Huijie Huangfu
Energizing Federated Learning via Filter-Aware Attention
Nov 18, 2023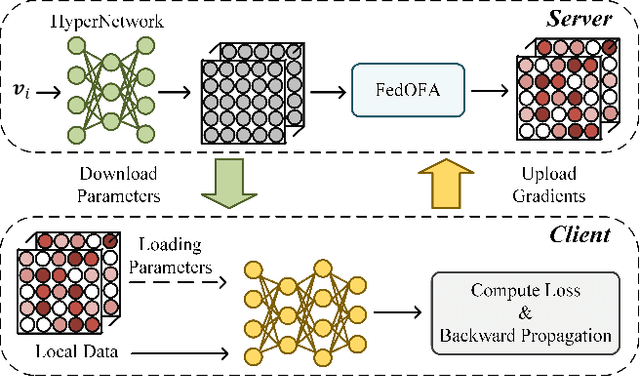
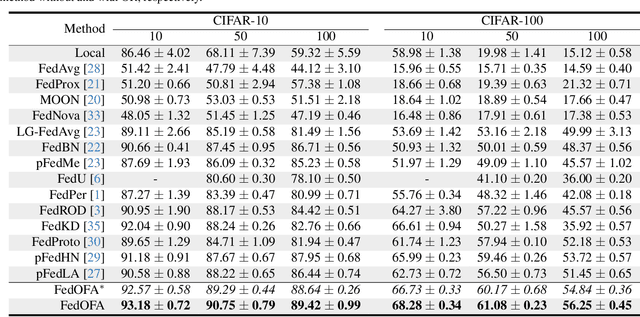
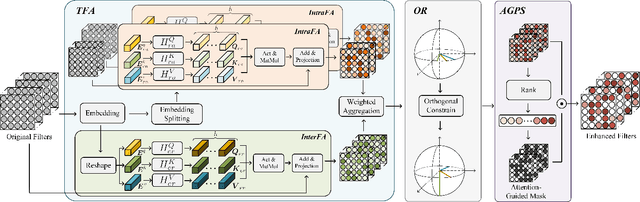
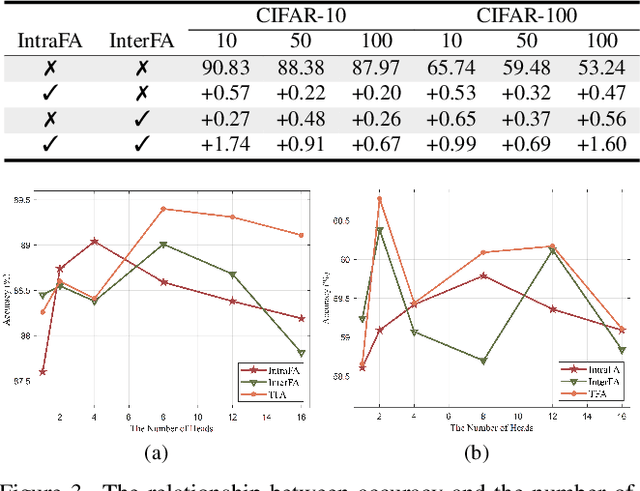
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a promising distributed paradigm, eliminating the need for data sharing but facing challenges from data heterogeneity. Personalized parameter generation through a hypernetwork proves effective, yet existing methods fail to personalize local model structures. This leads to redundant parameters struggling to adapt to diverse data distributions. To address these limitations, we propose FedOFA, utilizing personalized orthogonal filter attention for parameter recalibration. The core is the Two-stream Filter-aware Attention (TFA) module, meticulously designed to extract personalized filter-aware attention maps, incorporating Intra-Filter Attention (IntraFa) and Inter-Filter Attention (InterFA) streams. These streams enhance representation capability and explore optimal implicit structures for local models. Orthogonal regularization minimizes redundancy by averting inter-correlation between filters. Furthermore, we introduce an Attention-Guided Pruning Strategy (AGPS) for communication efficiency. AGPS selectively retains crucial neurons while masking redundant ones, reducing communication costs without performance sacrifice. Importantly, FedOFA operates on the server side, incurring no additional computational cost on the client, making it advantageous in communication-constrained scenarios. Extensive experiments validate superior performance over state-of-the-art approaches, with code availability upon paper acceptance.
SynFacePAD 2023: Competition on Face Presentation Attack Detection Based on Privacy-aware Synthetic Training Data
Nov 09, 2023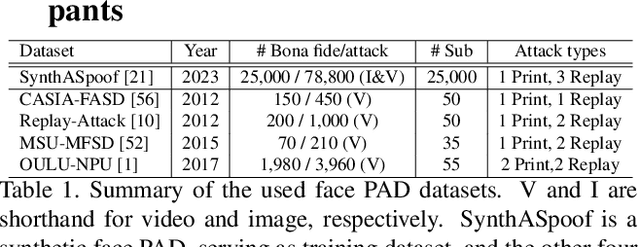

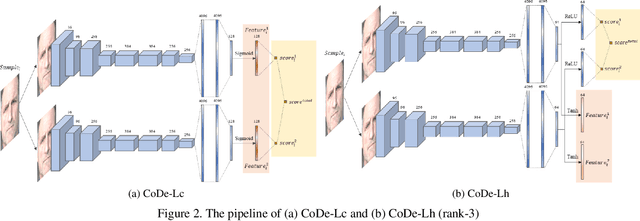
Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the Competition on Face Presentation Attack Detection Based on Privacy-aware Synthetic Training Data (SynFacePAD 2023) held at the 2023 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB 2023). The competition attracted a total of 8 participating teams with valid submissions from academia and industry. The competition aimed to motivate and attract solutions that target detecting face presentation attacks while considering synthetic-based training data motivated by privacy, legal and ethical concerns associated with personal data. To achieve that, the training data used by the participants was limited to synthetic data provided by the organizers. The submitted solutions presented innovations and novel approaches that led to outperforming the considered baseline in the investigated benchmarks.
Privacy-Preserving Encrypted Low-Dose CT Denoising
Oct 13, 2023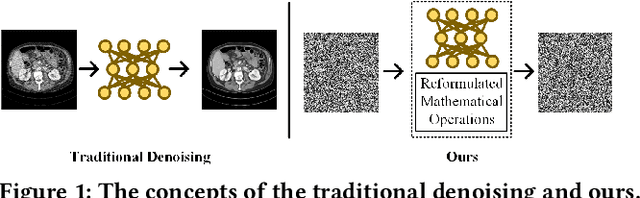

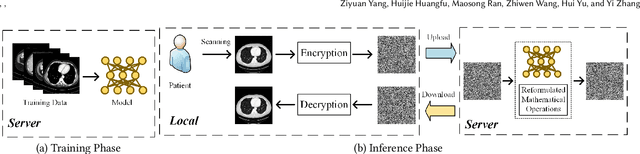
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has made significant advancements in tomographic imaging, particularly in low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) denoising. A recent trend involves servers training powerful models with large amounts of self-collected private data and providing application programming interfaces (APIs) for users, such as Chat-GPT. To avoid model leakage, users are required to upload their data to the server model, but this way raises public concerns about the potential risk of privacy disclosure, especially for medical data. Hence, to alleviate related concerns, in this paper, we propose to directly denoise LDCT in the encrypted domain to achieve privacy-preserving cloud services without exposing private data to the server. To this end, we employ homomorphic encryption to encrypt private LDCT data, which is then transferred to the server model trained with plaintext LDCT for further denoising. However, since traditional operations, such as convolution and linear transformation, in DL methods cannot be directly used in the encrypted domain, we transform the fundamental mathematic operations in the plaintext domain into the operations in the encrypted domain. In addition, we present two interactive frameworks for linear and nonlinear models in this paper, both of which can achieve lossless operating. In this way, the proposed methods can achieve two merits, the data privacy is well protected and the server model is free from the risk of model leakage. Moreover, we provide theoretical proof to validate the lossless property of our framework. Finally, experiments were conducted to demonstrate that the transferred contents are well protected and cannot be reconstructed. The code will be released once the paper is accepted.
Robust Split Federated Learning for U-shaped Medical Image Networks
Dec 13, 2022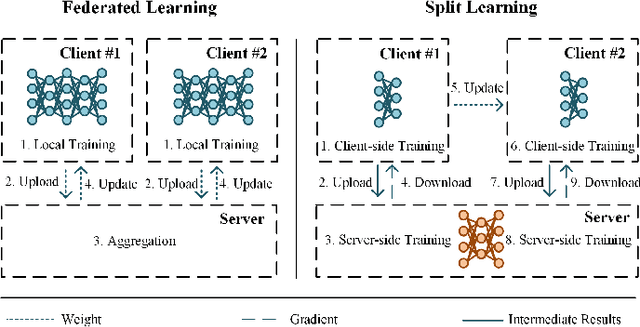
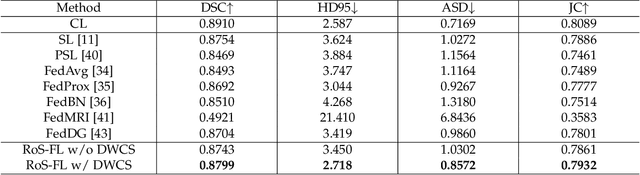
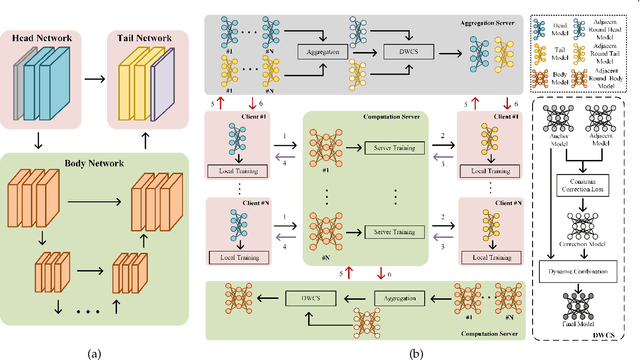
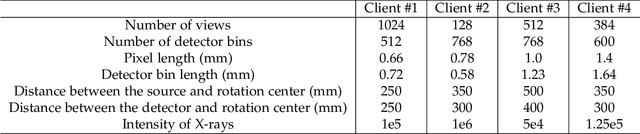
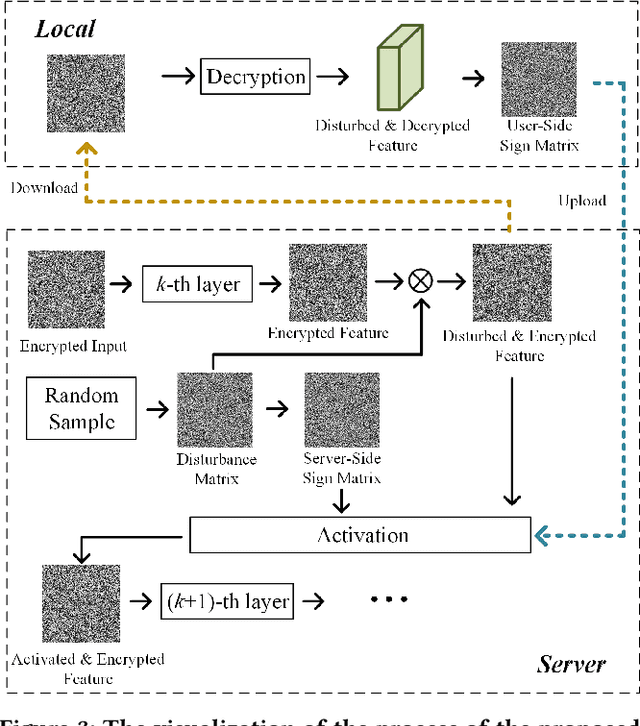
Abstract:U-shaped networks are widely used in various medical image tasks, such as segmentation, restoration and reconstruction, but most of them usually rely on centralized learning and thus ignore privacy issues. To address the privacy concerns, federated learning (FL) and split learning (SL) have attracted increasing attention. However, it is hard for both FL and SL to balance the local computational cost, model privacy and parallel training simultaneously. To achieve this goal, in this paper, we propose Robust Split Federated Learning (RoS-FL) for U-shaped medical image networks, which is a novel hybrid learning paradigm of FL and SL. Previous works cannot preserve the data privacy, including the input, model parameters, label and output simultaneously. To effectively deal with all of them, we design a novel splitting method for U-shaped medical image networks, which splits the network into three parts hosted by different parties. Besides, the distributed learning methods usually suffer from a drift between local and global models caused by data heterogeneity. Based on this consideration, we propose a dynamic weight correction strategy (\textbf{DWCS}) to stabilize the training process and avoid model drift. Specifically, a weight correction loss is designed to quantify the drift between the models from two adjacent communication rounds. By minimizing this loss, a correction model is obtained. Then we treat the weighted sum of correction model and final round models as the result. The effectiveness of the proposed RoS-FL is supported by extensive experimental results on different tasks. Related codes will be released at https://github.com/Zi-YuanYang/RoS-FL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge