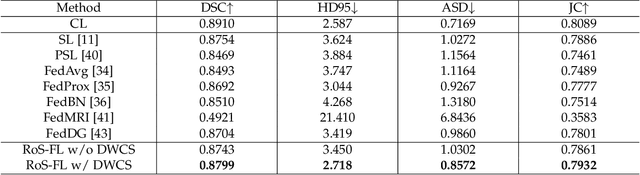
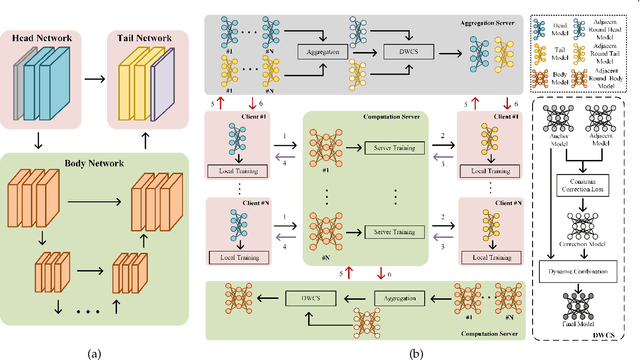
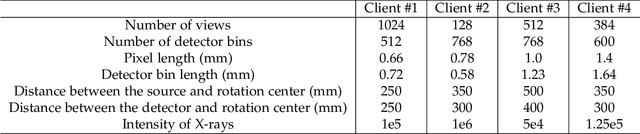
Abstract:U-shaped networks are widely used in various medical image tasks, such as segmentation, restoration and reconstruction, but most of them usually rely on centralized learning and thus ignore privacy issues. To address the privacy concerns, federated learning (FL) and split learning (SL) have attracted increasing attention. However, it is hard for both FL and SL to balance the local computational cost, model privacy and parallel training simultaneously. To achieve this goal, in this paper, we propose Robust Split Federated Learning (RoS-FL) for U-shaped medical image networks, which is a novel hybrid learning paradigm of FL and SL. Previous works cannot preserve the data privacy, including the input, model parameters, label and output simultaneously. To effectively deal with all of them, we design a novel splitting method for U-shaped medical image networks, which splits the network into three parts hosted by different parties. Besides, the distributed learning methods usually suffer from a drift between local and global models caused by data heterogeneity. Based on this consideration, we propose a dynamic weight correction strategy (\textbf{DWCS}) to stabilize the training process and avoid model drift. Specifically, a weight correction loss is designed to quantify the drift between the models from two adjacent communication rounds. By minimizing this loss, a correction model is obtained. Then we treat the weighted sum of correction model and final round models as the result. The effectiveness of the proposed RoS-FL is supported by extensive experimental results on different tasks. Related codes will be released at https://github.com/Zi-YuanYang/RoS-FL.
Hypernetwork-based Personalized Federated Learning for Multi-Institutional CT Imaging
Jun 09, 2022



Abstract:Computed tomography (CT) is of great importance in clinical practice due to its powerful ability to provide patients' anatomical information without any invasive inspection, but its potential radiation risk is raising people's concerns. Deep learning-based methods are considered promising in CT reconstruction, but these network models are usually trained with the measured data obtained from specific scanning protocol and need to centralizedly collect large amounts of data, which will lead to serious data domain shift, and privacy concerns. To relieve these problems, in this paper, we propose a hypernetwork-based federated learning method for personalized CT imaging, dubbed as HyperFed. The basic assumption of HyperFed is that the optimization problem for each institution can be divided into two parts: the local data adaption problem and the global CT imaging problem, which are implemented by an institution-specific hypernetwork and a global-sharing imaging network, respectively. The purpose of global-sharing imaging network is to learn stable and effective common features from different institutions. The institution-specific hypernetwork is carefully designed to obtain hyperparameters to condition the global-sharing imaging network for personalized local CT reconstruction. Experiments show that HyperFed achieves competitive performance in CT reconstruction compared with several other state-of-the-art methods. It is believed as a promising direction to improve CT imaging quality and achieve personalized demands of different institutions or scanners without privacy data sharing. The codes will be released at https://github.com/Zi-YuanYang/HyperFed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge